Configuring BGP-signaled L2VPN
Configuration Hierarchy
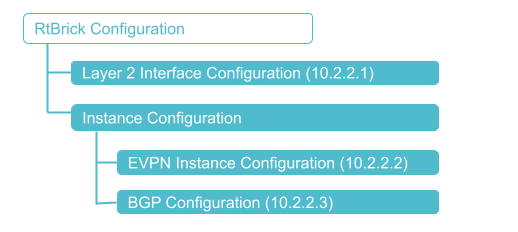
The diagram illustrates the BGP-signaled L2VPN configuration hierarchy. All BGP-signaled L2VPN configurations are done within an instance, such as the default instance or an EVPN service instance.
Configuration Syntax and Commands
The following sections describe the BGP-signaled L2VPN configuration syntax and commands.
Layer 2 Interface Configuration
BGP-signaled L2VPN supports the configuration of Layer 2 logical interfaces.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Specify the name of the interface. Example: ifp-0/0/1. |
|
Create a logical interface (also referred to as a sub-interface) under the physical interface |
|
Specify the type of the L2VPN interface. |
|
Sets the "port" match-type for the L2VPN VPWS untagged interfaces. For tagged interfaces, "port" match-type is not supported. Ensure that there are no other tagged configurations for the interfaces when the port match-type is configured. When port matching is configured, it will match all traffic regardless of whether it is untagged, single-tagged, or double-tagged VLANs. |
|
Outer VLAN ID. |
|
Inner VLAN ID. |
|
Assign the logical interface to an instance. |
The following example shows an untagged interface configuration along with "port" match-type for the L2VPN VPWS untagged interface.
set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 0 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 0 interface-type l2vpn-vpws set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 0 match-type port set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 0 instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 commit
The following example shows a single-tagged interface configuration:
set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 100 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 100 interface-type l2vpn-vpws set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 100 instance l2vpn_ce1 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 100 vlan 100 commit
The following example shows a double-tagged interface configuration:
set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 200 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 200 interface-type l2vpn-vpws set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 200 instance l2vpn_ce2 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 200 vlan 200 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 200 inner-vlan 201 commit
EVPN Instance Configuration
An EVPN Instance (EVI) is a routing and forwarding instance of EVPN that covers all the participating PE routers in a VPN. EVI is configured per customer on the PE routers. Each EVI has a unique route distinguisher and one or more route targets.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
A unique name for the EVPN routing instance. |
||
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported value: l2vpn |
||
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: vpls-vpws
|
||
|
Specifies the routing protocol |
||
|
The route distinguisher (RD) uniquely defines routes within an IPv4 network. PE routers use route distinguishers to identify which VPN a packet belongs to. Supported formats are <as-number:id> or <ipv4-address:id>. |
||
|
The router ID of the routing instance. |
||
|
Route targets (RT) are used to transfer routes between VPN instances. The RT identifies a subset of routes that should be imported to or exported from a particular VPN instance. You can configure an RT for importing or exporting routes or both. |
In the following configuration, VRF instance AFI has been set to AFI: l2vpn and SAFI: vpls-vpws.
set instance l2vpn_ce1 set instance l2vpn_ce1 ipv4-router-id 182.1.6.4 set instance l2vpn_ce1 route-distinguisher 182.1.6.4:65006 set instance l2vpn_ce1 address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws set instance l2vpn_ce1 address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws route-target import target:182.1.6.0:65006 set instance l2vpn_ce1 address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws route-target export target:182.1.6.0:65006 commit
BGP Configuration
BGP L2VPN VFT (Virtual Forwarding Table) Configuration
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Name of the routing instance |
||
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported value: l2vpn |
||
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported value: vpls-vpws
|
||
|
The AS number in four-byte format. The numbers allowed are from 1 to 4294967295. |
||
|
Interface that is bound to L2VPN |
||
|
Specify the local site ID that is used to establish an EVPN PW between two PEs |
||
|
Specify the remote site ID that is used to establish an EVPN PW between two PEs |
||
|
Specify the label base value. |
The following example configures l2vpn_ce1 instance for BGP L2VPN.
set instance l2vpn_ce1 protocol bgp local-as 65006 set instance l2vpn_ce1 protocol bgp address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws set instance l2vpn_ce1 protocol bgp address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws interface ifl-0/0/17/100 set instance l2vpn_ce1 protocol bgp address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws interface ifl-0/0/17/100 local-site-id 300 set instance l2vpn_ce1 protocol bgp address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws interface ifl-0/0/17/100 remote-site-id 301 set instance l2vpn_ce1 protocol bgp address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws interface ifl-0/0/17/100 label-base 150000 commit
BGP L2VPN Configuration
Configuring the BGP L2VPN Address Family
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name of the routing instance |
To configure BGP L2VPN VPLS on the default instance, enter the following command:
set instance default protocol bgp address-family l2vpn vpls commit
Configuring Address Families for Peer Groups
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported value: l2vpn. |
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported value: vpls |
|
Enable extended-next-hop encoding for BGP peer groups to allow the transfer of IPv4 prefixes over an IPv6 connection. |
|
BGP nexthop address for routes advertised to this peer group |
To configure BGP L2VPN Peer Group on the default instance, enter the following command:
set instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine address-family l2vpn vpls commit
Configuring Control Word for L2VPN Pseudowire
A control word can be inserted between the label stack and the MPLS payload. Control word is disabled by default.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name of the routing instance. |
|
Name of the interface. |
Example: Enter the following command to enable Control Word on the default instance.
set instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine address-family l2vpn vpls-vpws interface ifl-0/0/1/10 control-word enable commit
Configuring VLAN Tag Manipulation
The following section describes the VLAN tag manipulation configuration syntax and commands.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Specify the name of the interface. |
|
Specify the unit ID for the interface. |
|
Ingress VLAN mapping. |
|
Egress VLAN mapping |
|
Specify any of the VLAN operations supported: |
|
Specify the encapsulation type for the VLAN operation. Supported only 802.1q. |
|
Specify the outer VLAN for the VLAN operation specified. |
|
Specify the inner VLAN for the VLAN operation specified. |
Example for VLAN operation 'push' configuration
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config set interface ifp-0/1/4 unit 1000 set interface ifp-0/1/4 unit 1000 set interface ifp-0/1/4 unit 1000 interface-type l2vpn-vpws set interface ifp-0/1/4 unit 1000 input-vlan-map vlan-operation push set interface ifp-0/1/4 unit 1000 input-vlan-map vlan-id 1001 set interface ifp-0/1/4 unit 1000 instance l2vpn_ce1 set interface ifp-0/1/4 unit 1000 vlan 1000
Example: VLAN operation 'push' configuration output
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config interface ifp-0/1/4 unit 1000
{
"rtbrick-config:unit": [
{
"unit-id": 1000,
"interface-type": "l2vpn-vpws",
"input-vlan-map": {
"vlan-operation": "push",
"vlan-id": 1001
},
"instance": "l2vpn_ce1",
"vlan": 1000
}
]
}
Example for VLAN operation 'push-push' configuration
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config set interface ifp-0/1/5 unit 2000 set interface ifp-0/1/5 unit 2000 set interface ifp-0/1/5 unit 2000 interface-type l2vpn-vpws set interface ifp-0/1/5 unit 2000 input-vlan-map vlan-operation push-push set interface ifp-0/1/5 unit 2000 input-vlan-map vlan-id 2000 set interface ifp-0/1/5 unit 2000 input-vlan-map inner-vlan-id 2001 set interface ifp-0/1/5 unit 2000 instance l2vpn_ce1 set interface ifp-0/1/5 unit 2000 vlan 2000 set interface ifp-0/1/5 unit 2000 inner-vlan 2
Example: VLAN operation 'push-push' configuration
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config interface ifp-0/1/5 unit 2000
{
"rtbrick-config:unit": [
{
"unit-id": 2000,
"interface-type": "l2vpn-vpws",
"input-vlan-map": {
"vlan-operation": "push-push",
"vlan-id": 2000,
"inner-vlan-id": 2001
},
"instance": "l2vpn_ce1",
"vlan": 2000,
"inner-vlan": 2
}
]
}