L3VPN Configuration
Configuration Hierarchy
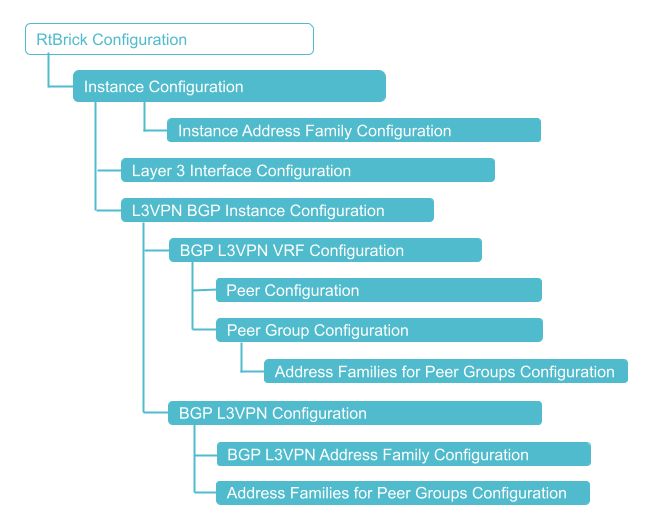
The diagram below shows the L3VPN configuration hierarchy.
Configuration Syntax and Commands
The following sections describe the BGP configuration syntax and commands.
Instance Configuration
Each VPN is associated with one or more VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) instances. A VRF defines the VPN membership of a customer site attached to a PE router. A VRF consists of the following components:
-
An IP version 4 (IPv4) 6 (IPv6) unicast routing table
-
A private FIB table
-
A set of interfaces that use the forwarding table
-
A set of rules and routing protocol parameters that control the information that is included in the routing table
These components are collectively called a VRF instance.
The instance configuration hierarchy includes parameters that are required for or used by BGP, but that are not part of the BGP protocol configuration hierarchy itself. Route distinguishers and router IDs are configured directly at the instance hierarchy.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Name of the routing instance |
||
|
The route distinguisher (RD) uniquely defines routes within an IPv4 network. PE routers use route distinguishers to identify which VPN a packet belongs to. Supported formats are <as-number:id> or <ipv4-address:id>.
|
||
|
The router ID of the routing instance. |
The following example configures tge instance identifier.
set instance l3vpn-ce1 set instance l3vpn-ce1 ipv4-router-id 172.16.3.10 set instance l3vpn-ce1 route-distinguisher 172.16.3.10:65001 commit
Example: Instance Identifier Configuration
supervisor@PE1: cfg> show config instance l3vpn-ce1
{
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "l3vpn-ce1",
"ipv4-router-id": "172.16.3.10",
"route-distinguisher": "172.16.3.10:65001",
<...>
Address Families
At the instance address family hierarchy, you can enable or disable address families for the instance, and configure parameters like route targets.
Please note default settings depend on the instance. For the 'default' instance, the IPv4 and IPv6 unicast, multicast, and labeled unicast, as well as the MPLS unicast address families are enabled by default. For any non-default instance, no address family is enabled by default and needs to be enabled by configuration.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, ipv6 |
||
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast |
||
|
Route targets (RT) are used to transfer routes between VPN instances. The RT identifies a subset of routes that should be imported to or exported from a particular VPN instance. You can configure an RT for importing or exporting routes or both.
|
||
|
There are two attachment points for BGP policies. At this configuration hierarchy, you can attach import or export policies to the instance. These policies apply when routes are imported from the BGP protocol into the instance, or exported from the instance to the BGP protocol. |
The following example configures the instance address families.
set instance l3vpn-ce1 address-family ipv4 unicast set instance l3vpn-ce1 address-family ipv4 unicast route-target import target:172.16.3.10:65001 set instance l3vpn-ce1 address-family ipv4 unicast route-target export target:172.16.3.10:65001 set instance l3vpn-ce1 address-family ipv6 unicast set instance l3vpn-ce1 address-family ipv6 unicast route-target import target:172.16.3.11:65001 set instance l3vpn-ce1 address-family ipv6 unicast route-target export target:172.16.3.11:65001 commit
Example: Instance Address Family Configuration
supervisor@PE1: cfg> show config instance l3vpn-ce1 address-family
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"route-target": {
"import": [
"target:172.16.3.10:65001"
],
"export": [
"target:172.16.3.10:65001"
]
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"route-target": {
"import": [
"target:172.16.3.11:65001"
],
"export": [
"target:172.16.3.11:65001"
]
}
}
]
}
Layer 3 Interface Configuration
L3VPN supports the configuration of Layer 3 logical interfaces.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Create a logical interface (also referred to as a sub-interface) under the physical interface. |
|
Inner VLAN ID. |
|
Assign the logical interface to an instance. |
|
Outer VLAN ID. |
The following example shows the interface configuration.
set interface ifp-0/0/2 unit 0 set interface ifp-0/0/2 unit 0 instance l3vpn-ce1 set interface ifp-0/0/2 unit 0 address ipv4 10.0.0.1/24 commit
Example: Interface Configuration
supervisor@PE1: cfg> show config interface ifp-0/0/2
{
"rtbrick-config:interface": [
{
"name": "ifp-0/0/2",
"unit": [
{
"unit-id": 0,
"instance": "l3vpn-ce1",
"address": {
"ipv4": [
{
"prefix4": "10.0.0.1/24"
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
Interface Address Configuration
This section describes how to configure interface IP addresses.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4 and ipv6 |
|
Assign IPv4 or IPv6 address to the interface unit. |
The following show the interface address configuration.
set interface ifp-0/0/2 unit 0 set interface ifp-0/0/2 unit 0 instance l3vpn-ce1 set interface ifp-0/0/2 unit 0 address ipv4 10.0.0.1/24 commit
Example: Interface Address Configuration
supervisor@PE1: cfg> show config interface ifp-0/0/2
{
"rtbrick-config:interface": [
{
"name": "ifp-0/0/2",
"unit": [
{
"unit-id": 0,
"instance": "l3vpn-ce1",
"address": {
"ipv4": [
{
"prefix4": "10.0.0.1/24"
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
L3VPN BGP Instance Configuration
BGP L3VPN VFT (Virtual Forwarding Table) Configuration
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name of the routing instance |
|
The name of the BGP host, to a maximum of 64 characters |
|
The name of the BGP routing domain, to a maximum of 64 characters |
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported value: ipv4, ipv6 |
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported value: unicast |
|
The AS number in four-byte format. The numbers allowed are from 1 to 4294967295. |
|
The BGP Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) value. The numbers allowed are from 0 to 4294967295. When an AS has multiple links to another AS, the MED value is used to determine the exit to use to reach the other AS. |
|
Router identifier in IPv4 format |
|
Hold timer in seconds. The valid range is 5 to 65535. |
|
Keep a live timer in seconds. The valid range is 5 to 65535. |
|
Enable the redistribution feature to dynamically inject specific types of routes into the BGP protocol. Supported route sources are |
|
Attach a policy to the redistribution process |
The following example configures BGP L3VPN VFT (Virtual Forwarding Table).
set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp domain-name PE1-AS1 set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp hostname PE1-AS1 set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp local-as 65001 set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp router-id 172.16.3.10 set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast commit
Example: BGP L3VPN VFT (Virtual Forwarding Table)
supervisor@PE1: cfg> show config instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
"domain-name": "PE1-AS1",
"hostname": "PE1-AS1",
"local-as": 65001,
"router-id": "172.16.3.10",
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
}
],
<...>
Peer Configuration
Once peer groups have been defined, BGP peers can be configured at the peer configuration hierarchy. A peer can be specified by address, or by interface when using IPv6 auto-discovered neighbors and link-local addresses. Furthermore, it is possible to configure TCP authentication and bind it to a peer.
Syntax to configure a BGP peer by address:
Syntax to configure a BGP peer using IPv6 link-local addresses:
Syntax to configure TCP Authentication for BGP peers:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable BGP peer using IPv6 link-local addresses |
|
IPv4 address of a BGP peer |
|
IPv6 address of a BGP peer |
|
Specify the value for allow-as-in. Allowed range of value 1 - 10. |
|
Local IP address to be used for the peering |
|
Assign the peer to a peer group |
|
Authentication identifier |
The following example configures a peer.
set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp peer ipv4 10.0.0.9 10.0.0.1 set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp peer ipv4 10.0.0.9 10.0.0.1 peer-group ce1 commit
Example: Peer Configuration
supervisor@PE1: cfg> show config instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp peer
{
"rtbrick-config:peer": {
"ipv4": [
{
"peer-address": "10.0.0.9",
"update-source": "10.0.0.1",
"peer-group": "ce1"
}
]
}
}
Peer Group Configuration
In BGP, neighbor peers with the same update policies can be grouped to simplify the initial configuration and updates. Peers share the same policies such as route maps, distribution lists, filter lists, update sources, and so on, so peer groups only need one configuration statement for these values.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Local AS number for the peer group |
|
Remote AS number for the peer group |
|
Enable dynamic AS negotiation for this peer group |
|
By default, the maximum number of hops between eBGP peers is 1 (direct connection). This hop count overrides the default behavior allowing connectivity between eBGP peers not directly connected. |
The following example configures a peer group.
set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp peer-group ce1 set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp peer-group ce1 remote-as 65009 commit
Example: Peer Group Configuration
supervisor@PE1: cfg> show config instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp peer-group
{
"rtbrick-config:peer-group": [
{
"pg-name": "ce1",
"remote-as": 65009,
<...>
Configuring Address Families for Peer Groups
At this configuration hierarchy, you can enable the address families that shall be supported for the group peers, and enable features specific to the address family.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, or ipv6 |
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast ` |
|
BGP nexthop address for routes advertised to this peer group |
|
Apply a routing policy to the peer group |
The following example configures the address families that shall be supported for the group peers
set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp peer-group ce1 address-family ipv4 unicast set instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp peer-group ce1 address-family ipv6 unicast commit
Example: Peer Groups Address Family Configuration
supervisor@PE1: cfg> show config instance l3vpn-ce1 protocol bgp peer-group ce1 address-family
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
}
]
}
BGP L3VPN Configuration
Configuring the BGP L3VPN Address Families
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name of the routing instance |
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, ipv6 |
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: vpn-unicast |
To configure BGP L3VPN on the default instance, enter the following command:
set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 vpn-unicast set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv6 vpn-unicast commit
Example: BGP L3VPN Address Family Configuration
supervisor@PE1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp address-family
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
}
]
}
Configuring Address Families for Peer Groups
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported value: ipv4, ipv6. |
|
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported value: vpn-unicast |
|
Negotiate additional path capabilities with these peers, so that more than one path can be active to the peers in the group |
|
Generate and advertise a default route to peers in the group |
|
Enable extended-next-hop encoding for BGP peer groups to allow the transfer of IPv4 prefixes over an IPv6 connection |
|
Set the advertised BGP nexthop to yourself, this is the default for eBGP |
|
Do not modify the advertised BGP nexthop, this is the default for iBGP |
|
BGP nexthop address for routes advertised to this peer group |
|
Remove private AS numbers from routes advertised to group peers |
|
Configure this peer as a route reflector client |
|
Apply a routing policy to the peer group |
To configure BGP L3VPN Peer Group on the default instance, enter the following command:
set instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2-AS1 address-family ipv4 vpn-unicast set instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2-AS1 address-family ipv6 vpn-unicast commit
Example: Configuring Address Families for Peer Groups
supervisor@PE1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer-group PE2-AS1
{
"rtbrick-config:peer-group": [
{
"pg-name": "PE2-AS1",
"remote-as": 4200000001,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
}
]
}
]
}