BGP Configuration
Configuration Hierarchy
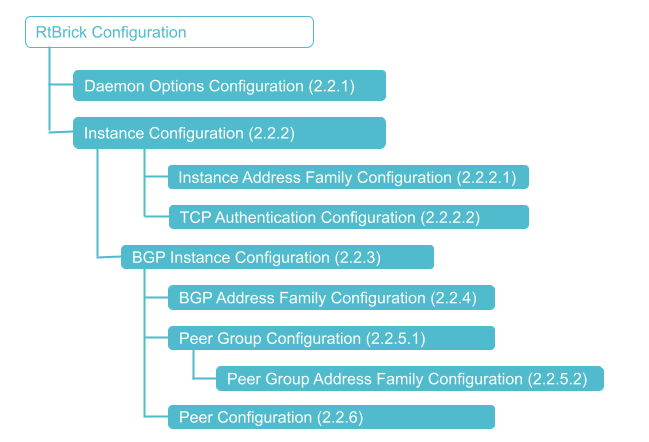
The diagram illustrates the BGP configuration hierarchy. All BGP configuration is done within an instance, for example the default instance or a VPN service instance. The instance configuration hierarchy includes parameters required for BGP but not part of the BGP configuration hierarchy itself. The BGP instance configuration hierarchy includes parameters which are generic to the respective BGP instance. The sub-hierarchies include parameters which are specific to address families, peer groups, and peers.
Configuration Syntax and Commands
The following sections describe the BGP configuration syntax and commands.
Instance Configuration
The instance configuration hierarchy includes parameters that are required for or used by BGP, but that are not part of the BGP protocol configuration hierarchy itself.
Route distinguishers and router IDs are configured directly at the instance hierarchy.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
The route distinguisher (RD) uniquely defines routes within an IPv4 network. PE routers use route distinguishers to identify which VPN a packet belongs to. Supported formats are <as-number:id> or <ipv4-address:id>.
|
||
|
The router ID of the routing instance. |
The example configuration below configures the IPv4 router ID and route distinguisher for the instance services.
set instance services ipv4-router-id 198.51.100.41 set instance services route-distinguisher 198.51.100.41:101 commit
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance services
{
"rtbrick-config:instance": {
"name": "services",
"ipv4-router-id": "198.51.100.41",
"route-distinguisher": "198.51.100.41:101",
<...>
}
}
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Address Families
At the instance address family hierarchy, you can enable or disable address families for the instance, and configure parameters like route targets.
| The default settings depend on the instance. For the 'default' instance, the IPv4 and IPv6 unicast, multicast, and labeled unicast, as well as the MPLS unicast address families are enabled by default. For any non-default instance, no address family is enabled by default and needs to be enabled by configuration. |
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, ipv6, or mpls |
||
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast, labeled-unicast, or multicast |
||
|
Route targets (RT) are used to transfer routes between VPN instances. The RT identifies a subset of routes that should be imported to or exported from a particular VPN instance. You can configure a RT for importing or exporting routes or both.
|
||
|
There are two attachment points for BGP policies. At this configuration hierarchy, you can attach import or export policies to the instance. These policies apply when routes are imported from the BGP protocol into the instance, or exported from the instance to the BGP protocol. |
The example configuration below defines policy and route targets for both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast address families within the services instance.
set instance services address-family ipv4 unicast policy export MY_V4_POLICY set instance services address-family ipv4 unicast route-target import target:198.51.100.70:14 set instance services address-family ipv4 unicast route-target export target:198.51.100.70:14 set instance services address-family ipv6 unicast policy export MY_V6_POLICY set instance services address-family ipv6 unicast route-target import target:198.51.100.70:16 set instance services address-family ipv6 unicast route-target export target:198.51.100.70:16 commit
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance services
{
"rtbrick-config:instance": {
"name": "services",
<...>
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"policy": {
"export": "MY_V4_POLICY"
},
"route-target": {
"import": "target:198.51.100.70:14",
"export": "target:198.51.100.70:14"
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"policy": {
"export": "MY_V6_POLICY"
},
"route-target": {
"import": "target:198.51.100.70:16",
"export": "target:198.51.100.70:16"
}
}
],
<...>
}
}
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
TCP Authentication Configuration
In the instance TCP authentication hierarchy, you can optionally enable MD5 or HMAC-SHA-1-96, HMAC-SHA-256-128, or AES-128-CMAC-96 authentication. Authentication is not configured for BGP directly but for the TCP sessions used by BGP. It is necessary to bind authentication to a peer in order for the authentication to work. For details about configuring a BGP Peer, see the section Peer Configuration.
| BGP TCP authentication is not backward compatible. |
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Authentication identifier |
|
Authentication identifiers such as MD5 |
|
Authentication identifiers such as MD5 or HMAC-SHA-1-96,HMAC-SHA-256-128 or AES-128-CMAC-96 |
|
Key ID1 of the receiver |
|
Encrypted text of key1 |
|
Plain text of key1 |
|
Key ID2 of the receiver |
|
Encrypted text of key2 |
|
Plain text of key2 |
The example below configures MD5 authentication with two keys for the default TCP instance.
set instance default tcp authentication auth1 type MD5 set instance default tcp authentication auth1 key1-id 10 set instance default tcp authentication auth1 key1-encrypted-text "$2784cfa7523916c8cc5dfeba83562cbb4" set instance default tcp authentication auth1 key2-id 20 set instance default tcp authentication auth1 key2-encrypted-text "$2e9bb845e3cfcf8173973029e5c1d90d6" commit
{
"rtbrick-config:tcp": {
"authentication": [
{
"authentication-id": "auth1",
"type": "MD5",
"key1-id": 10,
"key1-encrypted-text": "$2784cfa7523916c8cc5dfeba83562cbb4",
"key2-id": 20,
"key2-encrypted-text": "$2e9bb845e3cfcf8173973029e5c1d90d6"
}
]
}
}
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
BGP Instance Configuration
At this configuration hierarchy, you configure BGP protocol parameters which are generic to the BGP instance.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The name of the BGP host, to a maximum of 64 characters ` |
domain-name <domain-name>` |
The name of the BGP routing domain, to a maximum of 64 characters |
|
By default, the BGP routing process enforces the First AS feature. It discards updates received from an eBGP peer if the peer does not list its own AS number as the first segment in the AS_PATH BGP attribute. Disable the First AS feature to accept updates without the peer’s source AS matching the first AS in the AS_PATH attribute. |
|
The AS number in four-byte format. The numbers allowed are from 1 to 4294967295. |
|
The local preference for the BGP protocol. The numbers allowed are from 0 to 4294967295. The local preference is used to select the exit path for an AS. |
|
The BGP Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) value. The numbers allowed are from 0 to 4294967295. When an AS has multiple links to another AS, the MED value is used to determine the exit to use to reach the other AS. |
|
Protocol preference of routes learned by eBGP ('external'), iBGP ('internal'), or both. This preference is used to select routes learned from multiple protocols. Lower values indicate higher preference. Range: 1 - 255. |
|
Router identifier in IPv4 format |
|
The cluster ID associates routers in a group within a BGP routing instance. Routers belong to the same cluster if they have the same cluster-ID. The cluster ID is formatted as an IPv4 address. |
|
Hold timer in seconds. |
|
Keep a live timer in seconds. |
|
Modify the BGP Best Path selection algorithm. For details, see the section Configuring BGP Best Path Selection. |
|
Ignores malformed updates, allowing the BGP session to remain active. For details, see the section Options for Handling Malformed BGP Update Packets. |
The example below configures various global BGP parameters for the default instance, including cluster ID, domain name, host name, local AS, local preference, router ID, protocol preferences, and hold/keepalive timers.
set instance default protocol bgp cluster-id 198.51.100.51 set instance default protocol bgp domain-name rtbrick.com set instance default protocol bgp host-name spine1 set instance default protocol bgp local-as 4200000100 set instance default protocol bgp local-preference 50 set instance default protocol bgp router-id 198.51.100.51 set instance default protocol bgp protocol-preference internal 180 set instance default protocol bgp protocol-preference external 20 set instance default protocol bgp timer hold-time 30 set instance default protocol bgp timer keepalive 10 commit
supervisor@spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
"cluster-id": "198.51.100.51",
"domain-name": "rtbrick.com",
"host-name": "spine1",
"local-as": 4200000100,
"local-preference": 50,
"router-id": "198.51.100.51",
"protocol-preference": {
"internal": 180,
"external": 20
},
"timer": {
"hold-time": 30,
"keepalive": 10
},
<...>
}
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Configuring Protocol Preference Per Address Family
RBFS supports for protocol preference configuration per address family basis in BGP.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name of the routing instance. |
|
Name of the protocol (e.g., bgp). |
|
Address Family Identifier (e.g., ipv4, ipv6). |
|
Subsequent Address Family Identifier (e.g., unicast, labeled-unicast). |
|
Preference value for internal (IBGP) and external (EBGP) routes. Lower values indicate higher preference. Range: 1 - 255. |
The example below configures the protocol preference for external EBGP peer routes in the BGP labeled-unicast address family within the default routing instance. The preference value indicates the priority of the routes for RIB to choose best routing among different protocols of same prefix type, with lower values being more preferred.
set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast protocol-preference external 10 commit
supervisor@spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast protocol-preference
{
"rtbrick-config:protocol-preference": {
"external": 10
}
}
The example below configures the protocol preference for internal IBGP peer routes in the BGP labeled-unicast address family within the default routing instance. The preference value indicates the priority of the routes for RIB to choose best routing among different protocols of same prefix type, with lower values being more preferred.
set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast protocol-preference internal 10 commit
supervisor@spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast protocol-preference
{
"rtbrick-config:protocol-preference": {
"internal": 10
}
}
Configuring BGP Best Path Selection
RBFS can be configured to ignore certain criteria when selecting the BGP best route. It is recommended to exercise extreme caution when doing this, as this can cause unexpected results such as black holes and routing loops.
Syntax:
| Criteria to ignore | Description |
|---|---|
|
Ignore AS Path during best route selection |
|
Ignore cluster-length during best route selection |
|
Ignore igp metric during best route selection |
|
Ignore local-preference during best route selection |
|
Ignore MED during best route selection |
|
Ignore origin during best route selection |
|
Ignore route-source during best route selection |
|
Ignore RPKI validation state during best route selection |
The example below enables the BGP best path selection process to ignore the route source when determining the best route.
set instance default protocol bgp bestroute-selection ignore-route-source true
supervisor@rtbrick>LEAF01: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp bestroute-selection
{
"rtbrick-config:bestroute-selection": {
"ignore-route-source": "true"
}
}
Options for Handling Malformed BGP Update Packets
Enhancement ID #15566
A malformed Network Layer Reachability Information (NLRI) within a BGP UPDATE message typically results in a session reset, leading to route instability and flapping. To prevent this, a new CLI option has been introduced that will ignore such malformed updates (Per RFC 7606), allowing the BGP session to remain active.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance> |
Name of the routing instance. |
malformed-update ignore |
Ignores malformed updates, allowing the BGP session to remain active. |
The following example configures a network device to ignore malformed BGP update messages for the default BGP instance.
set instance default protocol bgp malformed-update ignore
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
"malformed-update": "ignore"
}
}
BGP Address Family Configuration
This configuration hierarchy refers to parameters that are specific to address families but generic to the BGP instance, as opposed to peer-group specific address families configuration. At this hierarchy, you can enable or disable address families for BGP, and configure various features specific to the address family.
RBFS offers support for a configurable route resolution policy. Initially, RBFS will attempt to resolve the BGP routes using primary resolve-nexthop afi/safi configuration. In case of failure, RBFS will then proceed to resolve the BGP routes using the secondary-nexthop afi/safi configuration.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, or ipv6 |
||
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast, labeled-unicast, vpn-unicast, multicast, or vpn-multicast |
||
|
Generate and distribute a default route information |
||
|
Forward packets over multiple paths, set maximum prefixes to use |
||
|
Enable load sharing among multiple BGP paths
|
||
|
Retain VPN routes for all route targets, by default this feature is enabled |
||
|
Address family to resolve the next-hop |
||
|
Sub-address family to resolve the next-hop |
||
|
Address family to resolve the next-hop when the primary route resolution fails |
||
|
Sub-address family to resolve the next-hop when the primary route resolution fails |
||
|
Enable the redistribution feature to dynamically inject specific types of routes into the BGP protocol. Supported route sources are |
||
|
Attach a policy to the redistribution process |
||
|
Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) start label. The SRGB is the range of label values reserved for segment routing (SR). These values are assigned as segment identifiers (SIDs) to SR-enabled network nodes and have global significance throughout the routing domain. SRGB is supported for labeled unicast only. |
||
|
Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) index |
||
|
Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) label range
|
||
inter-as-option-ab enable |
Enables Inter-AS Option AB for the specified address family. For details, see the Inter-AS Option A-B Configuration section of this guide. |
The example configuration below enables various IPv4 and IPv6 address families for the default BGP instance, including VPN unicast and labeled unicast with specific SRGB parameters.
set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 vpn-unicast set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast srgb base 5000 set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast srgb range 1000 set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast srgb index 11 set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv6 vpn-unicast commit
supervisor@spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
<...>
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast",
"srgb": {
"base": 5000,
"range": 1000,
"index": 11
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
}
],
<...>
}
}
The example configuration below redistributes direct, PPP, ARP-ND, and static routes into BGP for both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast address families within the services instance.
set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute direct set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute ppp set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute arp-nd set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute static set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute direct set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute ppp set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute static commit
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance services protocol bgp
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
<...>
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "arp-nd"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
}
]
}
}
The example configuration below shows how to redistribute direct, PPP, and static routes into BGP for both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast address families within a services instance.
set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute direct policy MY_REDISTRIBUTION_POLICY set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute ppp set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute static set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute direct policy MY_REDISTRIBUTION_POLICY set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute ppp set instance services protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast redistribute static commit
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance services protocol bgp
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
<...>
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
"policy": "MY_REDISTRIBUTION_POLICY"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
"policy": "MY_REDISTRIBUTION_POLICY"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
}
]
}
}
In the example below, RBFS would resolve the BGP routes in the IPv4 labeled-unicast RIB. If this fails, then the routes would be resolved in IPv4 unicast RIB.
set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast resolve-nexthop afi ipv4 set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast resolve-nexthop safi labeled-unicast set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast resolve-nexthop-secondary afi ipv4 set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast resolve-nexthop-secondary safi unicast commit
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"resolve-nexthop": {
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
"resolve-nexthop-secondary": {
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast"
}
}
]
}
The example below configures the BGP protocol for IPv4 unicast within the default instance. It then enables the redistribution of ARP and ND (Neighbor Discovery) entries into BGP, applying a policy named ARP_ND_SOURCE_MATCH to control which entries are redistributed.
set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute arp-nd set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute arp-nd policy ARP_ND_SOURCE_MATCH
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "arp-nd",
"policy": [
"ARP_ND_SOURCE_MATCH"
]
}
]
}
]
}
For details about matching ARP-ND source in policy, see the Matching ARP-ND Source in Policy section of the Policy User Guide.
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Peer Group Configuration
Peer Groups
In BGP, neighbor peers with the same update policies can be grouped to simplify the initial configuration and updates. Peers share the same policies such as route maps, distribution lists, filter lists, update sources, and so on, so peer groups only need one configuration statement for these values.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Local AS number for the peer group |
|
Remote AS number for the peer group |
|
Enable dynamic AS negotiation for this peer group |
|
By default, the maximum number of hops between eBGP peers is 1 (direct connection). This hop count overrides the default behavior allowing connectivity between eBGP peers not directly connected. |
|
Enable BGPv6 peerings using the IPv6 link-local addresses |
|
Do not prepend the local AS for advertisements to the peer |
|
Prepend only the local AS for advertisements to the peer |
|
Enables or disalbes Generalized TTL Security Mechanism (GTSM). |
|
Specifies the minimum TTL value of packets from the BGP neighbor for TTL Security. The valid range is 1 to 255. |
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Address Families
At this configuration hierarchy, you can enable the address families that shall be supported for the group peers, and enable features specific to the address family. By default, BGP neighbor sessions support the IP4v unicast and multicast address families.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, or ipv6 |
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast, labeled-unicast, vpn-unicast, multicast, or vpn-multicast |
|
Negotiate additional path capabilities with these peers, so that more than one path can be active to the peers in the group |
|
Generate and advertise a default route to peers in the group |
|
Enable extended-next-hop encoding for BGP peer groups to allow the transfer of IPv4 prefixes over an IPv6 connection |
|
Set the advertised BGP nexthop to yourself, this is the default for eBGP |
|
Do not modify the advertised BGP nexthop, this is the default for iBGP |
|
BGP nexthop address for routes advertised to this peer group |
|
Remove private AS numbers from routes advertised to group peers |
|
Configure this peer as a route reflector client |
|
Apply a routing policy to the peer group |
The example configuration below sets up a BGP peer-group named "spine" with specific parameters for IPv4 and IPv6 address families, including the use of link-local nexthops, a remote AS number, and extended nexthop and update nexthop settings for VPN unicast routes.
set instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine link-local-nexthop-only true set instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine remote-as 4200000100 set instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine address-family ipv4 vpn-unicast extended-nexthop true set instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine address-family ipv4 vpn-unicast update-nexthop ipv6-address 2001:db8:0:19:: set instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast set instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine address-family ipv6 unicast set instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine address-family ipv6 vpn-unicast update-nexthop ipv6-address 2001:db8:0:19:: commit
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine
{
"rtbrick-config:peer-group": {
"pg-name": "spine",
"link-local-nexthop-only": "true",
"remote-as": 4200000100,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"extended-nexthop": "true",
"update-nexthop": {
"ipv6-address": "2001:db8:0:19::"
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"update-nexthop": {
"ipv6-address": "2001:db8:0:19::"
}
}
]
}
}
The example configuration below defines a BGP peer-group named "ipv4_bgp" with a remote AS, enables TTL security with a limit of 253, and activates both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast address families for this peer-group.
set instance default protocol bgp peer-group ipv4_bgp remote-as 4200000100 set instance default protocol bgp peer-group ipv4_bgp ttl-security enable set instance default protocol bgp peer-group ipv4_bgp ttl-limit 253 set instance default protocol bgp peer-group ipv4_bgp address-family ipv4 unicast set instance default protocol bgp peer-group ipv4_bgp address-family ipv6 unicast commit
{
"rtbrick-config:peer-group": [
{
"pg-name": "ipv4_bgp",
"remote-as": 4200000100,
"ttl-security": "enable",
"ttl-limit": 253,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
}
]
}
]
}
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Maximum Prefix Limit
The BGP Maximum Prefix Limit feature enables you to set a limit for the maximum number of prefixes that a BGP router can receive from its peer router. If a BGP router receives prefixes that exceed the defined limit threshold, the BGP session gets reset and the session goes idle for a pre-defined period.
You can define a period as idle timeout so that the BGP peering gets re-established automatically after the specified time. If you do not specify the idle timeout, the BGP peering does not get re-established until or unless you execute the clear bgp peer command.
Before getting into inactive or idle mode, the router sends a notification message to the peer router about the exceeded threshold with the error code and the sub-code.
You can configure prefix limits for a peer group.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, or ipv6 |
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast, labeled-unicast, vpn-unicast, or vpn-multicast |
|
Number of maximum prefixes that the peer router is allowed to send. The default value is 0. It means no value is configured for prefix limit. |
|
Idle or inactive time after the maximum limit is reached (in minutes). The allowed range is 1 - 2400 min. The default is 'Forever'. |
The example configuration below configures a prefix limit of 100 with an idle timeout of 5 seconds for the IPv4 unicast address family within the BGP peer-group "PE2" in the default instance.
set instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-limit count 100 set instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2 address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-limit idle-timeout 5 commit
supervisor@L1-STD-2-2002>bm14-tst.fsn.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2 address-family ipv4 unicast
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"prefix-limit": {
"count": 100,
"idle-timeout": 5
}
}
]
}
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Configure Upstream BGP Route Export into VRFs of Peering Customers
For peering customers, it is required to select and install specific upstream routes in their own dedicated routing tables (VRFs). To achieve this, the routes from a single upstream peer must be distributed to multiple RIBs, one for each customer-specific VRF.
You can configure the Upstream BGP Route Export into VRFs of peering customers.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name of the routing instance. |
|
Name of the peer group. |
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, or ipv6 |
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast, labeled-unicast, vpn-unicast, or vpn-multicast |
|
Defines in which routing tables (RIBs) the routes from this peer will be installed. The option indicates that the routes learned from the BGP peer are to be installed in multiple RIBs. |
|
It specifies the default route that is to be installed in the customer’s routing table. |
The example configuration below configures default route advertisement and export of RIBs for IPv4 unicast within the BGP peer-group "PE2" to peers CE1, CE2, and CE3 in the default instance.
set instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2 address-family ipv4 unicast peer-default-route CE1 set instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2 address-family ipv4 unicast peer-default-route CE2 set instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2 address-family ipv4 unicast peer-default-route CE3 set instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2 address-family ipv4 unicast export-rib CE1 set instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2 address-family ipv4 unicast export-rib CE2 set instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2 address-family ipv4 unicast export-rib CE3 commit
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2 address-family ipv4 unicast
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"peer-default-route": [
"CE1",
"CE2",
"CE3"
],
"export-rib": [
{
"instance": "CE1"
},
{
"instance": "CE2"
},
{
"instance": "CE3"
}
]
}
]
}
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Peer Configuration
Once peer groups have been defined, BGP peers can be configured at the peer configuration hierarchy. A peer can be specified by address, or by interface when using IPv6 auto-discovered neighbors and link-local addresses. Furthermore, it is possible to configure TCP authentication and bind it to a peer.
Syntax to configure a BGP peer by address:
Syntax to configure a BGP peer using IPv6 link-local addresses:
Syntax to configure TCP Authentication for BGP peers:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable BGP peer using IPv6 link-local addresses |
|
IPv4 address of a BGP peer |
|
IPv6 address of a BGP peer |
|
Specify the value for allow-as-in. Allowed range of value 1 - 10. |
|
Local IP address to be used for the peering |
|
Assign the peer to a peer group |
|
Deactivate a configured peer |
|
Authentication identifier |
The example configuration below configures update source for a BGP peer to a specific IP address and assigns the peer to the "spine" peer-group within the default instance.
set instance default protocol bgp peer ipv4 peer-address 198.51.100.82 update-source 198.51.100.81 set instance default protocol bgp peer ipv4 peer-address 198.51.100.82 peer-group spine commit
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer
{
"rtbrick-config:peer": {
"ipv4": [
{
"peer-address": "198.51.100.82",
"update-source": "198.51.100.81",
"peer-group": "spine"
}
]
}
}
The example configuration below assigns a specific interface to the "spine" peer-group within the BGP protocol configuration of the default instance.
set instance default protocol bgp peer interface ifl-0/0/1/1 peer-group spine commit
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer
{
"rtbrick-config:peer": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1/1",
"peer-group": "spine"
}
]
}
}
The example configuration below applies an authentication ID to a BGP peer interface and assigns that interface to the "spine" peer-group within the default instance.
set instance default protocol bgp peer interface ifl-0/0/1/1 authentication-id auth1 set instance default protocol bgp peer interface ifl-0/0/1/1 peer-group spine commit
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer
{
"rtbrick-config:peer": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1/1",
"authentication-id": "auth1",
"peer-group": "spine"
}
]
}
}
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Inter-AS Option A-B Configuration
The VPN Option A-B Interconnect solution is aimed at conserving label space in spine devices by using a single static label for multiple VPN prefixes.
Option-B Label Space Conservation
The MSANs are connected via an L3VPN private network. Traditionally, spines allocate a new service label (Option B) for each next hop and label when advertising VPN prefixes to the Route Reflector (RR) in the IP2 core. This can lead to a large number of MPLS Option B labels being installed in the spines. This solution addresses this by enabling a more efficient label allocation.
To conserve label space, a new MSAN POTS instance is configured on the spines with a static label. All MSAN routes are installed in this instance, and their service labels are replaced with the single static label before being forwarded to the RR. When data packets arrive from the core, an IP lookup followed by an MPLS push is performed, and packets are forwarded towards the leaf using this single label.
The key features of this solution are:
-
Supports the static label for an address family (IPv4 unicast / IPv6 unicast).
-
Supports enabling/disabling of VPN address family (IPv4 vpn-unicast / IPv6 vpn-unicast).
-
Supports replacing the service label with the configured static instance label if the prefix RT matches the import RT of the instance.
Configuring Inter-AS Option A-B
The inter-as-option-ab parameter needs to be enabled within the BGP configuration for vpn-unicast address families (both IPv4 and IPv6) under the relevant instance.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI) for the address family ( |
<safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI) for the address family ( |
inter-as-option-ab enable |
Enables Inter-AS Option AB for the specified address family. |
The following example enables Inter-AS Option AB for both IPv4 and IPv6 VPN-unicast address families under the default instance:
set instance default protocol bgp local-as 65001 set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 vpn-unicast inter-as-option-ab enable set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv6 vpn-unicast inter-as-option-ab enable commit
Configuration Example:
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"protocol": {
"bgp": {
"local-as": 65001,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"inter-as-option-ab": "enable"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"inter-as-option-ab": "enable"
}
]
}
}
}
]
Configuring Static Label
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI) for the address family ( |
<safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI) for the address family ( |
<afi> <safi> label <label> |
Static label for IPv4/IPv6 unicast address family. |
The following example enables static label for both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast address families under the vrf1 instance:
set instance vrf1 protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast set instance vrf1 protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast label 400000 set instance vrf1 protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast set instance vrf1 protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast label 401000 commit
Configuration Example:
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"label": 400000
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"label": 401000
}
]
}
BGP Sample Configuration
Example 1: BGP Configuration of a Spine Switch (Default Instance only)
{
"ietf-restconf:data": {
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"ipv4-router-id": "198.51.100.51",
"protocol": {
"bgp": {
"domain-name": "rtbrick.com",
"host-name": "spine1",
"local-as": 4200000100,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast",
"srgb": {
"base": 5000,
"range": 1000,
"index": 11
},
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
}
],
"peer": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/1/1/1",
"authentication-id": "auth1",
"peer-group": "spine"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/2/1/1",
"peer-group": "leaf1"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/2/2/1",
"peer-group": "leaf2"
}
]
},
"peer-group": [
{
"pg-name": "leaf1",
"link-local-nexthop-only": "true",
"remote-as": 4200000201,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"extended-nexthop": "true",
"nexthop-unchanged": "true"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"nexthop-unchanged": "true"
}
]
},
{
"pg-name": "leaf2",
"link-local-nexthop-only": "true",
"remote-as": 4200000202,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"extended-nexthop": "true",
"nexthop-unchanged": "true"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"nexthop-unchanged": "true"
}
]
},
{
"pg-name": "spine",
"link-local-nexthop-only": "true",
"remote-as": 4200000100,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"extended-nexthop": "true"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast",
"nexthop-self": "true"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"nexthop-self": "true"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
Example 2: BGP Configuration of a Leaf Switch with one VPN Instance
{
"ietf-restconf:data": {
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"ipv4-router-id": "198.51.100.53",
"protocol": {
"bgp": {
"domain-name": "rtbrick.com",
"host-name": "leaf1",
"local-as": 4200000201,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast",
"srgb": {
"base": 5000,
"range": 1000,
"index": 13
},
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
}
],
"peer": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/1/1/1"
"authentication-id": "auth1",
"peer-group": "spine"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/1/2/1",
"peer-group": "spine"
}
]
},
"peer-group": [
{
"pg-name": "spine",
"link-local-nexthop-only": "true",
"remote-as": 4200000100,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"extended-nexthop": "true",
"update-nexthop": {
"ipv6-address": "2001:db8:0:19::"
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"update-nexthop": {
"ipv6-address": "2001:db8:0:19::"
}
}
]
}
]
}
}
},
{
"name": "services",
"ipv4-router-id": "198.51.100.41",
"route-distinguisher": "198.51.100.41:101",
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"policy": {
"export": "MY_V4_POLICY"
},
"route-target": {
"import": "target:198.51.100.70:14",
"export": "target:198.51.100.70:14"
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"policy": {
"export": "MY_V6_POLICY"
},
"route-target": {
"import": "target:198.51.100.70:16",
"export": "target:198.51.100.70:16"
}
}
],
"protocol": {
"bgp": {
"domain-name": "rtbrick.com",
"host-name": "leaf1",
"local-as": 65003,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}