Clock Synchronization
Overview
This guide provides an overview of high-precision clock synchronization mechanisms, including the Precision Time Protocol (PTP), a protocol for clock synchronization supported in RBFS, and covers its configuration and operational commands. PTP is used to synchronize clocks across a network with high precision, achieving accuracy in the nanosecond range.
PTP synchronizes clocks by exchanging timestamped messages between devices. The slave device calculates the clock offset and network delay, then continuously adjusts its clock using a servo algorithm for smooth and precise synchronization. A Hardware Clock (PHC) ensures nanosecond precision for timestamps.
The diagram below illustrates how the master clock serves as the reference time source, and the slave clocks (Switch-1 and Switch-2) synchronize their time to that of the master.
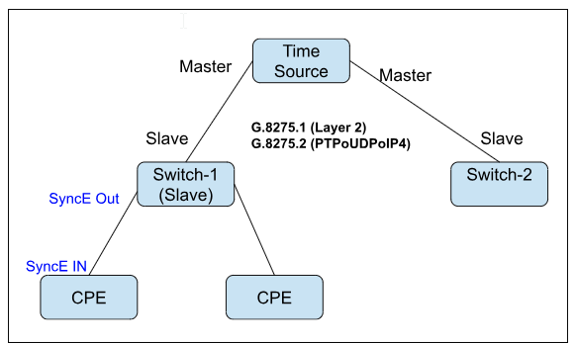
RBFS supports the following PTP profiles and standards:
-
IEEE 1588-2008: Describes the IEEE 1588-2008 standard for Precision Time Protocol (PTP) used in clock synchronization.
-
ITU-T G.8275.1: Defines the timing requirements for packet-based networks to support time-sensitive applications.
In addition, RBFS supports PTP operation at Layer 2.
SyncE ESMC Support
SyncE (Synchronous Ethernet) and ESMC (Ethernet Synchronization Messaging Channel) are crucial components for precise time synchronization in networks.
SyncE provides a mechanism for distributing frequency synchronization over Ethernet at the physical layer (Layer 1). It ensures that all connected network elements operate on the same clock frequency, preventing clock drifts and maintaining a stable timing reference.
ESMC is a Layer 2 protocol (EtherType: 0x8809) that complements SyncE by carrying Synchronization Status Messages (SSMs). These messages convey information about the quality of the clock source being used by SyncE. ESMC allows network devices to select the best available clock source and to automatically switch to a different, higher-quality source if the current one degrades or fails.
Licensing Requirements
Clock synchronization requires a separate license to be procured from RtBrick, in addition to other licenses.
Supported Platforms
Not all features are supported on every hardware platform. Refer to the Feature Support Matrix section of the Platform Guide for details about which features and sub-features are supported on each platform.