BGP Configuration
Configuration Hierarchy
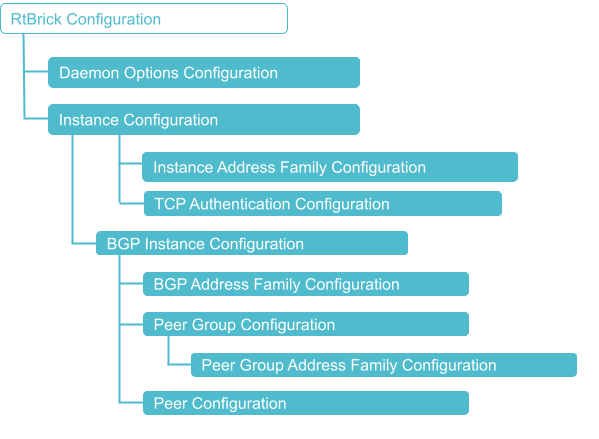
The diagram illustrates the BGP configuration hierarchy. All BGP configuration is done within an instance, for example the default instance or a VPN service instance. The instance configuration hierarchy includes parameters required for BGP but not part of the BGP configuration hierarchy itself. The BGP instance configuration hierarchy includes parameters which are generic to the respective BGP instance. The sub-hierarchies include parameters which are specific to address families, peer groups, and peers.
Configuration Syntax and Commands
The following sections describe the BGP configuration syntax and commands.
Daemon Options Configuration
This configuration associates the BGP daemons with routing instances, AFIs, and SAFIs.
| The BGP daemon option configurations have been deprecated. These will be removed in a subsequent release. |
Syntax:
set daemon-options <instance-name> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Name of the BGP instance |
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). |
<safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). |
<bd-type> |
Daemon type |
bd-name <bd-name> |
Daemon name |
Example: Daemon Configuration
{
"rtbrick-config:daemon-options": [
{
"instance-name": "*",
"afi": "*",
"safi": "*",
"bd-type": "bgp.appd",
"bd-name": "bgp.appd.1"
},
{
"instance-name": "*",
"afi": "*",
"safi": "*",
"bd-type": "bgp.iod",
"bd-name": "bgp.iod.1"
}
]
}
Instance Configuration
The instance configuration hierarchy includes parameters that are required for or used by BGP, but that are not part of the BGP protocol configuration hierarchy itself.
Route distinguishers and router IDs are configured directly at the instance hierarchy.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
route-distinguisher <as-number|ipv4-address:id> |
The route distinguisher (RD) uniquely defines routes within an IPv4 network. PE routers use route distinguishers to identify which VPN a packet belongs to. Supported formats are <as-number:id> or <ipv4-address:id>.
|
||
ipv4-router-id <ipv4-address> |
The router ID of the routing instance. |
Example: Instance Identifier Configuration
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance services
{
"rtbrick-config:instance": {
"name": "services",
"ipv4-router-id": "198.51.100.41",
"route-distinguisher": "198.51.100.41:101",
<...>
}
}
Address Families
At the instance address family hierarchy, you can enable or disable address families for the instance, and configure parameters like route targets.
Please note default settings depend on the instance. For the 'default' instance, the IPv4 and IPv6 unicast, multicast, and labeled unicast, as well as the MPLS unicast address families are enabled by default. For any non-default instance, no address family is enabled by default and needs to be enabled by configuration.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, ipv6, or mpls |
||
<safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast, labeled-unicast, or multicast |
||
route-target ( import | export ) <rt-value> |
Route targets (RT) are used to transfer routes between VPN instances. The RT identifies a subset of routes that should be imported to or exported from a particular VPN instance. You can configure a RT for importing or exporting routes or both.
|
||
policy ( import | export ) <policy-name> |
There are two attachment points for BGP policies. At this configuration hierarchy, you can attach import or export policies to the instance. These policies apply when routes are imported from the BGP protocol into the instance, or exported from the instance to the BGP protocol. |
Example: Instance Address Family Configuration
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance services
{
"rtbrick-config:instance": {
"name": "services",
<...>
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"policy": {
"export": "MY_V4_POLICY"
},
"route-target": {
"import": "target:198.51.100.70:14",
"export": "target:198.51.100.70:14"
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"policy": {
"export": "MY_V6_POLICY"
},
"route-target": {
"import": "target:198.51.100.70:16",
"export": "target:198.51.100.70:16"
}
}
],
<...>
}
}
TCP Authentication Configuration
In the instance TCP authentication hierarchy, you can optionally enable MD5 or HMAC SHA authentication. Authentication is not configured for BGP directly but for the TCP sessions used by BGP. It is necessary to bind authentication to a peer in order for the authentication to work.
| BGP TCP authentication is not backward compatible. |
Syntax:
set instance <instance> tcp authentication <authentication-id> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<authentication-id> |
Authentication identifier |
type <type> |
Authentication identifiers such as MD5 |
key1-id <key1-id> |
Key ID1 of the receiver |
key1-encrypted-text <key1-encrypted-text> |
Encrypted text of key1 |
key1-plain-text <key1-plain-text> |
Plain text of key1 |
key2-id <key2-id> |
Key ID2 of the receiver |
key2-encrypted-text <key2-encrypted-text> |
Encrypted text of key2 |
key2-plain-text <key2-plain-text> |
Plain text of key2 |
Example: BGP TCP Authentication Configuration
{
"rtbrick-config:tcp": {
"authentication": [
{
"authentication-id": "auth1",
"type": "MD5",
"key1-id": 10,
"key1-encrypted-text": "$2784cfa7523916c8cc5dfeba83562cbb4",
"key2-id": 20,
"key2-encrypted-text": "$2e9bb845e3cfcf8173973029e5c1d90d6"
}
]
}
}
BGP Instance Configuration
At this configuration hierarchy, you configure BGP protocol parameters which are generic to the BGP instance.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol bgp <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
host-name <host-name> |
The name of the BGP host, to a maximum of 64 characters |
domain-name <domain-name> |
The name of the BGP routing domain, to a maximum of 64 characters |
enforce-first-as <enable|disable> |
By default, the BGP routing process enforces the First AS feature. It discards updates received from an eBGP peer if the peer does not list its own AS number as the first segment in the AS_PATH BGP attribute. Disable the First AS feature to accept updates without the peer’s source AS matching the first AS in the AS_PATH attribute. |
local-as <as-number> |
The AS number in four-byte format. The numbers allowed are from 1 to 4294967285. |
local-preference <preference-value> |
The local preference for the BGP protocol. The numbers allowed are from 0 to 4294967285. The local preference is used to select the exit path for an AS. |
med <med-value> |
The BGP Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) value. The numbers allowed are from 0 to 4294967285. When an AS has multiple links to another AS, the MED value is used to determine the exit to use to reach the other AS. |
protocol-preference ( internal | external) <preference-value> |
Protocol preference of routes learned by eBGP ('external'), iBGP ('internal'), or both. This preference is used to select routes learned from multiple protocols. |
router-id <router-id> |
Router identifier in IPv4 format |
cluster-id <cluster-identifier> |
The cluster ID associates routers in a group within a BGP routing instance. Routers belong to the same cluster if they have the same cluster-ID. The cluster ID is formatted as an IPv4 address. |
timer hold-time <seconds> |
Hold timer in seconds. The valid range is 5 to 65535. |
timer keepalive <seconds> |
Keep a live timer in seconds. The valid range is 5 to 65535. |
type-of-service cost <low|normal> |
ToS cost field (bit 6) for BGP packets |
type-of-service delay <low|normal> |
ToS delay field (bit 3) for BGP packets |
type-of-service precedence <precedence> |
ToS IP precedence bits (0 - 2) for BGP packets. Valid precedences are critics, flash, flash-override, immediate, internetwork control, precedence, network control, priority, and routine. |
type-of-service reliability <high|normal> |
ToS reliability field (bit 5) for BGP packets |
type-of-service throughput <high|normal> |
ToS throughput field (bit 4) for BGP packets |
Example: BGP Instance Configuration
The following example shows some global BGP instance configuration attributes. The further BGP configuration like peer groups and peers is shown in the examples in the subsequent sections.
supervisor@spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
"cluster-id": "198.51.100.51",
"domain-name": "rtbrick.com",
"host-name": "spine1",
"local-as": 4200000100,
"local-preference": 50,
"router-id": "198.51.100.51",
"type-of-service": {
"precedence": "network-control"
},
"protocol-preference": {
"internal": 180,
"external": 20
},
"timer": {
"hold-time": 30,
"keepalive": 10
},
<...>
}
BGP Address Family Configuration
This configuration hierarchy refers to parameters that are specific to address families but generic to the BGP instance, as opposed to peer-group specific address families configuration. At this hierarchy, you can enable or disable address families for BGP, and configure various features specific to the address family.
Syntax:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, or ipv6 |
<safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast, labeled-unicast, vpn-unicast, multicast, or vpn-multicast |
default-information originate <true|false> |
Generate and distribute a default route information |
download-count <count> |
Forward packets over multiple paths, set maximum prefixes to use |
multipath <number> |
Enable load sharing among multiple BGP paths |
retain-route-target (enable|disable) |
Retain VPN routes for all route targets, by default this feature is enabled |
resolve-nexthop afi <afi> |
Address family to resolve the next-hop |
resolve-nexthop safi <safi> |
Sub-address family to resolve the next-hop |
redistribute <source> |
Enable the redistribution feature to dynamically inject specific types of routes into the BGP protocol. Supported route sources are |
redistribute <source> policy <policy> |
Attach a policy to the redistribution process |
srgb base <value> |
Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) start label. The SRGB is the range of label values reserved for segment routing (SR). These values are assigned as segment identifiers (SIDs) to SR-enabled network nodes and have global significance throughout the routing domain. SRGB is supported for labeled unicast only. |
srgb index <value> |
Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) index |
srgb range <value> |
Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) label range |
Example 1: BGP Address Family Configuration with Segment Routing
supervisor@spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
<...>
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast",
"srgb": {
"base": 5000,
"range": 1000,
"index": 11
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
}
],
<...>
}
}
Example 2: BGP Address Family Configuration with Redistribution
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance services protocol bgp
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
<...>
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
}
]
}
}
Example 3: BGP Address Family Configuration with Redistribution and Redistribution Policy
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance services protocol bgp
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
<...>
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
"policy": "MY_REDISTRIBUTION_POLICY"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
"policy": "MY_REDISTRIBUTION_POLICY"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
}
]
}
}
Peer Group Configuration
Peer Groups
In BGP, neighbor peers with the same update policies can be grouped to simplify the initial configuration and updates. Peers share the same policies such as route maps, distribution lists, filter lists, update sources, and so on, so peer groups only need one configuration statement for these values.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol bgp peer-group <peer-group-name> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
local-as <as-number> |
Local AS number for the peer group |
remote-as <as-number> |
Remote AS number for the peer group |
any-as <true|false> |
Enable dynamic AS negotiation for this peer group |
ebgp-multihop <hop-count> |
By default, the maximum number of hops between eBGP peers is 1 (direct connection). This hop count overrides the default behavior allowing connectivity between eBGP peers not directly connected. |
link-local-nexthop-only <true|false> |
Enable BGPv6 peerings using the IPv6 link-local addresses |
no-prepend <true|false> |
Do not prepend the local AS for advertisements to the peer |
replace-as <true|false> |
Prepend only the local AS for advertisements to the peer |
Address Families
At this configuration hierarchy, you can enable the address families that shall be supported for the group peers, and enable features specific to the address family. By default, BGP neighbor sessions support the IP4v unicast and multicast address families.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol bgp peer-group <peer-group-name> address-family <afi> <safi> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, or ipv6 |
<safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast, labeled-unicast, vpn-unicast, multicast, or vpn-multicast |
add-path |
Negotiate additional path capabilities with these peers, so that more than one path can be active to the peers in the group |
default-information originate <true|false> |
Generate and advertise a default route to peers in the group |
extended-nexthop |
Enable extended-next-hop encoding for BGP peer groups to allow the transfer of IPv4 prefixes over an IPv6 connection |
nexthop-self <true|false> |
Set the advertised BGP nexthop to yourself, this is the default for eBGP |
nexthop-unchanged <true|false> |
Do not modify the advertised BGP nexthop, this is the default for iBGP |
update-nexthop ( ipv4-address | ipv6-address ) <address> |
BGP nexthop address for routes advertised to this peer group |
remove-private-as <true|false> |
Remove private AS numbers from routes advertised to group peers |
route-reflect-client <true|false> |
Configure this peer as a route reflector client |
policy ( import | export ) <policy-name> |
Apply a routing policy to the peer group |
Example: BGP Peer Group Configuration
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine
{
"rtbrick-config:peer-group": {
"pg-name": "spine",
"link-local-nexthop-only": "true",
"remote-as": 4200000100,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"extended-nexthop": "true",
"update-nexthop": {
"ipv6-address": "2001:db8:0:19::"
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"update-nexthop": {
"ipv6-address": "2001:db8:0:19::"
}
}
]
}
}
Maximum Prefix Limit
The BGP Maximum Prefix Limit feature enables you to set a limit for the maximum number of prefixes that a BGP router can receive from its peer router. If a BGP router receives prefixes that exceed the defined limit threshold, the BGP session gets reset and the session goes idle for a pre-defined period.
You can define a period as idle timeout so that the BGP peering gets re-established automatically after the specified time. If you do not specify the idle timeout, the BGP peering does not get re-established until or unless you execute the clear bgp neighbor command.
Before getting into inactive or idle mode, the router sends a notification message to the peer router about the exceeded threshold with the error code and the sub-code.
You can configure prefix limits for a peer group.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol bgp peer-group <peer-group-name> address-family <afi> <safi> prefix-limit <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, or ipv6 |
<safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast, labeled-unicast, vpn-unicast, or vpn-multicast |
count <count> |
Number of maximum prefixes that the peer router is allowed to send. The default value is 0. It means no value is configured for prefix limit. |
idle-timeout <idle-timeout> |
Idle or inactive time after the maximum limit is reached (in minutes). The allowed range is 1 - 2400 min. The default is |
Example: BGP Maximum Prefix Limit Configuration
supervisor@leaf1: cfg> set instance default protocol bgp peer-group v4_100_as address-family ipv4 unicast prefix-limit count idle-timeout 5
{
"ietf-restconf:data": {
"rtbrick-config:daemon-options": [
{
"instance-name": "*",
"afi": "*",
"safi": "*",
"bd-type": "bgp.appd",
"bd-name": [
"bgp.appd.1"
]
},
{
"instance-name": "*",
"afi": "*",
"safi": "*",
"bd-type": "bgp.iod",
"bd-name": [
"bgp.iod.1"
]
}
],
"rtbrick-config:interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/0",
"host-if": "S1-1-S2",
"unit": [
{
"unit-id": 0,
"instance": "default",
"address": {
"ipv4": [
{
"prefix4": "198.51.100.91/24"
}
]
}
}
]
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1",
"host-if": "S1-2-S2",
"unit": [
{
"unit-id": 1,
"address": {
"ipv4": [
{
"prefix4": "198.51.100.102/24"
}
]
}
}
]
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/0",
"unit": [
{
"unit-id": 0,
"address": {
"ipv4": [
{
"prefix4": "198.51.100.46/24"
}
],
"ipv6": [
{
"prefix6": "2001:db8:0:27::/32"
}
]
}
}
]
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/1",
"unit": [
{
"unit-id": 1,
"address": {
"ipv4": [
{
"prefix4": "198.51.100.111/24"
}
],
"ipv6": [
{
"prefix6": "2001:db8:0:223::/32"
}
]
}
}
]
}
],
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "mpls",
"safi": "unicast"
}
],
"protocol": {
"bgp": {
"local-as": 200,
"router-id": "198.51.100.111",
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
}
],
"peer": {
"ipv4": [
{
"peer-address": "198.51.100.92",
"update-source": "198.51.100.91",
"peer-group": "v4_100_as"
}
]
},
"peer-group": [
{
"pg-name": "v4_100_as",
"local-as": 200,
"remote-as": 100,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"prefix-limit": {
"count": 100,
"idle-timeout": 5
}
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
Peer Configuration
Once peer groups have been defined, BGP peers can be configured at the peer configuration hierarchy. A peer can be specified by address, or by interface when using IPv6 auto-discovered neighbors and link-local addresses. Furthermore, it is possible to configure TCP authentication and bind it to a peer.
Syntax to configure a BGP peer by address:
set instance <instance-name> protocol bgp peer ( ipv4 | ipv6) <peer-address> <update-source> peer-group <peer-group>
Syntax to configure a BGP peer using IPv6 link-local addresses:
set instance <instance-name> protocol bgp peer interface <name> peer-group <peer-group>
Syntax to configure TCP Authentication for BGP peers:
set instance <instance-name> protocol bgp peer (ipv4 | ipv6) <peer-address> <update-source> authentication-id <authentication-id>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
interface <name> |
Enable BGP peer using IPv6 link-local addresses |
ipv4 <peer-address> |
IPv4 address of a BGP peer |
ipv6 <peer-address> |
IPv6 address of a BGP peer |
<update-source> |
Local IP address to be used for the peering |
peer-group <peer-group> |
Assign the peer to a peer group |
deactivate |
Deactivate a configured peer |
authentication-id <authentication-id> |
Authentication identifier |
Example 1: BGP peer specified by IP addresses
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer
{
"rtbrick-config:peer": {
"ipv4": [
{
"peer-address": "198.51.100.82",
"update-source": "198.51.100.81",
"peer-group": "spine"
}
]
}
}
Example 2: BGP peer using IPv6 link-local addresses
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer
{
"rtbrick-config:peer": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1/1",
"peer-group": "spine"
}
]
}
}
Example 3: BGP peer authentication
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer
{
"rtbrick-config:peer": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1/1",
"authentication-id": "auth1",
"peer-group": "spine"
}
]
}
}
Sample Configuration
Example 1: BGP Configuration of a Spine Switch (Default Instance only)
{
"ietf-restconf:data": {
"rtbrick-config:daemon-options": [
{
"instance-name": "*",
"afi": "*",
"safi": "*",
"bd-type": "bgp.appd",
"bd-name": "bgp.appd.1"
}
],
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"ipv4-router-id": "198.51.100.51",
"protocol": {
"bgp": {
"domain-name": "rtbrick.com",
"host-name": "spine1",
"local-as": 4200000100,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast",
"srgb": {
"base": 5000,
"range": 1000,
"index": 11
},
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
}
],
"peer": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/1/1/1",
"authentication-id": "auth1",
"peer-group": "spine"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/2/1/1",
"peer-group": "leaf1"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/2/2/1",
"peer-group": "leaf2"
}
]
},
"peer-group": [
{
"pg-name": "leaf1",
"link-local-nexthop-only": "true",
"remote-as": 4200000201,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"extended-nexthop": "true",
"nexthop-unchanged": "true"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"nexthop-unchanged": "true"
}
]
},
{
"pg-name": "leaf2",
"link-local-nexthop-only": "true",
"remote-as": 4200000202,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"extended-nexthop": "true",
"nexthop-unchanged": "true"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"nexthop-unchanged": "true"
}
]
},
{
"pg-name": "spine",
"link-local-nexthop-only": "true",
"remote-as": 4200000100,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"extended-nexthop": "true"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast",
"nexthop-self": "true"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"nexthop-self": "true"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
Example 2: BGP Configuration of a Leaf Switch with one VPN Instance
{
"ietf-restconf:data": {
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"ipv4-router-id": "198.51.100.53",
"protocol": {
"bgp": {
"domain-name": "rtbrick.com",
"host-name": "leaf1",
"local-as": 4200000201,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast",
"srgb": {
"base": 5000,
"range": 1000,
"index": 13
},
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast"
}
],
"peer": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/1/1/1" "authentication-id": "auth1",
"peer-group": "spine"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/1/2/1",
"peer-group": "spine"
}
]
},
"peer-group": [
{
"pg-name": "spine",
"link-local-nexthop-only": "true",
"remote-as": 4200000100,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"extended-nexthop": "true",
"update-nexthop": {
"ipv6-address": "2001:db8:0:19::"
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "vpn-unicast",
"update-nexthop": {
"ipv6-address": "2001:db8:0:19::"
}
}
]
}
]
}
}
},
{
"name": "services",
"ipv4-router-id": "198.51.100.41",
"route-distinguisher": "198.51.100.41:101",
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"policy": {
"export": "MY_V4_POLICY"
},
"route-target": {
"import": "target:198.51.100.70:14",
"export": "target:198.51.100.70:14"
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"policy": {
"export": "MY_V6_POLICY"
},
"route-target": {
"import": "target:198.51.100.70:16",
"export": "target:198.51.100.70:16"
}
}
],
"protocol": {
"bgp": {
"domain-name": "rtbrick.com",
"host-name": "leaf1",
"local-as": 65003,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
},
{
"source": "ppp"
},
{
"source": "static"
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}