IPoE Subscriber Management Configuration
IP-over-Ethernet (IPoE) is an access technology that uses DHCP for IPv4 and DHCPv6 for IPv6 where both protocols are handled in the IPoE daemon (ipoed). IPoE subscribers are identified by IFP, VLANs and client MAC addresses.
The dynamic creation of IPoE subscribers is triggered by DHCPv4 discover or DHCPv6 solicit request from the subscriber. Response is postponed until the subscriber is successfully authenticated using the known authentication methods such as local or RADIUS, however authentication is not mandatory. After the authentication phase, IPv4/IPv6/IPv6-PD address is allocated to the subscriber either from the local pool or from RADIUS.
For IPoE Subscriber Management, the following configurations are mandatory:
-
Access Interface Configuration
-
Access Profile Configuration
-
AAA (Authentication, Authorization and Accounting) Profile Configuration. Based on the authentication requirement, configure any one of the following:
-
Local Authentication
-
Pool Configuration
-
User Profile Configuration
-
-
RADIUS Authentication
-
RADIUS Profile Configuration
-
RADIUS Server Configuration
-
-
This solution section discusses RADIUS authentication.
NOTES:
-
Access interfaces can be configured without VLAN tags (untagged) and with one (single tagged) or two (double tagged) VLAN tags.
-
There can be more than one interface configured for subscriber management and each interface can reference the same profile.
Configuring IPoE Subscriber Management
For detailed information about the subscriber configuration options, see the Subscriber Management Configuration Guide.
-
Configure the access profile
ipoe.
set access access-profile ipoe set access access-profile ipoe protocol dhcp enable true set access access-profile ipoe protocol dhcp lease-time 60 set access access-profile ipoe protocol dhcpv6 enable true set access access-profile ipoe protocol dhcpv6 lifetime 60 set access access-profile ipoe address-family ipv4 enable true set access access-profile ipoe address-family ipv4 pool-name poolv4 set access access-profile ipoe address-family ipv4 instance default set access access-profile ipoe address-family ipv4 dad-enable true set access access-profile ipoe address-family ipv6 enable true set access access-profile ipoe address-family ipv6 pool-name poolv6 set access access-profile ipoe address-family ipv6 prefix-delegation-pool-name poolv6pd set access access-profile ipoe address-family ipv6 instance default set access access-profile ipoe address-family ipv6 dad-enable true commit
The access profile configuration is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show config access access-profile
{
"rtbrick-config:access-profile": [
{
"profile-name": "ipoe",
"protocol": {
"dhcp": {
"enable": "true",
"lease-time": 60
},
"dhcpv6": {
"enable": "true",
"lifetime": 60
}
},
"address-family": {
"ipv4": {
"enable": "true",
"pool-name": "poolv4",
"instance": "default",
"dad-enable": "true"
},
"ipv6": {
"enable": "true",
"pool-name": "poolv6",
"prefix-delegation-pool-name": "poolv6pd",
"instance": "default",
"dad-enable": "true"
}
}
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op>
-
Configure the Authentication and Accounting (AAA) profile for
aaa-profile.
set access aaa-profile aaa-profile set access aaa-profile aaa-profile session-timeout 0 set access aaa-profile aaa-profile idle-timeout 0 set access aaa-profile aaa-profile aaa-radius-profile radius-profile set access aaa-profile aaa-profile authentication order RADIUS set access aaa-profile aaa-profile accounting order RADIUS set access aaa-profile aaa-profile accounting interim-interval 86400 set access aaa-profile aaa-profile accounting ingress accounting-source POLICER set access aaa-profile aaa-profile accounting egress accounting-source CLASS commit
The access AAA configuration is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show config access aaa-profile
{
"rtbrick-config:aaa-profile": [
{
"profile-name": "aaa-profile",
"session-timeout": 0,
"idle-timeout": 0,
"aaa-radius-profile": "radius-profile",
"authentication": {
"order": "RADIUS"
},
"accounting": {
"order": "RADIUS",
"interim-interval": 86400,
"ingress": {
"accounting-source": "POLICER" },
"egress": {
"accounting-source": "CLASS"
}
}
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op>
-
Configure the access interface. Double-tagged interface is configured in this case as the access interface (
ifp-0/1/30). The interface configuration assigns the access type, access profile, AAA profile, and further optional attributes like service-profile to the specified access interface.
set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/1/30 1001 1100 1001 1100 set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/1/30 1001 1100 1001 1100 access-type IPoE set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/1/30 1001 1100 1001 1100 access-profile-name ipoe set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/1/30 1001 1100 1001 1100 service-profile-name qos_service set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/1/30 1001 1100 1001 1100 aaa-profile-name aaa-profile set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/1/30 1001 1100 1001 1100 gateway-ifl lo-0/0/1/0 commit
The double-tagged access interface configuration is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show config access interface
{
"rtbrick-config:interface": {
"double-tagged": [
{
"interface-name": "ifp-0/1/30",
"outer-vlan-min": 1001,
"outer-vlan-max": 1100,
"inner-vlan-min": 1001,
"inner-vlan-max": 1100,
"access-type": "IPoE",
"access-profile-name": "ipoe",
"service-profile-name": "qos_service",
"aaa-profile-name": "aaa-profile",
"gateway-ifl": "lo-0/0/1/0"
}
]
}
}
-
In this solution, we configure AAA authentication and accounting with RADIUS. To use RADIUS authentication and accounting both the RADIUS profile and RADIUS server configurations (see below) must be configured.
-
Configure RADIUS profile
radius-profile.
set access radius-profile radius-profile set access radius-profile radius-profile nas-ip-address 192.0.2.74 set access radius-profile radius-profile nas-port-format DEFAULT set access radius-profile radius-profile nas-port-type Ethernet set access radius-profile radius-profile authentication radius-server-profile-name radius set access radius-profile radius-profile accounting radius-server-profile-name radius commit
The RADIUS profile configuration is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show config access radius-profile radius-profile
{
"rtbrick-config:radius-profile": [
{
"profile-name": "radius-profile",
"nas-ip-address": "192.0.2.74",
"nas-port-format": "DEFAULT",
"nas-port-type": "Ethernet",
"authentication": {
"radius-server-profile-name": [
"radius"
]
},
"accounting": {
"radius-server-profile-name": [
"radius"
]
}
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op>
-
Configure the RADIUS server
radius.
set access radius-server radius set access radius-server radius address 192.0.2.34 set access radius-server radius source-address 192.0.2.74 set access radius-server radius secret-plain-text testing123 set access radius-server radius routing-instance default set access radius-server radius rate 300 set access radius-server radius authentication enable true set access radius-server radius authentication retry 3 set access radius-server radius authentication timeout 5 set access radius-server radius accounting enable true set access radius-server radius accounting timeout 30 set access radius-server radius coa enable true commit
The attribute` secret-plain-text` will be converted to secret-encrypted-text in the show command output and value will be hashed.
|
The RADIUS server configuration is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config access radius-server radius
{
"rtbrick-config:radius-server": [
{
"server-name": "radius",
"address": "192.0.2.34",
"source-address": "192.0.2.74",
"secret-encrypted-text": "$2b2feb12f730107454b1be6a0f8242b0f",
"routing-instance": "default",
"rate": 300,
"authentication": {
"enable": "true",
"retry": 3,
"timeout": 5
},
"accounting": {
"enable": "true",
"timeout": 30
},
"coa": {
"enable": "true"
}
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
-
Configure the IPv4 and IPv6 access pools.
set access pool poolv4 set access pool poolv4 ipv4-address low 203.0.113.1 set access pool poolv4 ipv4-address high 203.0.113.64 set access pool poolv6 set access pool poolv6 ipv6-prefix low 2001:db8:0:1::/64 set access pool poolv6 ipv6-prefix high 2001:db8:0:40::/64 set access pool poolv6pd set access pool poolv6pd ipv6-prefix low 2001:db8:0:100::/56 set access pool poolv6pd ipv6-prefix high 2001:db8:0:4000::/56 commit
The access pool configuration is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config access pool
{
"rtbrick-config:pool": [
{
"pool-name": "poolv4",
"ipv4-address": {
"low": "203.0.113.1",
"high": "203.0.113.64"
}
},
{
"pool-name": "poolv6",
"ipv6-prefix": {
"low": "2001:db8:0:1::/64",
"high": "2001:db8:0:40::/64"
}
},
{
"pool-name": "poolv6pd",
"ipv6-prefix": {
"low": "2001:db8:0:100::/56",
"high": "2001:db8:0:4000::/56"
}
}
]
}
IPoE Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
| The QoS model explained in this document uses a complex HQoS model with the intent to showcase the complete range of QoS features available in RBFS. However, it may not be needed or desirable for all deployments. In such a case it should be possible to conceive of a simple QoS model as required by simplifying the provided QoS model. |
Following are the steps involved in configuring and verifying IPoE QoS:
-
Configuring service profile to enable QoS on IPoE subscriber
-
Configuring downstream QoS
-
Configuring upstream QoS
-
Configuring QoS remarking
-
Configuring IPoE subscriber accounting for upstream and downstream traffic
-
Configuring IPoE subscribers QoS on BNG Blaster
-
Validating IPoE QoS on BNG Blaster
The figure below shows how QoS is configured for ingress and egress traffic.
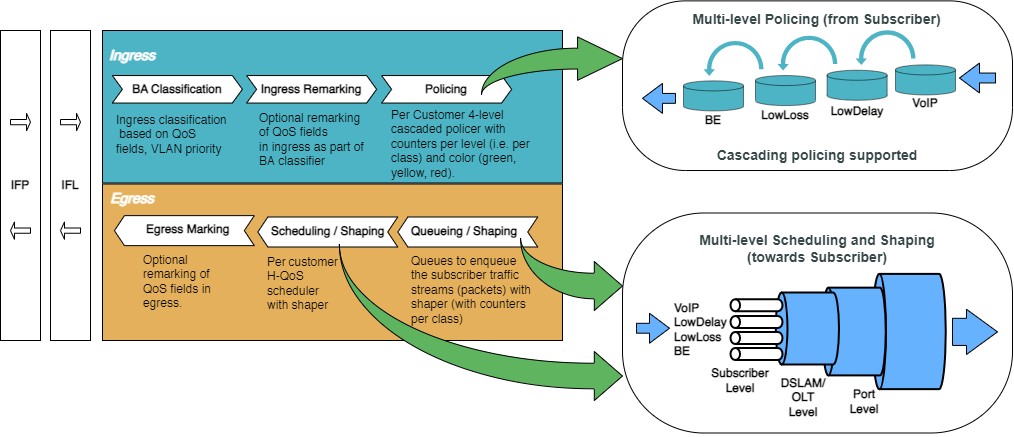
Fig. 2: Hierarchical Quality of Service primitives
For detailed information about the QoS configuration options, see the HQoS Configuration Guide.
Configure Service Profile
Service profile configuration in subscriber management allows to assign QoS configurations to a subscriber.
-
Configure the service profile to enable QoS. The service profile defined to enable Quality of Service with profile name is
residential.
set access service-profile qos_service qos profile residential commit
The configuration of the service profile named residential is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config access service-profile qos_service
{
"rtbrick-config:service-profile": [
{
"profile-name": "qos_service",
"qos": {
"profile": "residential"
}
}
]
}
-
Enable QoS on IPoE subscriber access interface (
ifp-0/1/30) to enable QoS for IPoE subscriber.
set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/1/30 1001 1100 1001 1100 service-profile-name qos_service commit
Below is the double-tagged access interface on which the service profile qos_service is configured.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config access interface double-tagged ifp-0/1/30
{
"rtbrick-config:double-tagged": [
{
"interface-name": "ifp-0/1/30",
"outer-vlan-min": 1001,
"outer-vlan-max": 1100,
"inner-vlan-min": 1001,
"inner-vlan-max": 1100,
"access-type": "IPoE",
"access-profile-name": "ipoe",
"service-profile-name": "qos_service",
"aaa-profile-name": "aaa-profile",
"gateway-ifl": "lo-0/0/1/0"
}
]
}
-
Configure QoS profile to enable on IPoE subscriber.
set forwarding-options class-of-service profile residential set forwarding-options class-of-service profile residential classifier-name subs-pbit-class set forwarding-options class-of-service profile residential class-queue-map-name subs-4queues set forwarding-options class-of-service profile residential remark-map-name subs-remarking-residential set forwarding-options class-of-service profile residential class-policer-map-name policer-map-residential set forwarding-options class-of-service profile residential scheduler-map-name subs-4queues-residential commit
The QoS Profile with all the primitives needed to enable traffic profiles on IPoE Subscribers is as follows:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service profile residential
{
"rtbrick-config:profile": [
{
"profile-name": "residential",
"classifier-name": "subs-pbit-class",
"class-queue-map-name": "subs-4queues",
"remark-map-name": "subs-remarking-residential",
"class-policer-map-name": "policer-map-residential",
"scheduler-map-name": "subs-4queues-residential"
}
]
}
Configure Downstream QoS
Downstream Quality of Service (QoS) is used to prioritize network traffic from the Internet to subscribers.
-
Enable global classification for downstream traffic.
set forwarding-options class-of-service global multifield-classifier-name global_mfc commit
Below is the multi-field-classifier (MFC) based classifier for global enabling of downstream traffic classification.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service global multifield-classifier-name
{
"rtbrick-config:multifield-classifier-name": "global_mfc"
}
-
Configure the MFC-based classifier with qualifiers and actions.
set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1001 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1001 match ipv4-tos 128 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1001 match source-ipv4-prefix 132.1.1.3/32 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1001 action forward-class class-0 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1002 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1002 match ipv4-tos 160 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1002 match source-ipv4-prefix 132.1.1.3/32 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1002 action forward-class class-1 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1003 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1003 match ipv4-tos 192 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1003 match source-ipv4-prefix 132.1.1.3/32 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1003 action forward-class class-2 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1004 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1004 match ipv4-tos 224 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1004 match source-ipv4-prefix 132.1.1.3/32 set forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc ordinal 1004 action forward-class class-3 commit
The configuration of the QoS MFC-based Classifier for classification of downstream traffic from the core towards IPoE Subscriber is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service multifield-classifier acl l3v4 rule global_mfc
{
"rtbrick-config:rule": [
{
"rule-name": "global_mfc",
"ordinal": [
{
"ordinal-value": 1001,
"match": {
"ipv4-tos": 128,
"source-ipv4-prefix": "132.1.1.3/32"
},
"action": {
"forward-class": "class-0"
}
},
{
"ordinal-value": 1002,
"match": {
"ipv4-tos": 160,
"source-ipv4-prefix": "132.1.1.3/32"
},
"action": {
"forward-class": "class-1"
}
},
{
"ordinal-value": 1003,
"match": {
"ipv4-tos": 192,
"source-ipv4-prefix": "132.1.1.3/32"
},
"action": {
"forward-class": "class-2"
}
},
{
"ordinal-value": 1004,
"match": {
"ipv4-tos": 224,
"source-ipv4-prefix": "132.1.1.3/32"
},
"action": {
"forward-class": "class-3"
}
}
]
}
]
}
-
Enqueue classified traffic to different queues using class-to-queue mapping.
set forwarding-options class-of-service queue-group subs-4queues queue-numbers 4 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-queue-map subs-4queues set forwarding-options class-of-service class-queue-map subs-4queues class class-0 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-queue-map subs-4queues class class-0 queue-name BE_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service class-queue-map subs-4queues class class-1 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-queue-map subs-4queues class class-1 queue-name LD_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service class-queue-map subs-4queues class class-2 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-queue-map subs-4queues class class-2 queue-name LL_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service class-queue-map subs-4queues class class-3 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-queue-map subs-4queues class class-3 queue-name VO_SUBS commit
Below is the QoS class-queue mapping configuration:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service class-queue-map subs-4queues class
{
"rtbrick-config:class": [
{
"class-type": "class-0",
"queue-name": "BE_SUBS"
},
{
"class-type": "class-1",
"queue-name": "LD_SUBS"
},
{
"class-type": "class-2",
"queue-name": "LL_SUBS"
},
{
"class-type": "class-3",
"queue-name": "VO_SUBS"
}
]
}
-
Configure the queues needed for enqueuing and dequeuing traffic streams.
set forwarding-options class-of-service queue BE_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service queue BE_SUBS queue-size 375000 set forwarding-options class-of-service queue LD_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service queue LD_SUBS queue-size 625000 set forwarding-options class-of-service queue LL_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service queue LL_SUBS queue-size 625000 set forwarding-options class-of-service queue VO_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service queue VO_SUBS queue-size 156250 set forwarding-options class-of-service queue VO_SUBS shaper-name shaper_VO commit
The queue Configuration is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service queue
{
"rtbrick-config:queue": [
{
"queue-name": "BE_SUBS",
"queue-size": 375000,
},
{
"queue-name": "LD_SUBS",
"queue-size": 625000,
},
{
"queue-name": "LL_SUBS",
"queue-size": 625000,
},
{
"queue-name": "VO_SUBS",
"queue-size": 156250,
"shaper-name": "shaper_VO",
}
]
}
-
Configure the scheduler needed by Subscriber/Session scheduler-map and OLT scheduler-map.
set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler pon0 set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler pon0 type fair_queueing set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler pon0 shaper-name gpon-shaper set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler subs-4queues set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler subs-4queues shaper-name shaper_session set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler subs-4queues type strict_priority set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler subs-4queues composite false commit
The configuration of the scheduler-map and OLT scheduler-map is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler
{
"rtbrick-config:scheduler": [
{
"scheduler-name": "pon0",
"shaper-name": "gpon-shaper",
"type": "fair_queueing"
},
{
"scheduler-name": "subs-4queues",
"shaper-name": "shaper_session",
"type": "strict_priority",
"composite": "false"
}
]
}
-
Configure the session/subscriber scheduler mapping for dequeuing traffic based on scheduler type for each queue:
set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map schedmap-olt set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map schedmap-olt scheduler-name pon0 set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map schedmap-olt scheduler-name pon0 port-connection scheduler_to_port set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name BE_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name BE_SUBS parent-flow high-flow set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name BE_SUBS parent-scheduler-name subs-4queues set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name BE_SUBS connection-point strict_priority_3 set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name LD_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name LD_SUBS parent-flow high-flow set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name LD_SUBS parent-scheduler-name subs-4queues set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name LD_SUBS connection-point strict_priority_1 set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name LL_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name LL_SUBS parent-flow high-flow set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name LL_SUBS parent-scheduler-name subs-4queues set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name LL_SUBS connection-point strict_priority_2 set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name VO_SUBS set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name VO_SUBS parent-flow high-flow set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name VO_SUBS parent-scheduler-name subs-4queues set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential queue-group-name subs-4queues queue-name VO_SUBS connection-point strict_priority_0 set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential scheduler-name subs-4queues set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential scheduler-name subs-4queues port-connection scheduler_to_port commit
The QoS Subscriber/Session Scheduler-Map configuration is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map subs-4queues-residential
{
"rtbrick-config:scheduler-map": [
{
"scheduler-map-name": "subs-4queues-residential",
"queue-group-name": [
{
"group-name": "subs-4queues",
"queue-name": [
{
"name": "BE_SUBS",
"parent-flow": "high-flow",
"parent-scheduler-name": "subs-4queues",
"connection-point": "strict_priority_3"
},
{
"name": "LD_SUBS",
"parent-flow": "high-flow",
"parent-scheduler-name": "subs-4queues",
"connection-point": "strict_priority_1"
},
{
"name": "LL_SUBS",
"parent-flow": "high-flow",
"parent-scheduler-name": "subs-4queues",
"connection-point": "strict_priority_2"
},
{
"name": "VO_SUBS",
"parent-flow": "high-flow",
"parent-scheduler-name": "subs-4queues",
"connection-point": "strict_priority_0"
}
]
}
],
"scheduler-name": [
{
"name": "subs-4queues",
"port-connection": "scheduler_to_port"
}
]
}
]
}
-
Configure the OLT scheduler-mapping for each PON to be scheduled according to the scheduler type.
set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map schedmap-olt set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map schedmap-olt scheduler-name pon0 set forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map schedmap-olt scheduler-name pon0 port-connection scheduler_to_port commit
The OLT Scheduler-Map configuration is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service scheduler-map schedmap-olt
{
"rtbrick-config:scheduler-map": [
{
"scheduler-map-name": "schedmap-olt",
"scheduler-name": [
{
"name": "pon0",
"port-connection": "scheduler_to_port"
}
]
}
]
}
-
Configure downstream traffic shaping for both session schedulers and queues.
| Queue Shaping is only on VO_SUBS Queue. |
set forwarding-options class-of-service shaper shaper_VO set forwarding-options class-of-service shaper shaper_VO shaping-rate-high 2000 set forwarding-options class-of-service shaper shaper_VO shaping-rate-low 0 set forwarding-options class-of-service shaper shaper_session set forwarding-options class-of-service shaper shaper_session shaping-rate-high 10000 set forwarding-options class-of-service shaper shaper_session shaping-rate-low 100 set forwarding-options class-of-service shaper gpon-shaper set forwarding-options class-of-service shaper gpon-shaper shaping-rate-high 2488000 set forwarding-options class-of-service shaper gpon-shaper shaping-rate-low 32000 commit
The shaping Configuration is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service shaper
{
"rtbrick-config:shaper": [
{
"shaper-name": "shaper_VO",
"shaping-rate-high": 2000,
"shaping-rate-low": 0
},
{
"shaper-name": "shaper_session",
"shaping-rate-high": 10000,
"shaping-rate-low": 100
},
{
"shaper-name": "gpon-shaper",
"shaping-rate-high": 2488000,
"shaping-rate-low": 32000
}
]
}
Configure Upstream QoS
-
Configure the BA Classifier for the classification of multiple traffic streams targeted at IPoE subscribers:
set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 1 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 1 class class-0 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 1 remark-codepoint 7 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 2 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 2 class class-1 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 2 remark-codepoint 7 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 3 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 3 class class-2 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 3 remark-codepoint 7 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 4 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 4 class class-3 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 4 remark-codepoint 7 commit
The configuration of the QoS BA-based Classifier for classification of upstream traffic towards IPoE Subscriber is shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class
{
"rtbrick-config:classifier": [
{
"classifier-name": "subs-pbit-class",
"match-type": [
{
"match-type": "ieee-802.1",
"codepoint": [
{
"codepoint": 1,
"class": "class-0",
"remark-codepoint": 7
},
{
"codepoint": 2,
"class": "class-1",
"remark-codepoint": 7
},
{
"codepoint": 3,
"class": "class-2",
"remark-codepoint": 7
},
{
"codepoint": 4,
"class": "class-3",
"remark-codepoint": 7
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
-
Configure multi-level policer to police 4-Level traffic.
set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level1-rates cir 2000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level1-rates cbs 1000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level1-rates pir 2500 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level1-rates pbs 1000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level2-rates cir 3000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level2-rates cbs 1000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level2-rates pir 3500 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level2-rates pbs 1000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level3-rates cir 4000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level3-rates cbs 1000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level3-rates pir 4500 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level3-rates pbs 1000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level4-rates cir 1000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level4-rates cbs 1000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level4-rates pir 1500 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential level4-rates pbs 1000 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential levels 4 set forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential type two-rate-three-color commit
The multi-level policer configuration is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service policer policer-residential
{
"rtbrick-config:policer": [
{
"policer-name": "policer-residential",
"level1-rates": {
"cir": 2000,
"cbs": 1000,
"pir": 2500,
"pbs": 1000
},
"level2-rates": {
"cir": 3000,
"cbs": 1000,
"pir": 3500,
"pbs": 1000
},
"level3-rates": {
"cir": 4000,
"cbs": 1000,
"pir": 4500,
"pbs": 1000
},
"level4-rates": {
"cir": 1000,
"cbs": 1000,
"pir": 1500,
"pbs": 1000
},
"levels": 4,
"type": "two-rate-three-color"
}
]
}
-
Map the classified traffic streams to different policer levels using class-to-policer mapping:
set forwarding-options class-of-service class-policer-map policer-map-residential set forwarding-options class-of-service class-policer-map policer-map-residential class class-0 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-policer-map policer-map-residential class class-0 policer-level level-1 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-policer-map policer-map-residential class class-1 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-policer-map policer-map-residential class class-1 policer-level level-2 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-policer-map policer-map-residential class class-2 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-policer-map policer-map-residential class class-2 policer-level level-3 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-policer-map policer-map-residential class class-3 set forwarding-options class-of-service class-policer-map policer-map-residential class class-3 policer-level level-4 commit
The class-policer-map configuration is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service class-policer-map policer-map-residential class
{
"rtbrick-config:class": [
{
"class": "class-0",
"policer-level": "level-1"
},
{
"class": "class-1",
"policer-level": "level-2"
},
{
"class": "class-2",
"policer-level": "level-3"
},
{
"class": "class-3",
"policer-level": "level-4"
}
]
}
Configure QoS Remarking
-
Remark downstream traffic egressing from subscriber interface (egress remarking).
set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 1 set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 1 color all set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 1 color all remark-codepoint 6 set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 2 set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 2 color all set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 2 color all remark-codepoint 6 set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 3 set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 3 color all set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 3 color all remark-codepoint 6 set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 4 set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 4 color all set forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential remark-type ieee-802.1 match-codepoint 4 color all remark-codepoint 6 commit
The remarking configuration is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service remark-map subs-remarking-residential
{
"rtbrick-config:remark-map": [
{
"remark-map-name": "subs-remarking-residential",
"remark-type": [
{
"remark-type": "ieee-802.1",
"match-codepoint": [
{
"match-codepoint": 1,
"color": [
{
"color": "all",
"remark-codepoint": 6
}
]
},
{
"match-codepoint": 2,
"color": [
{
"color": "all",
"remark-codepoint": 6
}
]
},
{
"match-codepoint": 3,
"color": [
{
"color": "all",
"remark-codepoint": 6
}
]
},
{
"match-codepoint": 4,
"color": [
{
"color": "all",
"remark-codepoint": 6
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
-
Remark upstream traffic ingressing to a subscriber’s interface [ingress remarking]
| In the upstream traffic classifier configuration shown below, remarking of all traffic streams with code point '7' is done. |
set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 1 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 1 class class-0 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 1 remark-codepoint 7 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 2 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 2 class class-1 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 2 remark-codepoint 7 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 3 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 3 class class-2 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 3 remark-codepoint 7 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 4 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 4 class class-3 set forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class match-type ieee-802.1 codepoint 4 remark-codepoint 7 commit
Below is the remarking configuration:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options class-of-service classifier subs-pbit-class
{
"rtbrick-config:classifier": [
{
"classifier-name": "subs-pbit-class",
"match-type": [
{
"match-type": "ieee-802.1",
"codepoint": [
{
"codepoint": 1,
"class": "class-0",
"remark-codepoint": 7
},
{
"codepoint": 2,
"class": "class-1",
"remark-codepoint": 7
},
{
"codepoint": 3,
"class": "class-2",
"remark-codepoint": 7
},
{
"codepoint": 4,
"class": "class-3",
"remark-codepoint": 7
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
Configure Mirroring for Downstream Traffic Remark Validation
Configure Mirroring for Downstream Traffic
set forwarding-options mirror m1 source interface ifp-0/1/30 set forwarding-options mirror m1 source direction egress set forwarding-options mirror m1 destination interface cpu-0/0/200 commit
Validate the downstream traffic remarking
| This validation requires mirroring the subscriber access interface on the C-BNG device. |
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options mirror
{
"rtbrick-config:mirror": [
{
"name": "m1",
"destination": {
"interface": "cpu-0/0/200"
},
"source": {
"direction": "egress",
"interface": "ifp-0/1/30"
}
}
]
}
The capture mirroring can be performed as shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> capture mirror
2023-04-03T13:58:59.651227+0000 e8:c5:7a:8f:76:f1 > 02:00:00:00:00:01, ethertype 802.1Q (0x8100), length 1022: vlan 1001, p 6, ethertype 802.1Q, vlan 1001, p 6, ethertype IPv4, (tos 0xe0, ttl 63, id 0, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 1000)
192.0.2.2.65056 > 203.0.113.1.65056: UDP, length 972
2023-04-03T13:58:59.651306+0000 e8:c5:7a:8f:76:f1 > 02:00:00:00:00:01, ethertype 802.1Q (0x8100), length 1022: vlan 1001, p 6, ethertype 802.1Q, vlan 1001, p 6, ethertype IPv4, (tos 0xe0, ttl 63, id 0, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 1000)
192.0.2.2.65056 > 203.0.113.1.65056: UDP, length 972
Configure Mirroring for Upstream Traffic Remark Validation
set forwarding-options mirror m1 source interface ifp-0/1/30 set forwarding-options mirror m1 source direction ingress set forwarding-options mirror m1 destination interface cpu-0/0/200 commit
Validating the upstream traffic remarking
| Mirror the core facing port on the C-BNG device as shown below. |
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options mirror m1
{
"rtbrick-config:mirror": [
{
"name": "m1",
"destination": {
"interface": "cpu-0/0/200"
},
"source": {
"direction": "ingress",
"interface": "ifp-0/1/30"
}
}
]
}
The capture mirroring can be performed as shown below. It confirms all four traffic streams noted with codepoint=7.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> capture mirror
2023-04-03T13:53:31.400011+0000 02:00:00:00:00:01 > e8:c5:7a:8f:76:f1, ethertype 802.1Q (0x8100), length 1022: vlan 1001, p 2, ethertype 802.1Q, vlan 1001, p 2, ethertype IPv4, (tos 0xa0, ttl 64, id 0, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 1000)
203.0.113.1.65056 > 192.0.2.2.65056: UDP, length 972
2023-04-03T13:53:31.400167+0000 02:00:00:00:00:01 > e8:c5:7a:8f:76:f1, ethertype 802.1Q (0x8100), length 1022: vlan 1001, p 3, ethertype 802.1Q, vlan 1001, p 3, ethertype IPv4, (tos 0xc0, ttl 64, id 0, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 1000)
203.0.113.1.65056 > 192.0.2.2.65056: UDP, length 972
Configure FreeRADIUS Server
Installation of FreeRADIUS
FreeRADIUS server can be installed on any Linux OS distribution. For information about installing FreeRADIUS, see Installing the FreeRADIUS Server.
Remove the Unsupported Files
It is necessary to remove echo, ntlm_auth, eap, echo, and mschap files once FreeRadius has been installed, since they are not required by this reference design. To remove these files, enter the following commands:
rm -rf /etc/freeradius/3.0/mods-enabled/echo rm -rf /etc/freeradius/3.0/mods-enabled/ntlm_auth rm -rf /etc/freeradius/3.0/mods-enabled/eap rm -rf /etc/freeradius/3.0/mods-enabled/echo rm -rf /etc/freeradius/3.0/mods-enabled/mschap
Configure the FreeRADIUS Files
It is necessary to configure the FreeRADIUS files once FreeRadius has been installed. The configuration files can be found under /etc/freeradius/3.0/.
authorize
Using the following command, one can view the authorize file in its default location.
~:/etc/freeradius/3.0 # cat mods-config/files/authorize
Replace the content of the authorize file with the following:
$INCLUDE /etc/freeradius/3.0/ipoe_users_file
| This file can also be downloaded from the appendix (Appendix C: RADIUS Server Configuration). |
ipoe_users_file
The IPoE Users file (ipoe_users_file) mentioned in the above section includes subscriber profile parameters as shown below.
"02:00:00:00:00:01@ipoe" Cleartext-Password := "ipoe"
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Class = IPOE,
Framed-IP-Address = 203.0.113.1,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.255,
RtBrick-DNS-Primary = 203.0.113.200,
RtBrick-DNS-Secondary = 203.0.113.201,
Framed-IPv6-Prefix = 2001:db8:0:1::1/128,
Delegated-IPv6-Prefix = 2001:db8:0:3::/64,
RtBrick-DNS-Primary-IPv6 = 2001:db8:0:20::1,
RtBrick-DNS-Secondary-IPv6 = 2001:db8:0:20::2,
Session-Timeout = 0,
Idle-Timeout = 0,
Reply-Message = "FOOBAR Internet",
Acct-Interim-Interval = 120,
RtBrick-QoS-Profile = "residential"
DEFAULT User-Name =~ '^[0-9a-f\:]+@ipoe$', Cleartext-Password := 'ipoe'
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Class = "IPOE",
Acct-Interim-Interval = 900
The ipoe_users_file can be created with the above content in the /etc/freeradius/3.0/ path. Alternatively, this file can be downloaded from the appendix section of this guide and placed at /etc/freeradius/3.0/.
clients.conf
Clients.conf file shall be configured with the expected RADIUS client IP address and secret.
~:/etc/freeradius/3.0 # cat clients.conf
client rtbrick {
ipaddr = 192.0.2.74
secret = testing123
shortname = rtbrick
nas_type = other
require_message_authenticator = no
}
The clients.conf file (/etc/freeradius/3.0/clients.conf) used for this reference design can be downloaded from the appendix section of this guide.
radiusd.conf
The radiusd.conf file should be configured with the expected RADIUS authentication and accounting parameters.
prefix = /usr
exec_prefix = /usr
sysconfdir = /etc
localstatedir = /var
sbindir = ${exec_prefix}/sbin
logdir = /var/log/freeradius
raddbdir = /etc/freeradius
radacctdir = ${logdir}/radacct
name = freeradius
confdir = ${raddbdir}
modconfdir = ${confdir}/mods-config
run_dir = ${localstatedir}/run/${name}
db_dir = ${raddbdir}
libdir = /usr/lib/freeradius
pidfile = ${run_dir}/${name}.pid
correct_escapes = true
max_request_time = 5
cleanup_delay = 0
max_requests = 16384
hostname_lookups = no
log {
destination = files
file = ${logdir}/radius.log
stripped_names = no
auth = yes
}
checkrad = ${sbindir}/checkrad
security {
# user = radius
# group = radius
allow_core_dumps = no
max_attributes = 200
reject_delay = 0
status_server = no
@openssl_version_check_config@
}
proxy_requests = no
$INCLUDE clients.conf
thread pool {
start_servers = 32
max_servers = 128
min_spare_servers = 8
max_spare_servers = 16
max_queue_size = 16384
max_requests_per_server = 0
auto_limit_acct = no
}
modules {
$INCLUDE mods-enabled/
}
instantiate {
files
linelog
}
server default {
listen {
type = auth
ipaddr = *
port = 1812
}
listen {
type = acct
ipaddr = *
port = 1813
}
authorize {
update request {
FreeRADIUS-Client-Shortname = "%{&request:Client-Shortname}"
}
if (&request:Client-Shortname == "rtbrick-server") {
rtbrick-server-log
}
files
pap
}
authenticate {
pap
}
post-auth {
if (&request:Client-Shortname == "rtbrick-server") {
rtbrick-server-log
}
Post-Auth-Type REJECT {
update reply {
Reply-Message := "Login Failed. Please check your username and password."
}
attr_filter.access_reject
}
}
preacct {
ok
}
accounting {
if (&request:Client-Shortname == "rtbrick-server") {
rtbrick-server-log
}
ok
}
session {
}
}
Radiusd.conf should be configured to use UDP ports 1812 and 1813 for authentication and accounting, respectively. Additionally, rtbrick-server-log should be added to the parameters for authorise, authenticate, and accounting.
The radiusd.conf file (/etc/freeradius/3.0/radiusd.conf) used for this reference design can be downloaded from the appendix section (Appendix C) of this guide.
detail
The detail file shall be configured for the RADIUS accounting logs.
/etc/freeradius/3.0 # cat mods-enabled/detail
permissions = 0666detail rtbrick-server-log {
filename = ${radacctdir}/rtbrick-server-detail.log
header = "%t;%{NAS-IP-Address};%I;%{Packet-Src-Port}"
log_packet_header = no
}
Ensure that rtbrick-server-log is specified in the detail file.
The detail file (/etc/freeradius/3.0/mods-enabled/detail) used for this reference design can be downloaded from the appendix section (Appendix C) of this guide.
dictionary.rtbrick
Add the RtBrick RADIUS dictionary (dictionary.rtbrick) to /usr/share/freeradius/dictionary.rtbrick and include it in` /usr/share/freeradius/dictionary`.
The dictionary.rtbrick contains the RBFS attributes in FreeRADIUS format.
Click here to download the radius_config.zip, which contains the dictionary.rtbrick file.
Stopping and Starting the FreeRADIUS Server for any Changes
For any changes, stop and restart the FreeRADIUS server.
To stop the server, enter the following command:
sudo service freeradius stop
To start the server, enter the following command:
sudo service freeradius start
The FreeRadius server is now ready to provide AAA (Authentication, Accounting & Authorization) services to logging in subscribers.
Validating IPoE Subscriber Bring-Up
Using traffic streams on both upstream and downstream directions with traffic packets and bytes statistics, IPoE Subscriber sessions can be "ESTABLISHED".
The validation can be performed in two steps:
-
Establishing the IPoE subscriber
-
Pinging the subscriber IPv4/IPv6 address
BNG Blaster - IPoE Subscribers with Traffic Streams
Using BNG Blaster, which emulates IPoE clients, session traffic("session-traffic") and streams traffic with different code-points("streams"), one can test IPoE subscriber management feature.
The data traffic can be defined in Blaster by configuring session/streams traffic.
-
Session Traffic in Blaster can be enabled by specifying
"autostart": true. Once the session is established, traffic starts automatically. Eventually if you want to stop or start the traffic (session or streams), press F7/F8. -
Streams traffic in Blaster can be enabled by specifying
stream-group-idat both streams ("streams":) and access interface levels (interfaces:access).
For information about using BNG Blaster, see [starting-bng-blaster].
Validating the IPoE Session on BNG Blaster
To validate the IPoE Session on BNG Blaster, switch to the Service Node. On the BNG Blaster terminal, the count of the "Established" session will be 1. Also, the logging of the same terminal will display "ALL SESSIONS ESTABLISHED" and "ALL SESSION TRAFFIC FLOWS VERIFIED" as highlighted in the below image.
In the image below, one can see the details of the established Single Subscriber session.
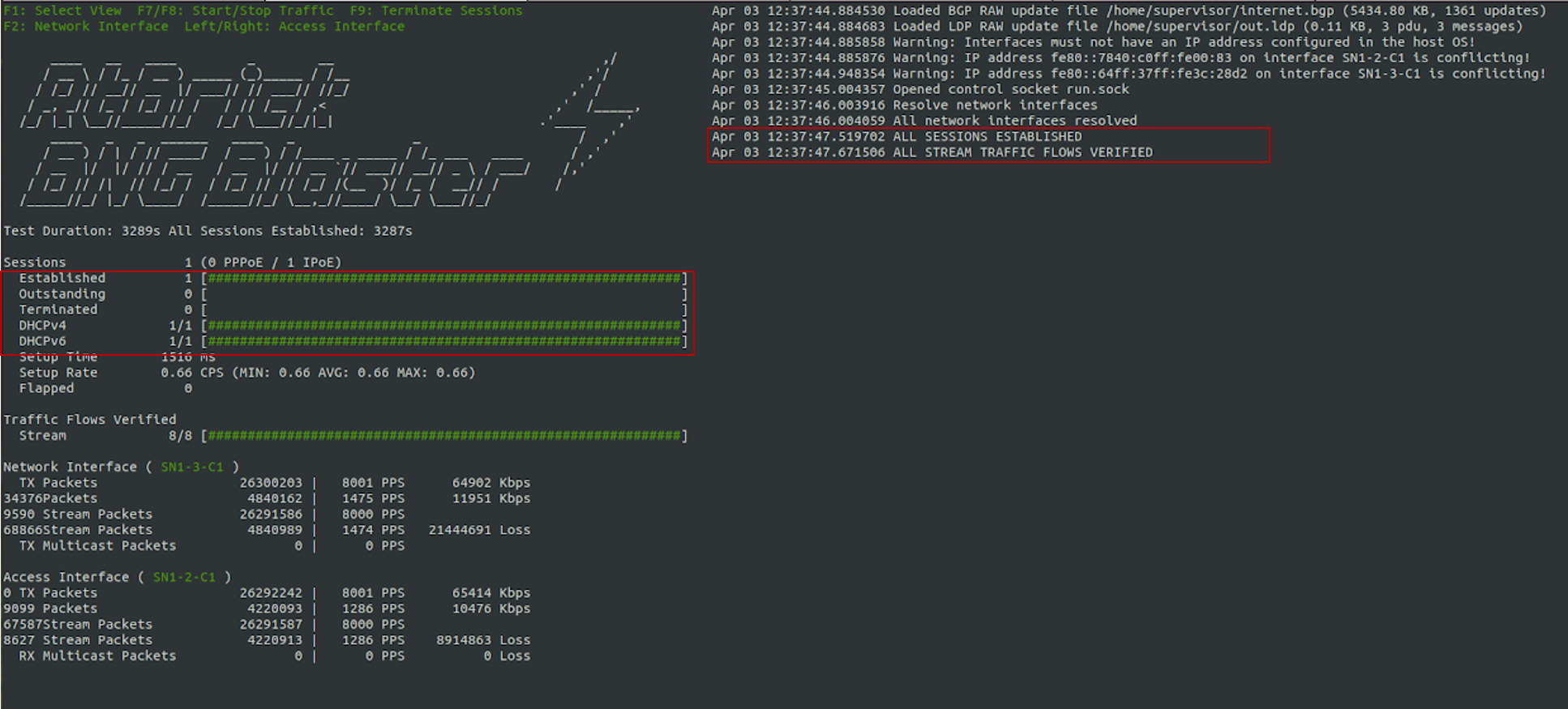
Fig 3: BNG Blaster terminal view
Visit the following URL for more information on BNG Blaster:
Viewing the Subscribers and the Subscriber Details on RBFS
Enter the following command to view the list of subscribers.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show subscriber Subscriber-Id Interface VLAN Type State 216454257090494470 ifp-0/1/30 1001:1001 IPoE ESTABLISHED supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
Enter the following command to view the details of the subscriber with ID 216454257090494470.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show subscriber 216454257090494470 detail
Subscriber-Id: 216454257090494470
Type: IPoE
State: ESTABLISHED
Created: Mon Apr 03 13:51:17 GMT +0000 2023
Interface: ifp-0/1/30
Outer VLAN: 1001
Inner VLAN: 1001
Client MAC: 02:00:00:00:00:01
Server MAC: e8:c5:7a:8f:76:f1
IFL: ipoe-0/1/30/216454257090494470
Username: 02:00:00:00:00:01@ipoe
Access-Profile: ipoe
AAA-Profile: aaa-profile
Service-Profile: qos_service
Reply-Message: FOOBAR Internet
Session-Timeout: 0 (disabled)
Idle-Timeout: 0 (disabled)
MTU: 1500 Profile: N/A
IPv4:
Instance: default
Address: 203.0.113.1/255.255.255.255
Address Active: True
Primary DNS: 203.0.113.200
Secondary DNS: 203.0.113.201
IPv6:
Instance: default
RA Prefix: 2001:db8:0:1::1/128
RA Prefix Active: True
Delegated Prefix (DHCPv6): 2001:db8:0:3::/64
Delegated Prefix Active: True
Primary DNS: 2001:db8:0:20::1
Secondary DNS: 2001:db8:0:20::2
Accounting:
Session-Id: 216454257090494470:1680529877
Start-Time: 2023-04-03T13:51:18.543868+0000
Interims Interval: 120 seconds
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
Pinging the Subscriber (source: IPOE) from C-BNG
Before pinging a subscriber, use the show route <…> command to display the subscriber IPs at the C-BNG.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show route ipv4 unicast source ipoe Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: unicast Prefix/Label Source Pref Next Hop Interface 203.0.113.1/32 ipoe 7 - ipoe-0/1/30/216454257090494470 supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show route ipv6 unicast source ipoe Instance: default, AFI: ipv6, SAFI: unicast Prefix/Label Source Pref Next Hop Interface 2001:db8:0:1::1/128 ipoe 7 - ipoe-0/1/30/216454257090494470 2001:db8:0:3::/64 ipoe 7 fe80::ffff:ffff:ff00:1 ipoe-0/1/30/216454257090494470
From the above list, ping 203.0.113.1 as shown below.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> ping 203.0.113.1 68 bytes from 203.0.113.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.3463 ms 68 bytes from 203.0.113.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=10.5234 ms 68 bytes from 203.0.113.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=9.8053 ms 68 bytes from 203.0.113.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=11.0041 ms 68 bytes from 203.0.113.1: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=10.9300 ms Statistics: 5 sent, 5 received, 0% packet loss supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
Validating Traffic Streams
Traffic streams can be used to perform various forwarding verifications.
For upstream traffic capture, enter the following command:
capture interface ifp-0/1/30 direction in
For downstream traffic capture, enter the following command:
capture interface ifp-0/1/30 direction out
Here, ifp-0/1/30 refers to the access interface.
Validating the IPoE QoS on BNG Blaster
To validate the IPoE QoS on BNG Blaster, switch to the Service Node. Navigate to the Streams and Session Traffic terminal by pressing F1 function key in your keyboard.
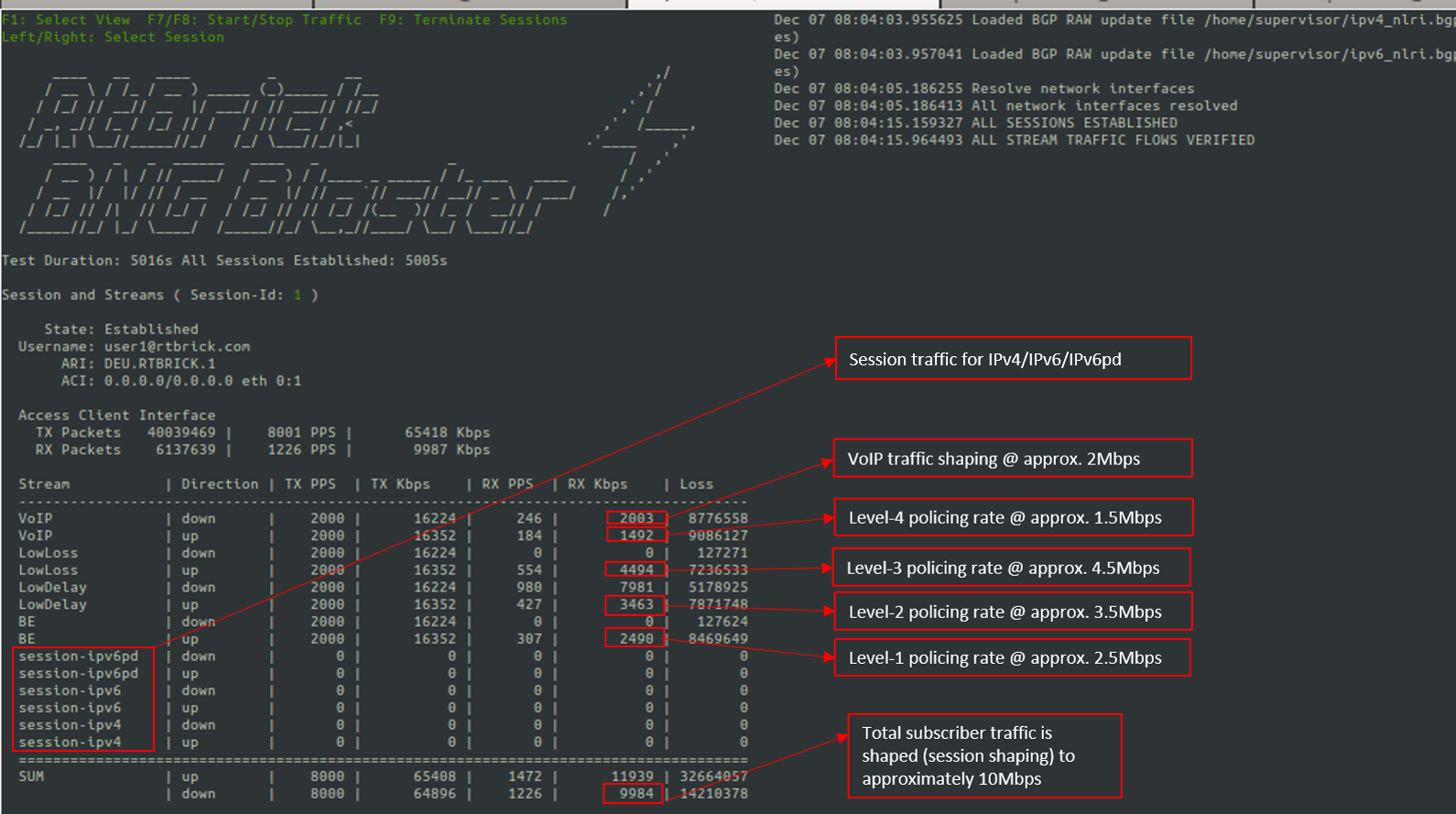
Fig 4: Reading output from BNG Blaster
As shown in the above image, the VoIP downstream traffic has been shaped (session shaping) to 2Mbps. Similarly, the total subscriber traffic has been shaped approximately to 10Mbps.
Following are the upstream traffic rates of different policer levels:
-
Level-1 Rates ~=2.5Mbps
-
Level-2 Rates ~=3.5Mbps
-
Level-3 Rates ~=4.5Mbps
-
Level-4 Rates ~=1.5Mbps
IPoE Subscriber Accounting for Upstream and Downstream Traffic
Run the "show subscriber" command to view the list of subscribers.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show subscriber Subscriber-Id Interface VLAN Type State 216454257090494470 ifp-0/1/30 1001:1001 IPoE ESTABLISHED ESTABLISHEDsupervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
Specify the Subscriber-ID to find the specific subscriber’s accounting details:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show subscriber 216454257090494470 accounting
Subscriber-Id: 216454257090494470
IFL: ipoe-0/1/30/216454257090494470
Start Timestamp: Mon Apr 03 13:51:18 GMT +0000 2023
Idle Timestamp: Mon Apr 03 13:51:38 GMT +0000 2023
Session-Timeout: 0 seconds
Idle-Timeout: 0 seconds
Session Statistics:
Ingress: 28185 packets 27339450 bytes
Egress: 23990 packets 23990000 bytes
LIF Statistics:
Ingress: 0 packets 0 bytes
Egress: 0 packets 0 bytes
Egress Class (Queue) Statistics:
class-0: 4 packets 4000 bytes dropped: 0 packets 0 bytes
class-1: 19191 packets 19191000 bytes dropped: 0 packets 0 bytes
class-2: 3 packets 3000 bytes dropped: 0 packets 0 bytes
class-3: 4792 packets 4792000 bytes dropped: 0 packets 0 bytes
class-4: 0 packets 0 bytes dropped: 0 packets 0 bytes
class-5: 0 packets 0 bytes dropped: 0 packets 0 bytes
class-6: 0 packets 0 bytes dropped: 0 packets 0 bytes
class-7: 0 packets 0 bytes dropped: 0 packets 0 bytes
Ingress Policer Statistics:
Level 1: 5819 packets 5644430 bytes dropped: 31270 packets 30331900 bytes
Level 2: 8170 packets 7924900 bytes dropped: 29029 packets 28158130 bytes
Level 3: 10540 packets 10223800 bytes dropped: 26638 packets 25838860 bytes
Level 4: 3656 packets 3546320 bytes dropped: 33614 packets 32605580 bytes
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>