Platform Overview
RBFS allows customers to select their preferred hardware platforms. This document provides information about RBFS-supported hardware platforms and the features available on each platform. It also includes information on firmware versions, the feature support matrix, and resource limits. This guide helps you understand the various supported platforms and their capabilities and help you evaluate and choose the right platform for your needs.
The RBFS Software runs as an LXC container on the RtBrick Host system, deployed on bare-metal switches. The switch can function independently as standalone unit leveraging all functionalities into a single platform or can be combined into a leaf-spine architecture for scalable deployments. The software supports Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) installation and provides REST-based APIs for configurations and operations.
The guide is organized into the following sections:
-
Platform Overview: A high-level summary of the platforms.
-
Platform Hardware Information: Detailed specifications of the hardware, including CPU, ASIC, Form Factors, memory, storage, and network interfaces.
-
Firmware Versions: Information on supported firmware versions and their compatibility with RBFS.
-
Feature Support Matrix: Information about RBFS features supported on various platforms and for various roles.
-
Resource Limits/Feature Support: Details on resource allocation, such as maximum routes and interfaces.
The following image shows a high-level overview of the platform architecture.
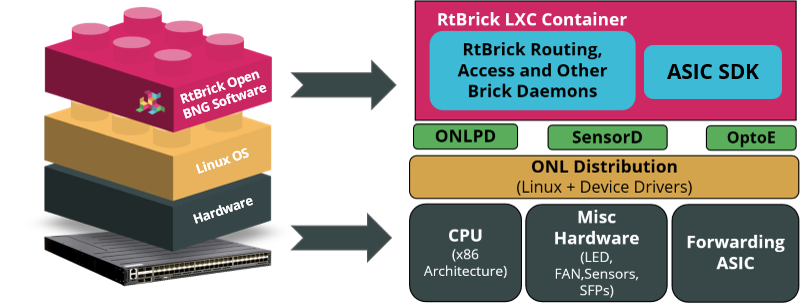
Platform hardware consists of forwarding ASICs and an RtBrick Host operating system. A RBFS container that resides on top of this software includes all necessary packages to deliver access and routing protocols.
Supported Platforms
RtBrick’s software has been validated on the following hardware platforms.
| Hardware Platform | Switch ASIC | Role |
|---|---|---|
Q2A |
Multiservice Edge |
|
Q2A |
Multiservice Edge |
|
Q2C |
Access Leaf, Multiservice Edge |
|
Q2C |
Access Leaf, Multiservice Edge |
|
Q2C |
Spine |
|
Q2C |
Spine |
|
Q2C |
Access Leaf, Multiservice Edge |
|
QAX |
L2 Wholesale (L2BSA) |
For a list of features and sub-features supported by each platform, see Feature Support Matrix.
End-of-Life Policy
RtBrick periodically introduces software support for new hardware platforms and use cases. Likewise, support for older software is discontinued to ensure that RtBrick can provide appropriate attention to software critical to drive business functions. The End-of-Life Policy page details the platforms that are no longer supported or have limited support from RtBrick.
Guidelines and Limitations
QAX-based Platforms
-
An additional restriction applies to ports belonging to a port group on QAX-based platforms. For more information, see section Guidelines and Limitations of the Interfaces User Guide.
-
MPLS forwarding is not supported on double-tagged interfaces. It is supported only on untagged and single-tagged interfaces.
Brick Daemon (BD)
RBFS runs multiple Brick Daemons (BD). Every application that runs within RBFS is fundamentally a brick daemon. For example, forwarding daemon (fibd), configuration daemon (confd), BGP (bgp.iod or bgp.appd), or interface management daemon (ifmd).
Brick Daemon (BD) Restartability
If a brick daemon fails, RBFS will restart it automatically. All microservices can restart automatically for an unlimited number of times. It improves system resilience in the event of recoverable failures. If the automatic restart does not succeed, you can use the Ubuntu system control to start a daemon.
For more information about troubleshooting the Brick Daemons, see section "2.2. Brick Daemons" of the RBFS NOC Troubleshooting Guide.
Limited Core Files to Save Disk Space
RBFS can prevent disk space exhaustion caused by repeated process crashes. Each process is allowed to retain up to three core files. When a new core file is generated, the oldest file will be automatically deleted. It improves disk space management while retaining recent crash data for debugging.
Setting Up System Parameters
You can configure basic host system parameters such as 'element name' and 'pod name' using the set system host command.
Syntax:
set system host <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
element-name <element-name> |
Specify the name of the element (container). A pod can contain a group of elements. |
pod-name <pod-name> |
Specifies the name of the Pod. Pod stands for point (zone) of deployment. |
nameserver <nameserver> |
Specify the IP address of the DNS server. It is allowed to configure a maximum of three servers. |
role |
Specify the role of the element. Roles include Spine, Access Leaf, Border Leaf, and so on. |
The hostname is defined in the DHCP server. The maximum length of the hostname is restricted to 64 characters.
|
Example: System Parameters Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>LEAF01: op> show config system host
{
"rtbrick-config:host": {
"element-name": "ufi10.q2c.u9.r4.nbg.rtbrick.net",
"pod-name": "nbg4"
}
}CPU Watchdog Timer Utility for Hardware Platforms
The CPU watchdog timer utility is located in BMC and helps to detect any CPU failure. It also enables the CPU to recover from faults. By default, Watchdog Timer functionality is enabled, and it does not require any configuration from users. However, you can configure it to change the default settings.
Enable CPU Watchdog Timer in Hardware
Use the following command to enable watchdog timer on the hardware.
Syntax:
set system platform-management watchdog CPU <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
action |
Specifies the possible timeout actions:
Default value: power-cycle. |
interval |
Specifies the watchdog timer interval in seconds. Default value: 1800 seconds. |
Example: Enable CPU Watchdog Timer
supervisor@rtbrick>LEAF01: op> show config system platform-management watchdog
{
"rtbrick-config:watchdog": [
{
"type": "CPU",
"action": "hard-reset",
"interval": 3600
}
]
}You can use the ipmitool utility to view the status of the CPU watchdog timer.
Log into the RtBrick Host and enter the command as shown below to validate CPU watchdog timer functionality.
supervisor@onl>rtbrick:~ $ sudo ipmitool mc watchdog get
Watchdog Timer Use: OS Load (0x43)
Watchdog Timer Is: Started/Running
Watchdog Timer Actions: Power Cycle (0x03)
Pre-timeout interval: 0 seconds
Timer Expiration Flags: 0x00
Initial Countdown: 1800 sec
Present Countdown: 1795 secDisplaying Platform Information
To display platform information, use the show platform command, as shown in the example below.
supervisor@rtbrick>LEAF01: op> show platform
x86_64-ufispace_s9600_72xc-r0
Role : multiservice-edge
Platform : q2c(BCM88820_A1)
External Processor : OP2(model: X register-value: 0x69A)
Vendor : Ufi Space
Manufacturer : Ufi Space
Manufacture date : 06/28/2021 10:51:29
MAC address : E8:C5:7A:8F:78:0D
Part number : S9600-72XC-RB6B
Serial number : WJ91B67T00009B3
Product name : S9600-72XC-R
ONIE version : 2022.02v04
Label revision : N/A
Diag version : 0.1.4
Country code : CN
Device version : 1
|
Displaying RBFS Version Information
To display RBFS version information, use the show version command, as shown in the example below.
supervisor@rtbrick>LEAF01: op> show version
UUID : 4e83e9a4-eb65-4ab0-a756-3ae3536dd6ad
Version : 25.4.0-g6daily.20251126013758+Bdevelopment.C0313b7f9
Role : multiservice-edge
Platform : q2c
Format : lxd
Build date : 2025-11-26 01:37:58 UTCTo display detailed version information for RBFS along with library versions, use the show version detail command, as shown in the example below.
supervisor@rtbrick>LEAF01: op> show version detail
UUID : 4e83e9a4-eb65-4ab0-a756-3ae3536dd6ad
Version : 25.4.0-g6daily.20251126013758+Bdevelopment.C0313b7f9
Role : multiservice-edge
Platform : q2c
Format : lxd
Build date : 2025-11-26 01:37:58 UTC
Component Version Timestamp Branch
alertmanager ....0-g6daily.20251112122211+Bdevelopment.Cfd733666 2025-11-11 10:41:02 development
cligen 0.1.0-g6daily.20251105111321+Bdevelopment.Cd8964728 2025-11-05 10:12:50 development
clixon 4.3.1-g6daily.20251125140131+Bdevelopment.Cfc95084c 2025-11-13 03:40:34 development
ems-service-event 0.2.0-g6daily.20251104173513+Bdevelopment.Cd923496f 2025-10-28 09:33:01 development
etcd ....0-g6daily.20251105113559+Bdevelopment.C8987db4e 2025-10-28 09:32:14 development
fwd-plugin-bcm-q2c-s96... 4.2.0-g6daily.20251126010001+Bdevelopment.Cca388617 2025-11-26 00:40:28 development
hostconfd ....0-g6daily.20251121153022+Bdevelopment.C4b49f4ba 2025-11-21 08:26:47 development
hostnetconfd 0.7.0-g6daily.20251119153025+Bdevelopment.C0a756d06 2025-11-19 08:13:05 development
json-builder 0.1.0-g6daily.20251105112151+Bdevelopment.C7bf78ef6 2025-10-28 09:26:24 development
json-parser 1.1.0-g6daily.20251104173526+Bdevelopment.C95257c44 2025-10-28 09:25:00 development
libbgp 1.2.0-g6daily.20251126005928+Bdevelopment.Cb86c1199 2025-11-21 11:52:25 development
libcjson 1.0.0-g6daily.20251104173453+Bdevelopment.C1bfaae2f 2025-10-28 09:24:36 development
libconfd 1.1.1-g6daily.20251125140948+Bdevelopment.C6f603a5b 2025-11-04 12:37:53 development
libdict 1.0.1-g6daily.20251104173534+Bdevelopment.C3698deb7 2025-10-28 09:28:14 development
libegrep 1.1.0-g6daily.20251104173611+Bdevelopment.Cd8731a66 2025-10-28 09:28:29 development
libforwarding 4.2.0-g6daily.20251126005549+Bdevelopment.Cca388617 2025-11-26 00:40:28 development
libh2o 2.2.6-g6daily.20251105112618+Bdevelopment.Ccabf806c 2025-10-28 09:28:27 development
libigmp 1.1.0-g6daily.20251126005259+Bdevelopment.C63aa1a88 2025-10-28 09:24:52 development
libisis 1.2.0-g6daily.20251126005938+Bdevelopment.Cae8678be 2025-11-26 00:38:37 development
liblacp 0.2.0-g6daily.20251126010938+Bdevelopment.C6b68d457 2025-11-04 12:37:48 development
libldp 0.3.0-g6daily.20251126005023+Bdevelopment.C01e28f15 2025-11-05 06:11:14 development
liblldp 1.1.1-g6daily.20251126010933+Bdevelopment.C81ae1f31 2025-10-28 09:24:48 development
liblwip 1.2.0-g6daily.20251105112452+Bdevelopment.C7c22f157 2025-11-04 08:51:45 development
libnat 1.4.0-g6daily.20251126005258+Bdevelopment.C8f3e30ca 2025-11-05 06:15:54 development
libng-access 1.2.0-g6daily.20251126005302+Bdevelopment.C470442a6 2025-11-19 17:15:01 development
<...>Configuring Platform Profiles
Network operators can determine ASIC scale profiles and features to meet their specific business requirements. Currently, the platform profile configuration is supported on the Multiservice Edge image on the Q2C and Q2A platforms. The profiles can be viewed using the show platform-profile command.
Guidelines & Limitations
-
The system only allows the configuration of the profiles and features it supports.
-
This system allows to configure any one of the supported profiles.
-
You can configure multiple features for one profile.
-
You can make changes to the features, such as removing or modifying them.
-
A system reboot is required for the changes to take effect.
Platform Profile Support
| Platform | Supported Profile | Supported Features | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
Q2C Multiservice Edge |
|
IPoE N:1, sFlow, and so on. |
4q |
Q2A Multiservice Edge |
|
IPoE N:1, sFlow, access-multifield-classifier, and so on. |
4q (ipoe-n-1) |
To configure profile for a specific platform, use the command below.
Syntax:
set system platform profile <profile_name>
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
<profile-name> |
Specifies the profile that you want to activate. Supported platform profiles include |
||
feature <feature> |
Specifies the feature that enabled along with the profile. |
||
<profile_name> |
Specifies the profile that you want to activate. Supported platform profiles include |
||
<feature> |
Specifies the feature that is enabled along with the profile.
|
||
ipoe mode |
Choose the desired redundancy mode: |
Example: Configuring 1q platform profile
set system platform set system platform profile 1q
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config system platform
{
"rtbrick-config:platform": {
"profile": [
{
"profile_name": "1q"
}
]
}
}
Example: Enabling the feature ipoe-n-1 for the profile nat_1q
supervisor@switch: cfg> set system platform profile nat_1q feature ipoe-n-1
"rtbrick-config:system": {
"platform": {
"profile": [
{
"profile_name": "nat_1q"
}
]
}
}
"rtbrick-config:system": {
"platform": {
"profile": [
{
"profile_name": "nat_1q",
"feature": [
"ipoe-n-1"
]
}
]
}
}
Example: Enabling the redundancy mode for the profile nat_1q
supervisor@switch: cfg>set system platform profile nat_1q ipoe-mode standby-non-forwarding
platform": {
"profile": [
{
"profile_name": "nat_1q",
"feature": [
"ipoe-n-1"
],
"ipoe-mode": "standby-non-forwarding"
}
]
}
To view the profiles configured for a platform after reboot, use the show platform-profile command as shown in the example below
Example: Viewing Platform Profile on the Q2A Platform
supervisor@rtbrick>LEAF01: op>show platform-profile
Platform-profile: 4q
Role: multiservice-edge
MDB Profile: custom_q2a_scale_4q
Counter Profile: multiservice_edge
Features: -|ipoe-n-1|-|-
supervisor@rtbrick>LEAF01: op>show platform-profile
Platform-profile: nat_4q
Address Translation Service: True
Role: multiservice-edge
MDB Profile: custom_q2a_scale_nat
Counter Profile: multiservice_edge_nat_extend
Features: -|ipoe-n-1|-|sflow
Example: Viewing Platform Profile on the Q2C Platform
supervisor@rtbrick>LEAF01: op> show platform-profile
Platform-profile: nat_4q
External Processor Variant: OP2_M
Address Translation Service: True
Role: multiservice-edge
MDB Profile: custom_rtb_multiservice_edge_nat
Counter Profile: multiservice_edge_nat_extend
Forwarding Routes on External Processor: False
Ingress Accounting is External: False
Egress Accounting is External: True
The following example configures the platform profile named 4q to enable the 400Gx1 feature, which activates support for one 400G transceiver on the system.
set system platform profile 4q feature 400Gx1
"rtbrick-config:system": {
"platform": {
"profile": [
{
"profile_name": "4q",
"feature": [
"400Gx1"
]
}
]
}
}
For more information about the 400G ZR+ Optics, see the Support for 400G ZR+ Optics on UfiSpace S9510-28DC Platform section.
Port Configuration for 400G Optics
The table below provides a summary of the ports NIF for 400G ZR+ optics on the UfiSpace S9510-28DC platform in both modes (mode_1_400G and mode_2_400G).
| Mode | Resource | Ports | Port Type | Speed | Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
mode_1_400G |
400G |
1 |
NIF |
400 |
400 |
100G |
3 |
NIF |
100 |
300 |
|
25G |
4 |
NIF |
25 |
100 |
|
10G |
20 |
NIF |
10 |
200 |
|
OAM |
1 |
Internal |
10 |
10 |
|
OLP |
1 |
Internal |
10 |
10 |
|
Eventor |
1 |
Internal |
10 |
10 |
|
ERP |
1 |
Internal |
10 |
10 |
|
KR Port |
4 |
Internal |
10 |
40 |
|
SAT Interface |
1 |
Internal |
100 |
100 |
|
mode_2_400G |
400G |
2 |
NIF |
400 |
800 |
100G |
2 |
NIF |
100 |
200 |
|
OAM |
1 |
Internal |
10 |
10 |
|
OLP |
1 |
Internal |
10 |
10 |
|
Eventor |
1 |
Internal |
10 |
10 |
|
ERP |
1 |
Internal |
10 |
10 |
|
KR Port |
4 |
Internal |
10 |
40 |
|
SAT Interface |
1 |
Internal |
100 |
100 |
The mode_1_400G mode supports one 400G port and all twenty-eight ports can be used, whereas in the mode_2_400G mode, two 400G ports are supported and only four ports can be used.
|
The show interface physical command output below shows the ports that are availble for UfiSpace S9510-28DC platform in the mode_2_400G mode.
supervisor@rtbrick.net: op> show interface physical
Interface Admin Link Oper Damp MAC Address Speed Duplex Uptime
ifp-0/0/0 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:8f:f9 400G Full Tue Dec 02 10:12:59 GMT +0000 2025
ifp-0/0/1 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:01 400G Full Tue Dec 02 10:12:59 GMT +0000 2025
ifp-0/0/2 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:09 100G Full Tue Dec 02 10:12:53 GMT +0000 2025
ifp-0/0/3 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:0d 100G Full Tue Dec 02 10:12:53 GMT +0000 2025Viewing Transceiver Details
The operational commands such as show transceiver, show interface physical, and show transceiver <interface> displays current status, high-level inventory, and detailed diagnostic information for the 400G optics and physical network interfaces on the UfiSpace S9510-28DC platform.
Viewing Transceiver Summary:
The show transceiver command provides a list of all installed transceivers across various interfaces on the platform, detailing their module type, name, connector type, power class, vendor, part number, and serial number.
supervisor@rtbrick.net: op> show transceiver Interface Module Type Transceiver Name Connector Type PC Vendor Part Number Serial Number Material Number ifp-0/0/0 QSFP-DD ZR400-OFEC-16QAM LC (Lucent Connector) 8(14.0W) FLEXOPTIX D.CO164HG.16.yTM F824HMC n/a ifp-0/0/1 QSFP-DD ZR400-OFEC-16QAM LC (Lucent Connector) 8(14.0W) FLEXOPTIX D.CO164HG.16.yTM F824GSF n/a ifp-0/0/2 QSFP28 100GBASE-LR4 LC (Lucent Connector) 5(4.0W) LambdaGain LL1S31B0A L16C8M0034 T-UNIQSF40907039 ifp-0/0/3 QSFP28 100GBASE-LR4 LC (Lucent Connector) 5(4.0W) LambdaGain LL1S31B0A L16D1O0019 T-UNIQSF40907039 ifp-0/0/4 SFP 10GBASE-CR Passive Copper Pigtail n/a FS SFPP-PC01 S2108213165-1 n/a
Viewing Physical Interfaces
The show interface physical command displays the status of all physical interfaces on the platform, including their administrative and operational state, link status, MAC address, configured speed and duplex, and uptime. This summary confirms that the interfaces (like the 400G and 100G ports) are currently operational and stable.
supervisor@rtbrick.net: op> show interface physical Interface Admin Link Oper Damp MAC Address Speed Duplex Uptime ifp-0/0/0 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:8f:f9 400G Full Tue Nov 11 09:48:51 GMT +0000 2025 ifp-0/0/1 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:01 400G Full Tue Nov 11 09:48:51 GMT +0000 2025 ifp-0/0/2 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:09 100G Full Tue Nov 11 09:48:45 GMT +0000 2025 ifp-0/0/3 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:0d 100G Full Tue Nov 11 09:48:45 GMT +0000 2025 cpu-0/0/200 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:c0 100G Full Tue Nov 11 09:48:43 GMT +0000 2025 recycle-0/0/211 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:cb 100G Full Tue Nov 11 09:48:43 GMT +0000 2025 recycle-0/0/212 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:cc 100G Full Tue Nov 11 09:48:43 GMT +0000 2025 recycle-0/0/213 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:cd 100G Full Tue Nov 11 09:48:43 GMT +0000 2025 recycle-0/0/214 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:ce 100G Full Tue Nov 11 09:48:43 GMT +0000 2025 recycle-0/0/215 Up Up Up stable 5c:07:58:78:90:cf 100G Full Tue Nov 11 09:48:43 GMT +0000 2025
Viewing 400G Transceiver Details
This example below provides detailed information for the 400G QSFP-DD optical transceiver named ZR400-OFEC-16QAM, including its vendor, part number, power class, connector type (LC), and capability to support a 600km link.
supervisor@rtbrick.net: op> show transceiver ifp-0/0/0
ifp-0/0/0
Transceiver name: ZR400-OFEC-16QAM, Vendor name: FLEXOPTIX, Module type: QSFP-DD, Serial number: F824HMC
Part number: D.CO164HG.16.yTM, Material number: n/a
Power class: 8(14.0W), Power class mode: HIGH
Connector type: LC (Lucent Connector), Link length support: 600km(smf), Wavelength: 1552.50 nm
Capabilities: [Tx-Disable, Diagnostic Monitoring, Supply Voltage Monitoring, Temperature Monitoring, Transmitter Power Measurement]
Manufactured date: Mon Jul 15 00:00:00 GMT +0000 2024
Transceiver Diagnostic Monitoring
Attribute Value High Alarm High Warn Low Alarm Low Warn
Temperature 45.9453 C False False False False
Voltage 3.2724 V False False False False
Transceiver Lane Diagnostic Monitoring
Lane: 0
Attribute Value High Alarm High Warn Low Alarm Low Warn
RxPower -15.2290 dBm False False False False
TxPower -0.1060 dBm False False False False
TxBiascurrent 53.1600 mA False False False False