IS-IS Configuration
Configuration Hierarchy
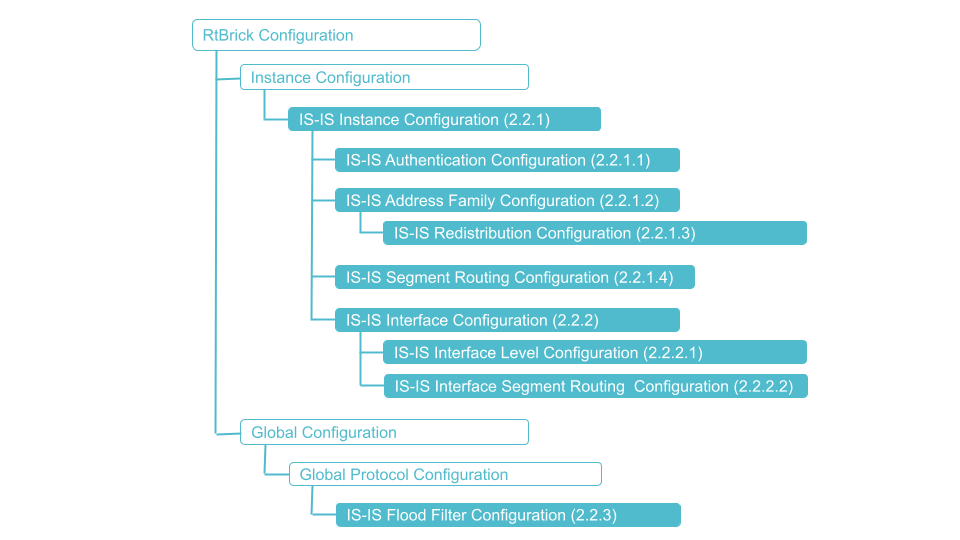
The diagram below illustrates the IS-IS configuration hierarchy.
Configuration Syntax and Commands
The following sections describe the IS-IS configuration syntax and commands.
Instance Configuration
The instance configuration hierarchy includes parameters that are required for or used by IS-IS.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Name of the IS-IS instance |
||
|
IS-IS area-address. The area can be represented in 1, 3, 5, 13 bytes format. |
||
|
Specifies the authentication scheme for IS-IS. Refer to section IS-IS Authentication Configuration for the IS-IS authentication configuration details. |
||
|
Specifies how long a neighbor should consider this routing device to be operative without receiving another hello packet. Default value: 30 seconds Range: 3 to 180 seconds |
||
|
Specifies the hostname mapped to the system identifier. |
||
|
This configuration allows you to enable the routing device to ignore the attached bit on incoming Level 1 link-state PDUs. If the attached bit is ignored, no default route, which points to the routing device which has set the attached bit, is installed. |
||
|
Name of the interface. Refer to section Configuring IS-IS Interface for the interface configuration details. |
||
|
Specifies whether the ipv6-disable configuration is enabled or not. When you set this value to "true", it indicates that IPv6 configuration is disabled. |
||
|
Protocol ISIS level-1/level-2 address-family configuration. Refer to section IS-IS Address-Family Configuration for the address family configuration details. |
||
|
Specifies whether the level1-to-level2 route-leak is enabled or not. When set to disable, IS-IS will not leak routing information from a Level 1 area to a Level 2 area. By default, this option is enabled. |
||
|
IS-IS link-state PDUs maximum lifetime. Default value: 65535 seconds |
||
|
Load sharing among multiple IS-IS paths.
|
||
|
When set to true, IS-IS will not install segment routing transit path. Default: false |
||
|
When set to true, IS-IS overload bit is set. Default: false |
||
|
ISIS router identifier (ipv4 format: A.B.C.D) |
||
|
Specifies the system ID of the device. |
Example: IS-IS Instance Configuration
The following configuration defines the instance 'default'.
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg>show config instance default protocol isis
{
"rtbrick-config:isis": {
"system-id": "1921.6800.1001",
"area": [
"49.0001/24"
],
"hostname": "isr1",
<...>Example: Disabling IS-IS Route Leaking from a Level 1 Area to a Level 2 Area
The following configuration defines IS-IS route leaking behavior between Level 1 and Level 2 routing domains.
set instance default protocol isis level1-to-level2 route-leak disable
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis level1-to-level2
{
"rtbrick-config:level1-to-level2": {
"route-leak": "disable"
}
} To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
IS-IS Authentication Configuration
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies an authentication check to reject PDUs that do not match the type or key requirements. You can enable or disable the authentication check. |
|
The key ID allows you to specify the key identifiers for level-1/level-2 authentication. |
|
Authentication key1 and key 2 encrypted text |
|
The level-1/level-2 authentication keys specify the authentication keys (passwords) that are used by the neighboring routing devices to verify the authenticity of packets sent from this interface. For the key to work, you also must include the authentication-type statement. |
|
Enables you to specify the authentication type for IS-IS. If you enable authentication, you must specify a password by including the authentication-key statement. The following authentication types are supported:
|
Example configuration for IS-IS authentication.
The following configuration sets up authentication for IS-IS protocol at both level-1 and level-2. For both level-1 and level-2, the authentication type is set to 'md5'. It indicates that MD5 will be used to secure IS-IS routing updates. The authentication keys for level-1: key1-encrypted-text is set to "$24a6f10525a11077bec3b451be8855877" and for level-2 key1-encrypted-text is set to "$2d787015bf84f3b58d5fd393a96c9639c". These key1-encrypted-text values are the encrypted (hashed) passwords used for authentication at each level.
set instance default protocol isis authentication level-1 type md5
set instance default protocol isis authentication level-1 key1-encrypted-text "$24a6f10525a11077bec3b451be8855877"
set instance default protocol isis authentication level-2 type md5
set instance default protocol isis authentication level-2 key1-encrypted-text "$2d787015bf84f3b58d5fd393a96c9639c"supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis authentication
{
"rtbrick-config:authentication": {
"level-1": {
"type": "md5",
"key1-encrypted-text": "$24a6f10525a11077bec3b451be8855877"
},
"level-2": {
"type": "md5",
"key1-encrypted-text": "$2d787015bf84f3b58d5fd393a96c9639c"
}
}
}
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
IS-IS Address-Family Configuration
The address-family command allows you to enable the address families that IS-IS will route and configure settings that are specific to that address family.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, ipv6 |
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast or labeled-unicast |
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI (level-1), click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI (level-1), click
here.
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI (level-2), click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI (level-2), click
here.
Configuring Route Redistribution
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, ipv6 |
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast or labeled-unicast |
|
Specifies the source from which the routes are to be redistributed from. The available options include |
|
Specifies the name of the policy map. The redistribute attach point allows routes from other sources to be advertised by IS-IS. Policy can be applied only to the routes that are redistributed from other sources to IS-IS. The support for inter-level leaking through policy is unavailable. |
Example: IS-IS address-family and route redistribution configuration
The following configuration defines how the IS-IS protocol at Level 1 will redistribute static routes for both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast address families. It sets up the IS-IS protocol within the "default" instance, specifically targeting Level 1 of the IS-IS hierarchy. For the IPv4 unicast address family, it specifies that routes learned from a static source should be redistributed. The policy applied during this redistribution is referred to as 'filter-link-address'.
Similarly, the configuration addresses the IPv6 unicast address family, redistributing routes from a static source. The policy applied is named 'filter-link6-address', which will be enforced during the redistribution of IPv6 routes.
set instance default protocol isis level-1 address-family ipv4 set instance default protocol isis level-1 address-family ipv4 safi unicast set instance default protocol isis level-1 address-family ipv4 redistribute static set instance default protocol isis level-1 address-family ipv4 redistribute static policy filter-link-address set instance default protocol isis level-1 address-family ipv6 set instance default protocol isis level-1 address-family ipv6 safi unicast set instance default protocol isis level-1 address-family ipv6 redistribute static set instance default protocol isis level-1 address-family ipv6 redistribute static policy filter-link6-address
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis level-1
{
"rtbrick-config:level-1": {
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "static",
"policy": "filter-link-address"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "static",
"policy": "filter-link6-address"
}
]
}
]
}
} To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI (level-1), click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI (level-1), click
here.
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI (level-2), click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI (level-2), click
here.
Segment Routing Configuration
IS-IS segment routing extensions allow to advertise labels with prefixes.
RBFS currently supports the following IS-IS segment routing features:
-
MPLS data plane
-
IPv4 prefixes (TLV 135) and IPv6 prefixes (TLV 236)
-
Prefix SID with node flag (Node SID) on loopback interface
-
Anycast SID
-
A single global SRGB block
-
Adjacency SIDs
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
`srgb base <srgb base>' |
Specifies the segment routing global block (SRGB) in source packet routing. SRGB is used for prefix SIDs. |
||
|
IS-IS system range of labels from the base label.
|
||
|
Specifies the segment routing local block (SRLB) in source packet routing. SRLB is used for adjacency SIDs. |
||
|
IS-IS system range of labels from the base label.
|
Example: IS-IS Segment Routing Configuration
This configuration establishes segment routing for the IS-IS instance. It defines two Segment Routing Global Blocks (SRGBs) and two Segment Routing Label Blocks (SRLBs). The SRLB has a base value of 2000 and a range of 1000, which means it will use labels from 2000 to 2999. Similarly, the SRGB has a base value of 1000 and a range of 1000, allowing it to use labels from 1000 to 1999. These values are essential for assigning Segment Identifiers (SIDs) within a Segment Routing domain.
set instance default protocol isis segment-routing srlb base 2000 set instance default protocol isis segment-routing srlb range 1000 set instance default protocol isis segment-routing srgb base 1000 set instance default protocol isis segment-routing srgb range 1000
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis segment-routing
{
"rtbrick-config:segment-routing": {
"srlb": {
"base": 2000,
"range": 1000
},
"srgb": {
"base": 1000,
"range": 1000
}
}
} To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Configuring IS-IS Interface
By default, there are no interfaces associated with IS-IS. You must configure at least one IS-IS interface for IS-IS adjacency formation.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Specifies the name of the IS-IS interface. IS-IS can be configured on both numbered and unnumbered interfaces. |
||
|
Specifies the IS-IS flood filter name |
||
|
Specifies IS-IS system interface hello interval.
|
||
|
Specify IS-IS interface level configuration. Refer to section IS-IS Interface Level Configuration for the IS-IS interface level configuration details. |
||
|
IS-IS system interface LSP interval. Default value: 100 |
||
|
Enable interface in passive mode. Default: false |
||
|
Interface level system id |
||
|
Specifies the type of the IS-IS system interface. Default: point-to-point. broadcast—Specifies a broadcast (or LAN) interface. |
||
|
Enable LDP IGP synchronization. Default: disable |
||
|
Enables (true) or disables (false) no-penultimate-hop-pop. Default: false |
||
|
Enables (true) or disables (false) explicit-null. Default: false. |
Example: IS-IS Interface Configuration
The following configuration defines the IS-IS protocol settings for three interfaces: ifl-0/0/2/0, ifl-0/0/2/1, and lo-0/0/0/0. It specifies parameters such as interface types (point-to-point and broadcast), authentication settings, LSP (Link State Protocol) intervals, LDP (Label Distribution Protocol) synchronization, metrics, priorities, and hello intervals for both Level-1 and Level-2 IS-IS on each of these interfaces. Also, it configures Segment Routing with IPv4 and IPv6 SID (Segment Identifier) indices for the loopback interface.
For the interface ifl-0/0/2/0, the type is set to point-to-point, indicating that this interface is configured for a direct, one-to-one connection. The passive setting is set to false, meaning IS-IS will send and receive hello messages on this interface. Both SNP (Synchronized Network Protocol) and hello authentication for Level-1 are disabled.
For the interface ifl-0/0/2/1, a flood filter named spine1_lsr1_flood_filter is applied to control the flooding of IS-IS LSPs. This interface type is defined as broadcast, indicating that it is a multi-access interface. The LSP interface interval is set to 200, which determines the time interval at which LSPs are generated. LDP synchronization is enabled that allows synchronization between IS-IS and LDP. For the interface lo-0/0/0/0, the passive setting is true, which means IS-IS will not send hello messages or LSPs on this interface.
set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/0 passive false set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/0 level-1 snp-authentication disable set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/0 level-1 hello-authentication disable set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 flood-filter spine1_lsr1_flood_filter set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 type broadcast set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/0 type point-to-point set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 lsp-interval 200 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 ldp-synchronization enable set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 snp-authentication enable set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 hello-authentication enable set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 metric 1000 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 adjacency-disable false set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 priority 100 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 hello-interval 20 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-2 priority 100 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-2 hello-interval 20 set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 passive true set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv4 index 100 set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv6 index 102
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis interface
{
"rtbrick-config:interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/2/0",
"type": "point-to-point",
"passive": "false",
"level-1": {
"snp-authentication": "disable",
"hello-authentication": "disable"
},
"level-2": {}
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/2/1",
"flood-filter": "spine1_lsr1_flood_filter",
"type": "broadcast",
"lsp-interval": 200,
"ldp-synchronization": "enable",
"level-1": {
"snp-authentication": "enable",
"hello-authentication": "enable",
"metric": 1000,
"adjacency-disable": "false",
"priority": 100,
"hello-interval": 20
},
"level-2": {
"priority": 100,
"hello-interval": 20
}
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/0/0",
"passive": "true",
"segment-routing": {
"ipv4": {
"index": 100
},
"ipv6": {
"index": 102
}
},
"level-1": {},
"level-2": {}
}
]
}Example: IS-IS Interface Level Flood Filter Configuration
This configuration sets a flood filter named 'spine1_lsr1_flood_filter' on the interface 'ifl-0/0/2/1' for S-IS protocol to control the flooding of routing updates.
set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 flood-filter spine1_lsr1_flood_filter
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 flood-filter
{
"rtbrick-config:flood-filter": "spine1_lsr1_flood_filter"
}Example: IS-IS Interface Configuration with enabled LDP synchronization
set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 ldp-synchronization enable
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 ldp-synchronization
{
"rtbrick-config:ldp-synchronization": "enable"
}Example: IS-IS Interface Configuration for a Broadcast Interface.
This configuration enables LDP synchronization on the interface 'ifl-0/0/2/1' for the default instance for the IS-IS routing protocol.
set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 ldp-synchronization enable
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 type
{
"rtbrick-config:type": "broadcast"
}Example: P/E Flags Configuration for SID in IS-IS Segment Routing
set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/1 segment-routing ipv4 no-penultimate-pop true
The following command configures to assign an explicit null label for the penultimate router on the egress LSP. The configuration sets the 'lo-0/0/0/0' interface for the default IS-IS protocol instance. This interface is configured as passive for IS-IS and enables Segment Routing for both IPv4 and IPv6. The configuration includes assigning Segment Identifiers, enabling 'no-penultimate-pop' behavior, and advertising explicit null labels for both IPv4 and IPv6.
set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 passive true set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv4 index 100 set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv4 no-penultimate-pop true set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv4 explicit-null true set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv6 index 106 Set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv6 no-penultimate-pop true set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv6 explicit-null true
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0
{
"rtbrick-config:interface": [
{
"name": "lo-0/0/0/0",
"passive": "true",
"segment-routing": {
"ipv4": {
"index": 100,
"no-penultimate-pop": "true",
"explicit-null": "true"
},
"ipv6": {
"index": 106,
"no-penultimate-pop": "true",
"explicit-null": "true"
}
}
}
]
}
 To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
IS-IS Interface Level Configuration
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Specify the level-1/level-2 adjacency on an interface. Default: false. |
|
Authentication on hello packets. |
|
Specifies the length of time between the sending of IS-IS hello PDUs. Default: 10. The hello interval can be set for both |
|
Specify the priority on a broadcast interface. Default: 64. |
|
Level-1/Level-2 metric on an interface. Default: 1000000. |
|
Authentication on CSNP/PSNP packets. |
Example: IS-IS Interface Level Configuration
This configuration defines the parameters for the IS-IS interface 'ifl-0/0/2/1'. It includes various Level 1 and Level 2 parameters such as authentication for SNPs and hello messages, metrics, priorities, and hello intervals. It also defines the broadcast type, LSP intervals, and LDP synchronization.
For Level 1, snp-authentication and hello-authentication are enabled. The metric is set to 1000 or determining optimal paths. The adjacency-disable option is set to 'false', allowing Level 1 adjacencies. The priority is set to 100, and the hello-interval defines the interval for sending Level 1 Hello PDUs as 20 seconds.
For Level 2, the priority is also set to 100, influencing the Level 2 Designated Intermediate System (DIS) election, and the hello-interval is similarly set to 20 seconds for sending Level 2 Hello PDUs.
set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 flood-filter spine1_lsr1_flood_filter set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 type broadcast set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 lsp-interval 200 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 ldp-synchronization enable set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 snp-authentication enable set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 hello-authentication enable set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 metric 1000 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 adjacency-disable false set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 priority 100 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-1 hello-interval 20 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-2 priority 100 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 level-2 hello-interval 20
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1
{
"rtbrick-config:interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/2/1",
"flood-filter": "spine1_lsr1_flood_filter",
"type": "broadcast",
"lsp-interval": 200,
"ldp-synchronization": "enable",
"level-1": {
"snp-authentication": "enable",
"hello-authentication": "enable",
"metric": 1000,
"adjacency-disable": "false",
"priority": 100,
"hello-interval": 20
},
"level-2": {
"priority": 100,
"hello-interval": 20
}
}
]
} To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
Interface-level Segment Routing Configuration
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Anycast index segment-ID. The prefix SIDs and anycast SIDs are applied on loopback interface only. |
|
Prefix index segment ID. |
|
Adjacency index segment-ID. The adjacency SIDs are applied on active IS-IS interfaces on which adjacencies are established. |
Example: IS-IS Interface Level Segment Routing Configuration for Prefix and Anycast SID
This configuration establishes IS-IS Interface Level Segment Routing for both IPv4 and IPv6 on two loopback interfaces. The interface 'lo-0/0/0' is assigned unique Segment Identifier indices: 100 for IPv4 and 200 for IPv6. These SIDs are utilized for prefix routing, allowing for the identification of specific network segments. Also, the loopback interface 'lo-0/0/1' is configured with anycast SID indices of 110 for IPv4 and 210 for IPv6. This configuration enables segment routing on both of the interfaces.
set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0 set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0 segment-routing ipv4 set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0 segment-routing ipv4 index 100 set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0 segment-routing ipv6 set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0 segment-routing ipv6 index 200 set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/1 segment-routing ipv4 anycast-index 110 set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/1 segment-routing ipv6 anycast-index 210
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis interface
{
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"protocol": {
"isis": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "lo-0/0/0",
"segment-routing": {
"ipv4": {
"index": 100
},
"ipv6": {
"index": 200
}
}
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/1",
"segment-routing": {
"ipv4": {
"anycast-index": 110
},
"ipv6": {
"anycast-index": 210
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}Example: IS-IS Interface Level Segment Routing Configuration for Adjacency SID
This configuration establishes IS-IS Interface Level Segment Routing for both IPv4 and IPv6 on two loopback interfaces. The interface 'lo-0/0/0' is assigned unique Segment Identifier indices: 100 for IPv4 and 200 for IPv6. These SIDs are utilized for prefix routing. Also, the loopback interface 'lo-0/0/1' is configured with anycast SID indices '110', for IPv4 and 210 for IPv6. It enables segment routing on both of the interfaces.
set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/0 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/0 segment-routing point-to-point ipv4 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/0 segment-routing point-to-point ipv4 adjacency-index 111 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/0 segment-routing point-to-point ipv6 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/0 segment-routing point-to-point ipv6 adjacency-index 112
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/0 segment-routing
{
"rtbrick-config:segment-routing": {
"point-to-point": {
"ipv4": {
"adjacency-index": 111
},
"ipv6": {
"adjacency-index": 112
}
}
}
} To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
To access the RESTCONF API that corresponds to this CLI, click
here.
IS-IS Global Configuration
IS-IS Flood Filter Configuration
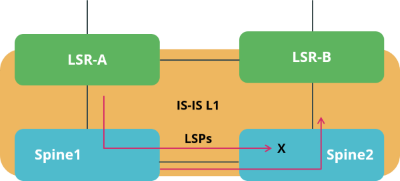
In IS-IS, by default all routers flood link-state packets, so that all routers will have a complete topology view. IS-IS flood filters allow to modify this behavior and limit the exchange of LSPs. For example, if two spine routers in a spine/leaf fabric are symmetrically connected to two upstream label-switch routers (LSR) like shown in the figure below, you can use a flood filter to not advertise LSPs learned from LSR A back to the LSR B via the second spine switch.
The flooding filter configuration is part of the global configuration hierarchy and therefore you can configure filtering globally, i.e. not per instance, so that the filter configurations can be reused across instances.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Filter-name which binds a flooding filter to an IS-IS interface |
|
Number to filter rule |
|
Action required to flood or not |
|
Name for the filter rule |
|
IS-IS instance system-id |
|
System ID mask on which the filter should match |
Example: IS-IS Flood Filter Configuration
This configuration sets up a flood filter named 'spine1_lsr1_flood_filter' for the interface 'ifl-0/0/2/1'.
set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 flood-filter flood-filter spine1_lsr1_flood_filter
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/0/2/1 flood-filter
{
"rtbrick-config:flood-filter": "spine1_lsr1_flood_filter"
}Level 2 to Level 1 Policy Configuration
The policy configuration allows to define a policy for leaking all the level 2 routes to level 1.
For more information about Policy configuration, see the Policy User Guide.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
ordinal <value> |
Specifies the ordinal value. |
rule <number> |
Specify the action rule number. |
operation return-permit |
Stops policy execution and return result as permit. |
The following configuration defines a routing policy named 'isis_l2tol1_leak' that permits all routes to be leaked from IS-IS Level 2 into Level 1. The policy contains a rule (ordinal 1) with an action to 'return-permit'. Since no specific prefixes are matched, the permit action applies to all routes by default. This configuration allows all Level 2 routes to be leaked into Level 1 routers.
set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action rule 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action rule 1 operation return-permit
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config policy
{
"rtbrick-config:policy": {
"statement": [
{
"name": "isis_l2tol1_leak",
"ordinal": [
{
"ordinal": 1,
"action": {
"rule": [
{
"rule": 1,
"operation": "return-permit"
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
}
Level 2 to Level 1 Policy Configuration for a Specific IPv4 Route
The policy configuration allows to define a policy for leaking a specific IPv4 level 2 routes to level 1.
For more information about Policy configuration, see the Policy User Guide.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies the match rule number. |
|
Specifies the attribute type. |
|
Specifies the match type. |
|
Attribute value. This is the actual value of the attribute to match, for example an IP prefix. |
|
Attribute value type. |
The following policy configuration allows only a specific IPv4 route to be leaked from level2 to level1 and blocking the other level2 route leaking to level1. It defines a routing policy named 'isis_l2tol1_leak' that controls which IS-IS Level 2 routes are leaked into Level 1. The rule 'ordinal 1' matches the exact IPv4 prefix 192.168.1.3/32 and allows it to be leaked from Level 2 to Level 1. The second rule 'ordinal 10' is as a default deny (return-deny), preventing any other prefixes from being leaked. This ensures only the explicitly defined route is distributed to Level 1 routers. The policy contains rules to leak a specific route to Level 1 routers and to deny all other routes from leaking.
set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match rule 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match rule 1 type ipv4-prefix set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match rule 1 value-type discrete set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match rule 1 match-type exact set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match rule 1 value 192.168.1.3/32 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action rule 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action rule 1 operation return-permit set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 10 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 10 action set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 10 action rule 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 10 action rule 1 operation return-deny
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config policy
{
"rtbrick-config:policy": {
"statement": [
{
"name": "isis_l2tol1_leak",
"ordinal": [
{
"ordinal": 1,
"match": {
"rule": [
{
"rule": 1,
"type": "ipv4-prefix",
"value-type": "discrete",
"match-type": "exact",
"value": [
"192.168.1.3/32"
]
}
]
},
"action": {
"rule": [
{
"rule": 1,
"operation": "return-permit"
}
]
}
},
{
"ordinal": 10,
"action": {
"rule": [
{
"rule": 1,
"operation": "return-deny"
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
}
IS-IS Level 2 to Level 1 Route Leaking Configuration
This configuration associates level2 to level1 route leaking policy with the IS-IS instance.
| Level 2 to Level 1 route leaking policy must be created prior to referencing it to the IS-IS instance. |
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies the name of the instance. |
|
Specify name of the route leak policy. |
Example: IS-IS Level 2 to Level 1 Route Leaking Configuration
This following configuration enables route leaking from IS-IS Level 2 to Level 1 within the default routing instance. It allows specific Level 2 routes to be advertised into the Level 1 area using the defined route policy 'isis_l2tol1_leak'. The policy determines which routes are eligible for leaking and provides controlled redistribution between IS-IS levels for improved reachability.
set instance default protocol isis level2-to-level1 route-leak policy isis_l2tol1_leak
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis level2-to-level1
{
"rtbrick-config:level2-to-level1": {
"route-leak": {
"policy": [
"isis_l2tol1_leak"
]
}
}
}
Level 2 to Level 1 Policy Configuration
The policy configuration allows to define a policy for leaking all the level 2 routes to level 1.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
ordinal <value> |
Specifies the ordinal value. |
rule <number> |
Specify the action rule number. |
operation return-permit |
Stops policy execution and return result as permit. |
The following configuration defines a routing policy named 'isis_l2tol1_leak' that permits all routes to be leaked from IS-IS Level 2 into Level 1. The policy contains a rule (ordinal 1) with an action to 'return-permit'. Since no specific prefixes are matched, the permit action applies to all routes by default. This configuration allows all Level 2 routes to be leaked into Level 1 routers.
set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action rule 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action rule 1 operation return-permit
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config policy
{
"rtbrick-config:policy": {
"statement": [
{
"name": "isis_l2tol1_leak",
"ordinal": [
{
"ordinal": 1,
"action": {
"rule": [
{
"rule": 1,
"operation": "return-permit"
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
}
Level 2 to Level 1 Policy Configuration for a Specific IPv4 Route
The policy configuration allows to define a policy for leaking a specific IPv4 level 2 routes to level 1.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies the match rule number. |
|
Specifies the attribute type. |
|
Specifies the match type. |
|
Attribute value. This is the actual value of the attribute to match, for example an IP prefix. |
|
Attribute value type. |
The following policy configuration allows only a specific IPv4 route to be leaked from level2 to level1 and blocking the other level2 route leaking to level1. It defines a routing policy named 'isis_l2tol1_leak' that controls which IS-IS Level 2 routes are leaked into Level 1. The rule 'ordinal 1' matches the exact IPv4 prefix 192.168.1.3/32 and allows it to be leaked from Level 2 to Level 1. The second rule 'ordinal 10' is as a default deny (return-deny), preventing any other prefixes from being leaked. This ensures only the explicitly defined route is distributed to Level 1 routers. The policy contains rules to leak a specific route to Level 1 routers and to deny all other routes from leaking.
set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match rule 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match rule 1 type ipv4-prefix set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match rule 1 value-type discrete set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match rule 1 match-type exact set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 match rule 1 value 192.168.1.3/32 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action rule 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 1 action rule 1 operation return-permit set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 10 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 10 action set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 10 action rule 1 set policy statement isis_l2tol1_leak ordinal 10 action rule 1 operation return-deny
supervisor@rtbrick.net: cfg> show config policy
{
"rtbrick-config:policy": {
"statement": [
{
"name": "isis_l2tol1_leak",
"ordinal": [
{
"ordinal": 1,
"match": {
"rule": [
{
"rule": 1,
"type": "ipv4-prefix",
"value-type": "discrete",
"match-type": "exact",
"value": [
"192.168.1.3/32"
]
}
]
},
"action": {
"rule": [
{
"rule": 1,
"operation": "return-permit"
}
]
}
},
{
"ordinal": 10,
"action": {
"rule": [
{
"rule": 1,
"operation": "return-deny"
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
}