Administration
Managing Webhooks
A webhooks is a registered HTTP endpoint that forwards notifications from RBMS to an external endpoint.
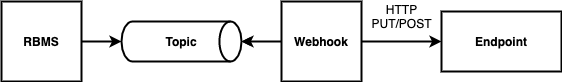
RBMS stores a domain event if a status in RBMS has changed. An event is only created when the transaction was comitted. An event is not fired when the transaction rolls back.
The events are grouped in different topics:
-
element, the element topic contains all element-related messages
-
image, the image topic contains all image-related messages
An event has a descriptive name that describes what state change is being reported. All events have a unique ID to identify different instances of the same event unambiguously.
For example, the ElementRenamedEvent informs about an element being renamed. The event is stored in the element topic.
A webhook subscribes a topic and calls the configured endpoint for all events that match the specified name filter. By default, the message send to the endpoint contains the JSON representation of the domain event. An optional template allows rewriting the event message.
The authentication can be done via HTTP Basic Authorization or bearer token. RBMS stores the provided credentials AES-protected in the database.
The AES secret and initialization vector (IV) can be specified in the master.secret and master.iv environment variables.
|
Unauthenticated endpoint calls are also supported.
A webhook invocation is considered successful if a HTTP success family status code is returned. For all other status codes the invocation is considered as failed.
A webhook can retry all failed messages. In addition, a webhook can be reset to a certain message to process this message and all subsequent messages again.
The complete message processing lifecycle is shown below:
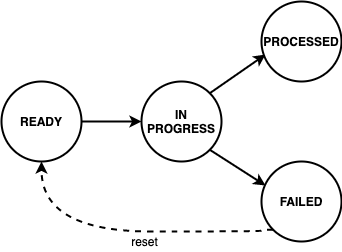
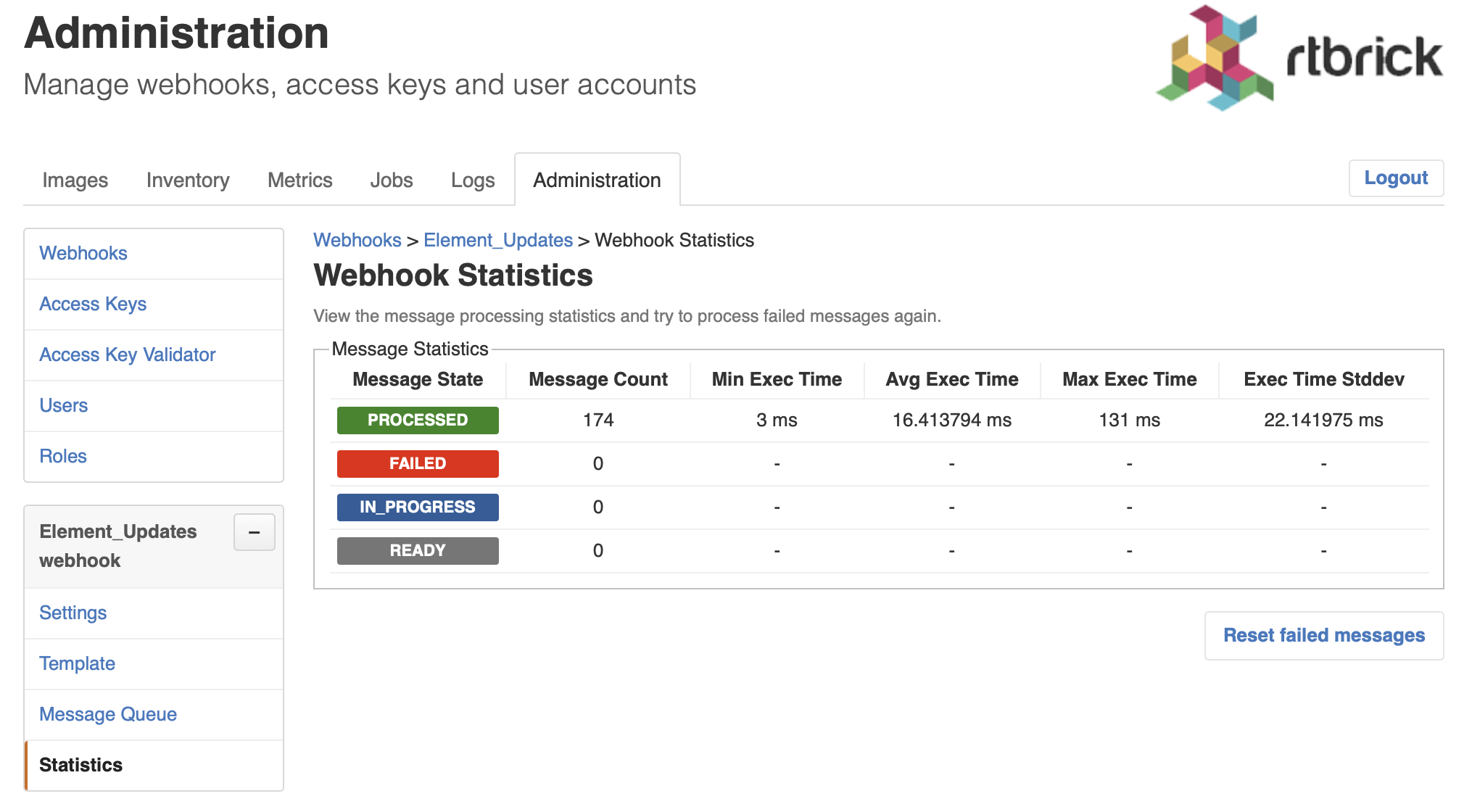
New domain event messages are READY for being processed. The state changes to IN PROGRESS when the processing has begun and eventually to PROCESSED if the endpoint processed the message successfully and to FAILED otherwise respectively.
A webhook can be disabled to temporarily suspend the event processing. All events that occured while the webhook was disabled are processed when the webhook gets enabled again unless the event got dropped because the topic buffering capacity was exceeded.
Viewing Webhooks
To view the list of webhooks
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Webhooks in the left navigation pane. The list of all webhooks appear.
-
Click the name of the webhook that you want to view.
Adding Webhooks
To add a webhook
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Webhooks in the left navigation pane. The list of all webhooks appear.
-
Click Add webhook
-
Specify the general, subscription and authentication information about the webhook.
-
Click Save webhook.
Disabling a Webhook
To disable a webhook
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Webhooks in the left navigation pane. The list of all webhooks appear.
-
Select the webhook to be disabled.
-
Click Disable webhook.
Enabling a Webhook
To enable a webhook
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Webhooks in the left navigation pane. The list of all webhooks appear.
-
Select the webhook to be enabled.
-
Click Enable webhook.
Reset a Webhook
To reset a webhook
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Webhooks in the left navigation pane. The list of all webhooks appear.
-
Select the webhook to be reset.
-
Click Message Queue in the left navigation pane. The list of the last 100 processed messages appear.
-
Enter the event ID in the Filter field and click Filter.
-
Open the displayed message.
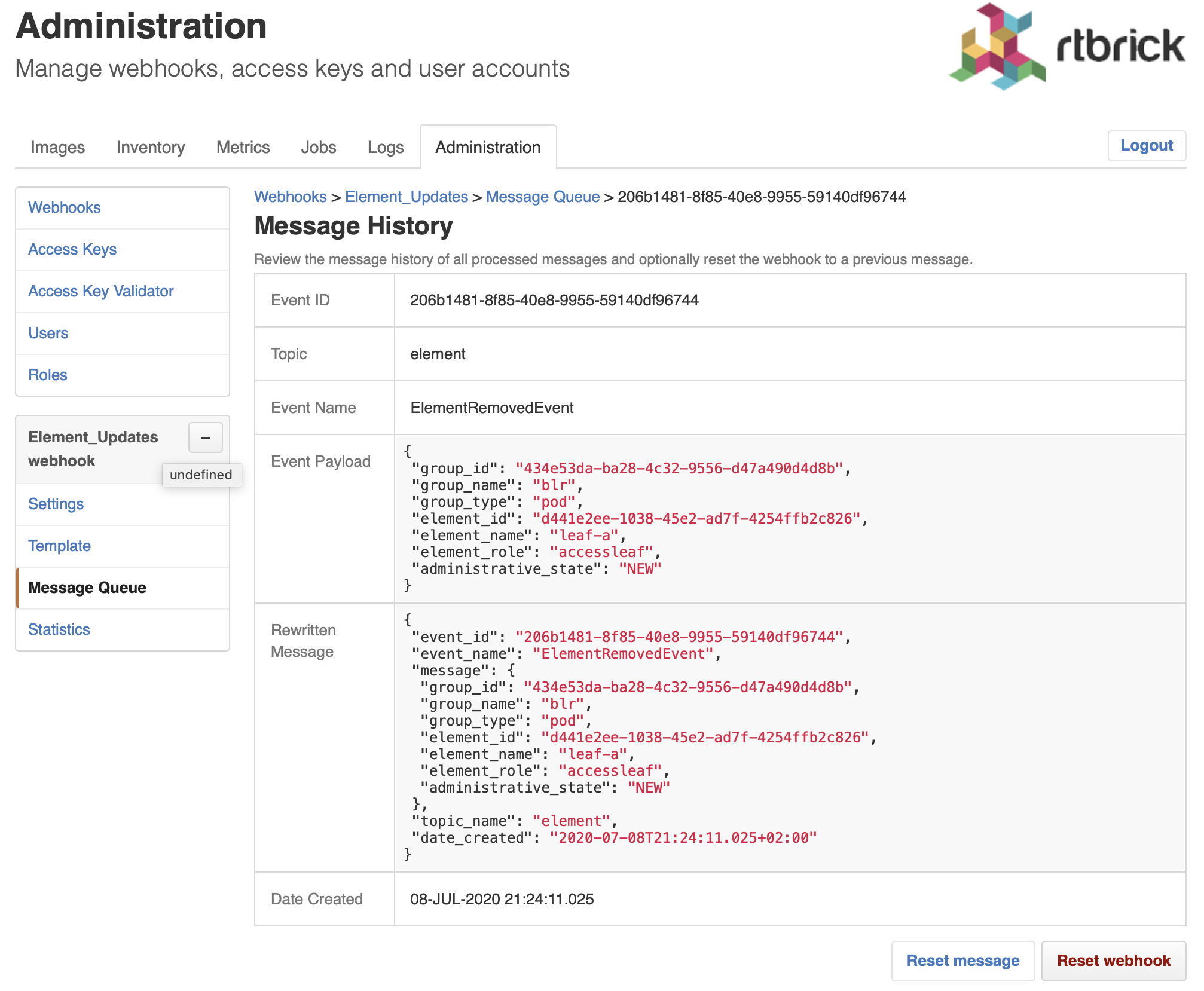
-
Click Reset webhook to process the message and all subsequent messages again. The message queue view appears.
Viewing Webhook Statistics
The webhook statistics provides information about processing times and the message count grouped by the processing state.
To view the webhook statistics
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Webhooks in the left navigation pane. The list of all webhooks appear.
-
Select the webhook for which to retry the failed invocations.
-
Click Statistics in the left navigation pane. The webhook statistics appear.
Retrying Failed Webhook Invocations
To retry failed webhook invocations
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Webhooks in the left navigation pane. The list of all webhooks appear.
-
Select the webhook for which to retry the failed invocations.
-
Click Statistics in the left navigation pane. The message statistics appear.

-
Click Reset failed messages to reset all failed messages to ready state.
Managing Users
| This section outlines how to manage users in the RBMS built-in user repository. If RBMS is connected to an authorization service the users are configured in the authorization service. |
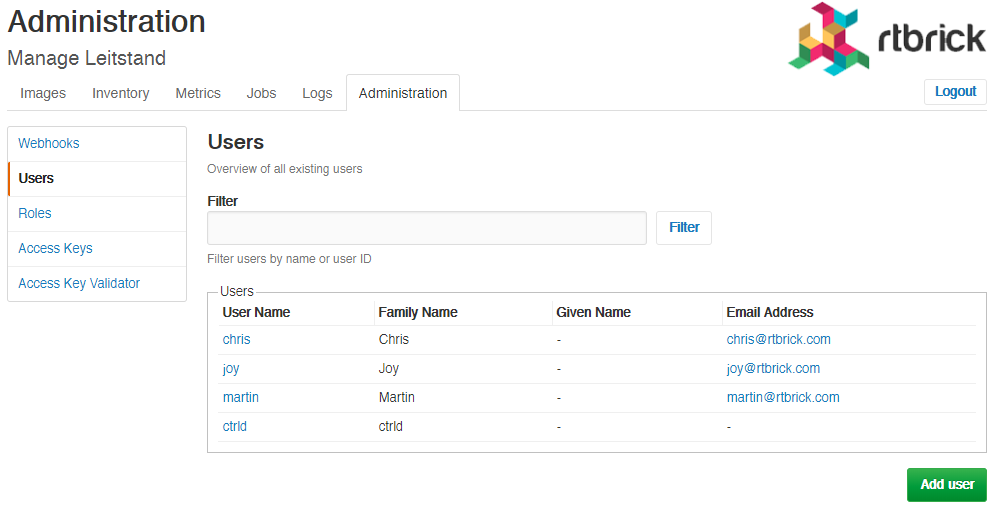
Viewing all existing users
To view all existing users
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Users in the left navigation pane. The list of all existing users appear.
-
Click the name of the user whose details you want to view.
Adding users
You can add a new users to the user repository.
To add a user
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Users in the left navigation pane. The list of all existing users appear.
-
On the Users page, click Add user.
-
Specify user details such as username, password, and access token.
-
Click Add user.
Removing users
To remove a user
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Users in the left navigation pane. The list of all existing users appear.
-
Click the name of the user whom you want to remove.
-
On the User Settings page, click Remove user.
Resetting Password
To reset a user password
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Users in the left navigation pane. The list of all existing users appear.
-
Click the name of the user whom you want to remove.
-
On the User Settings page, click Reset password. The Reset Password page appears.
-
Enter the new password.
-
Re-type the new password in order to detect accidental typos.
-
Click Reset Password.
Managing Roles
| This section outlines how to manage roles in the RBMS built-in user repository. If RBMS is connected to an authorization service the roles are be configured in the authorization service. See Scopes for more information about the existing acccess scopes. |
Creating Roles
To create a role
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Roles in the left navigation pane. The list of all existing users appear.
-
On the Roles page, click Add role.
-
Specify the details of the new role such as role name, Accessible Resource Scopes, and description.
-
Click Add role.
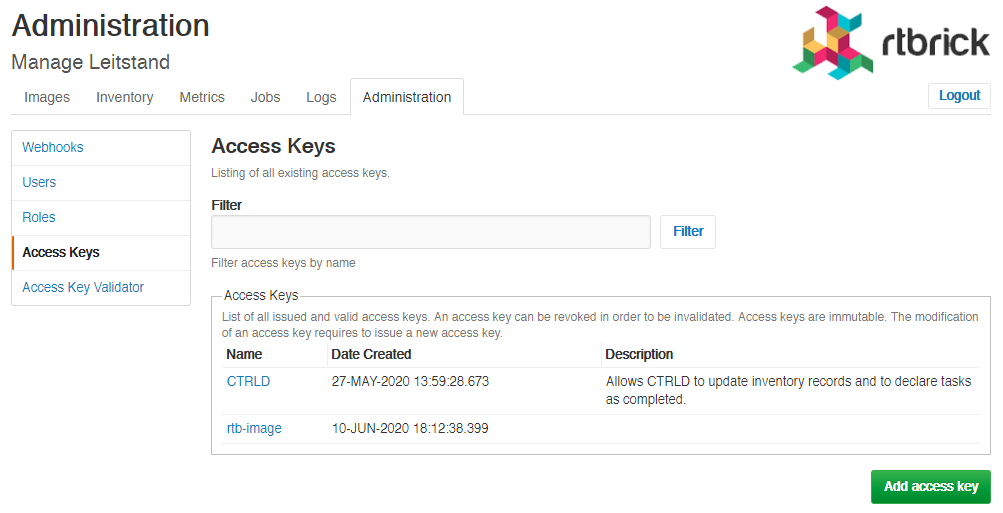
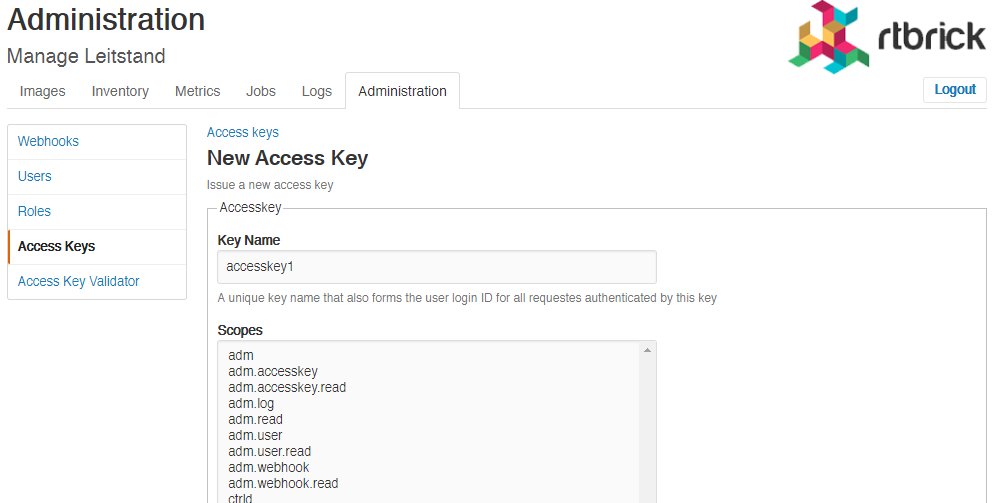
Creating Access Keys
To create an access key
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Access Keys in the left navigation pane. The list of all existing access keys appear.
-
On the Access Keys page, click Add access key.
-
Specify the details of the new access key such as key name, scopes, and description.
-
Click Create access key.
Revoking an access key
To revoke an access key
-
Click the Administration tab.
-
Click Access Key in the left navigation pane. The list of all existing access keys appear.
-
Click the access key that you want to revoke.
-
On the <access key name> accesskey page, click Revoke access key.
Scopes
Access to RBMS is granted through an access token. The access token is either issued by an OAuth2 compliant authorization service or by RBMS itself, depending on whether RBMS delegates to an authorization service or the RBMS built-in user repository is used.
The access token conveys the list of scopes the user is allowed to access. The table below lists all existing scopes:
Scope |
Description |
adm |
Full access to the RBMS administration API and UI. |
adm.read |
Readonly access to the RBMS administration API and UI. |
adm.accesskey |
Full access to the RBMS access key administration API and UI. |
adm.accesskey.read |
Readonly access to the RBMS access key administration API and UI. |
adm.user |
Full access to the RBMS user management API and UI. |
adm.user.read |
Readonly access to te RBMS user management API and UI. |
adm.webhook |
Full access to the RBMS webhook management API and UI. |
adm.webhook.read |
Readonly access to the RBMS webhook management API and UI. |
ctrld |
Full access to all CTRLD actions that can be triggered from RBMS. |
ctrld.reinstall |
Permission to trigger CTRLD to run ZTP sequence for an software image upgrade again. |
ctrld.settings |
Permissions to update the CTRLD settings on the switch via RBMS. |
ivt |
Full access to the resource inventory. |
ivt.read |
Readonly access to the resource inventory. |
ivt.element |
Manage elements in the resource inventory. |
ivt.element.settings |
Manage element settings in the resource inventory. |
ivt.element.config |
Manage element configuration in the resource inventory. |
ivt.element.dns |
Manage element DNS records in the resource inventory. |
ivt.element.module |
Manage element hardware module information in the resource inventory. |
ivt.group |
Manage element grouos in the resource inventory. |
ivt.group.settings |
Manage element group settings in the resource inventory. |
ivt.image |
Manage software images in the resource inventory. |
ivt.rack |
Manage racks in the resource inventory. |
job |
Full access to the RBMS job API and UI. |
job.read |
Readonly access to the RBMS job API and UI |
job.task |
Manage job tasks via RBMS Job API or UI. |
tmy |
Full access to the RBMS metric API and UI. |
tmy.read |
Readonly access to the RBMS metric API and UI. |
tmy.metrics |
Full access to manage RBMS metrics. |
tmy.metrics.read |
Readonly access to metrics. |
Scopes are cumulative by convention. For example, the ivt.elment scope includes the ivt.element.settings scope.
|
For UI access always grant the read scope in combination with a specific write scope to avoid trouble. For example, grant ivt.element.settings in combination with ivt.read. Otherwise a user might not be able to navigate to the view to apply the changes.
|