AAA Profile Configuration
Table: global.access.aaa.profile.config
The AAA profile for subscriber access is a mandatory configuration that serves as a cornerstone for managing and tracking subscriber activities. It ensures that all subscribers are authenticated before accessing services, authorized to use those services, and accounted for billing and monitoring purposes.
The following diagram illustrates how the AAA profile is associated with various subscriber management tasks.
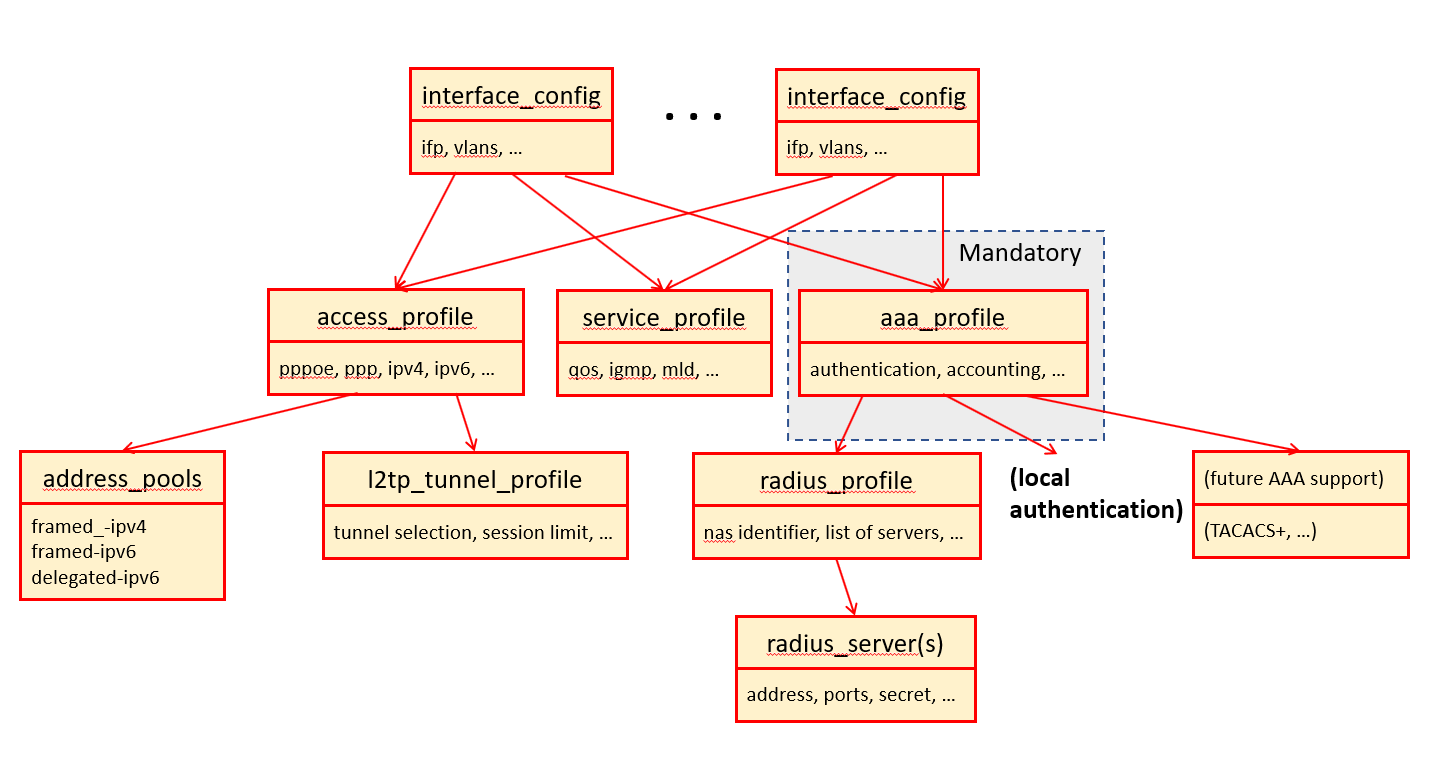
Configuring the AAA Profile
The following command and options allow you to configure an AAA profile.
supervisor@switch: cfg> set access aaa-profile <profile-name> Name of the AAA profile supervisor@switch: cfg> set access aaa-profile aaa-example <cr> aaa-radius-profile AAA RADIUS profile name accounting Accounting options authentication Authentication options idle-timeout Idle timeout in seconds (0 == infinity) [Range: <0-4294967295>] session-timeout Session timeout in seconds (0 == infinity) [Range: <0-4294967295>]
This following example demonstrates a typical AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) profile configuration for RADIUS authentication and accounting. The profile name is 'aaa-radius.
The session-timeout value is set to '0', meaning there is no session timeout and the session can remain active indefinitely. The idle timeout value is also '0', indicating no idle timeout, so the session will not be terminated due to inactivity.
The parameter aaa-radius-profile is set to 'radius-default', which maps the AAA profile to the specific RADIUS profile named 'radius-default'. The RADIUS profile contains the necessary configuration details for communicating with the RADIUS server. In this profile, RADIUS is the selected method for handling all authentication requests. The order parameter indicates that RADIUS is the primary and only method of authentication configured.
For accounting, the order is specified as RADIUS, indicating that all accounting data is sent to the RADIUS server.
The ingress accounting-source is "POLICER", and the egress accounting source is "CLASS". "POLICER" indicates that the accounting data is based on a traffic policer, while "CLASS" indicates that the accounting data is based on traffic classes.
The class-byte-adjustment-value parameter is set to 16, adjusting the byte count for outgoing traffic by a specific value (16).
supervisor@switch: cfg> show config access aaa-profile aaa-radius
{
"rtbrick-config:aaa-profile": {
"profile-name": "aaa-radius",
"session-timeout": 0,
"idle-timeout": 0,
"aaa-radius-profile": "radius-default",
"authentication": {
"order": "RADIUS"
},
"accounting": {
"order": "RADIUS",
"session-id-format": "DEFAULT",
"ingress": {
"accounting-source": "POLICER"
},
"egress": {
"accounting-source": "CLASS",
"class-byte-adjustment-value": 16
}
}
}
}
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
The session timeout defines the maximum (uptime) duration, in seconds, that a subscriber can remain connected before the session is automatically terminated. The value '0' indicates that the session has no time limit and can continue indefinitely. Default: 0 Range: 0 - 4294967295 |
|
The idle timeout is the time, in seconds, after which a subscriber will be disconnected if no data is being transmitted through their outgoing logical interface (IFL). Control traffic is not included in these statistics. The subscriber is not considered idle as long as outgoing traffic is detected. The idle timeout is not limited but should be set to at least double the time of the logical interface statistics counter update interval (between 5 to 45 seconds). The idle timeout does not have a specific limit, but it is recommended to set it to at least double the time of the logical interface statistics counter update interval (which is between 5 to 45 seconds). Therefore, it is advisable to set a minimum idle timeout of 90 seconds. The value '0' means that the timeout is infinite. Default: 0 Range: 0 - 4294967295 |
|
The RADIUS profile, (for more details, see RADIUS Profile Configuration), which is used if RADIUS authentication or accounting is enabled. |
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Configuring Authentication
RBFS supports the authentication methods: NONE, LOCAL, RADIUS and LOCAL_RADIUS.
-
NONE: Disables authentication, accepting all credentials without verification.
-
LOCAL: Authenticates the subscriber based on locally defined user profiles. For more details, refer to User Profile Configuration.
-
RADIUS: Authenticates the subscriber remotely by sending an authentication request to the configured RADIUS servers.
-
LOCAL_RADIUS: Authenticates the subscriber based on locally defined user profiles. If no matching local user is found, the system attempts authentication via RADIUS. If a local user is found but the password does not match, the subscriber is immediately rejected, and no RADIUS request is made.
The following command and options allow you to define the order of authentication methods.
supervisor@switch: cfg> set access aaa-profile aaa-default authentication <cr> order Authentication order
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
This option defines the order of authentication methods. Default: NONE Values: NONE, LOCAL, RADIUS, LOCAL_RADIUS |
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Configuring Accounting
Subscriber accounting involves tracking and recording a subscriber’s session duration and data usage. This process includes two main components:
-
Time Accounting: Measures the duration of a subscriber’s session.
-
Volume Accounting: Tracks the number of packets and bytes transmitted or received.
Volume accounting operates in both directions (ingress and egress), and these can be configured independently.
| Currently, RBFS supports RADIUS as the only accounting method. |
The following command and options are used to configure accounting for the default AAA profile named aaa-default. The 'egress' option allows you configure accounting for outgoing traffic, and the 'ingress' option allows to set accounting for incoming traffic. The 'interim-interval' option sets the interval, in seconds, for sending interim accounting updates. The 'order' option determines the sequence in which accounting records are processed or sent. This is helpful when multiple accounting methods are used.
supervisor@switch: cfg> set access aaa-profile aaa-default accounting <cr> egress Egress volume accounting options ingress Ingress volume accounting options interim-interval Accounting interim interval in seconds (0 == disabled) [Range: <0-4294967295>] order Accounting order
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
This option defines the order of accounting methods. Default: NONE |
|
The interim interval specifies the time between interim accounting requests in seconds where 0 means disabled. Default: 0 Range: 0 - 4294967295 |
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Configuring Accounting Adjustments
The accounting adjustment feature enables basic counter modifications for the configured accounting method, such as RADIUS accounting. This configuration is necessary to normalize counters across different platforms in each direction. On Broadcom Q2C and Q2A based platforms, packets are counted in the size they enter the switch. Without adjustment, egress accounting would count downstream traffic as received from the core, complete with MPLS labels, while ingress accounting typically includes VLAN headers and/or PPPoE headers.
This counter adjustment aims to normalize counters with diverse encapsulations (double-tagged, untagged, and so on), potentially aligning to L3 counters (IP header and payload) as an example, or exclusively adapting egress traffic to match the outgoing packet encapsulation. The possibility for separate adjustment configurations per direction allows parity in the counters for both ingress and egress.
Example Scenario:
In a scenario where packets enter a device with various encapsulations like PPPoE headers, MPLS labels, or VLAN tags, the system may count these additional headers in the packet size if the adjustment feature is not enabled. This can cause discrepancies in accounting reports.
For instance, an egress interface where traffic exits the device and goes to subscribers. If this traffic originally came from the core network with MPLS labels attached, the system counts the bytes of those labels in its accounting, inflating the byte count. Similarly, on the ingress side, the device counts VLAN tags or PPPoE headers, further impacting accurate accounting reports. To address this issue, you can configure a byte adjustment on both the ingress and egress sides to normalize these counters.
In RBFS, two configuration options are available for to achieve this: the byte adjustment value and the byte adjustment factor. The option byte adjustment value, which can be positive or negative (for example, -20 or 20), adjusts the byte count by a specific amount. Any decimal digits in the adjustment value are rounded to the nearest whole number (for example, 20.2 becomes 20). The option byte adjustment factor, which is less commonly used, adjusts the byte count by a percentage. It accepts positive values and considers up to two decimal places, such as 0.98 for a 2% reduction or 1.02 for a 2% increase.
Ingress Accounting
Subscriber ingress accounting refers to the process of measuring and recording the data usage or traffic that enters a subscriber interface (upstream).
The following command and options allow you to set data usage accounting for incoming traffic.
supervisor@switch: cfg> set access aaa-profile aaa-default accounting ingress <cr> accounting-source Source of session ingress counter byte-adjustment-factor Adjust ingress IFL counters by factor (executed after adjustment value) [Range: <0.00-2.00>] byte-adjustment-value Adjust ingress IFL counters by N bytes per packet [Range: <-32-32>] policer-byte-adjustment-factor Adjust ingress policer counters by factor (executed after adjustment value) [Range: <0.00-2.00>] policer-byte-adjustment-value Adjust ingress policer counters by N bytes per packet [Range: <-32-32>]
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
This option provides control over the counters used for subscriber ingress accounting when RADIUS accounting is enabled. The counters in question are the RADIUS attributes
By default, the policer statistics Alternatively, the logical interface (IFL) statistics can be used, which capture all received traffic, including control traffic and the traffic that is dropped by the ingress policer. It is important to note that this option may NOT be available on all platforms. Default: POLICER Values: POLICER, IFL |
|
Adjusts ingress IFL counters by +/- N bytes per packet. It allows you to adjust the ingress IFL counters by adding or subtracting a specified number of bytes per packet. Default: 0.00 Range: -32 to 32 |
|
Adjust the ingress IFL counters by applying a specified factor. (This adjustment is made after the Default: 1.00 Range: 0.00 - 2.00 |
|
Adjusts ingress POLICER counters by +/- N bytes per packet. It adjusts the ingress POLICER counters by adding or subtracting a specified number of bytes per packet. Default: 0.00 Range: -32 to 32 |
|
Adjusts the ingress POLICER counters by applying a specified factor. This adjustment is also executed after the Default: 1.00 Range: 0.00 - 2.00 |
Egress Accounting
Subscriber egress accounting refers to the process of measuring and recording the data usage or traffic that is sent from a subscriber interface (downstream).
The following command and options allow you to set data usage accounting for outgoing traffic.
supervisor@switch: cfg> set access aaa-profile aaa-default accounting egress <cr> accounting-source Source of session egress counter byte-adjustment-factor Adjust egress IFL counters by factor (executed after adjustment value) [Range: <0.00-2.00>] byte-adjustment-value Adjust egress IFL counters by N bytes per packet [Range: <-32-32>] class-byte-adjustment-factor Adjust egress class counters by factor (executed after adjustment value) [Range: <0.00-2.00>] class-byte-adjustment-value Adjust egress class counters by N bytes per packet [Range: <-32-32>]
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
This option provides control over the counters used for egress session accounting when
RADIUS accounting is enabled. The counters are the RADIUS attributes:
By default, the class statistics ( As an alternative, the logical interface (IFL) statistics can be used to account for all transmitted traffic, excluding control traffic. However, this option may not be supported on all platforms. Default: CLASS Values: CLASS, IFL |
|
Adjust egress IFL counters by +/- N bytes per packet. That is, adjust egress IFL counters by adding or subtracting a specified number of bytes per packet. Default: 0.00 Range: -32 to 32 |
|
Adjust egress IFL counters by applying a specified factor. This adjustment is made after the Default: 1.00 Range: 0.00 to 2.00 |
|
Adjusts egress CLASS (queue) counters by adding or subtracting a specified number of bytes per packet (+/- N bytes per packet). Default: 0.00 Range: -32 to 32 |
|
Adjust egress CLASS (queue) counters by applying a specified factor. This adjustment is also made after the Default: 1.00 Range: 0.00 to 2.00 |