Introduction
The Multicast VPN (MVPN) feature provides the ability to support multicast over a Layer 3 VPN. Multicast allows the efficient distribution of information between a single multicast source and multiple receivers. IP multicast is used to stream video, voice, and data to an MPLS VPN network core. The RBFS MVPN implementation is based on RFC 6513 “Multicast in MPLS/BGP IP VPNs” and RFC 6514 “BGP Encodings and Procedures for Multicast in MPLS/BGP IP VPNs”.
| RFC and draft compliance are partial except as specified. |
RBFS can operate in a spine/leaf fabric as shown in the diagram. The leaf device delivers access services to subscribers or assets, and the spine device provides connectivity to the core network. In such a scenario, IPv4 multicast traffic is carried in a multicast VPN instance. This also allows to deliver IPv4 multicast traffic across an IPv6-only fabric. In terms of MVPN, both leaf and spine devices act as Provider Edge (PE) routers.
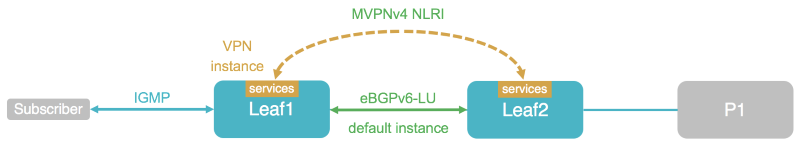
Multicast subscribers will typically join multicast streams via IGMP. Leaf switches will translate and signal the join messages to the spines using BGP MVPN routes. Spine switches will further forward the join messages towards the source to the upstream core router.
Multicast Address Families
In MVPN, there are two type of instances and address families involved:
-
Within the multicast VPN instance, joins are represented as multicast routes. These are AFI 1 (IPv4), SAFI 2 (Multicast). The IPv4 multicast address family needs to be enabled in the VPN service instance as well as for BGP in the VPN instance.
-
In the Multicast VPN itself, messages like joins or active sources are advertised using BGP MVPN routes. These are AFI 1 (IPv4), SAFI 5 (MVPN). The BGP peerings that carry the MVPN routes typically run in the default instance. Therefore the MVPN address family needs to be enabled in the default instance, both for the BGP instance itself as well as for the BGP peerings.
In summary, the following address families need to be enabled by configuration:
-
The IPv4 multicast address family in the VPN service instance.
-
The IPv4 multicast address family for BGP in the VPN service instance.
-
The Multicast VPN address family in the BGP default instance.
-
The Multicast VPN address family in the BGP peerings in the default instance.