Introduction
Lawful Interception (LI) is a legal requirement in most of the countries. It enables the legal authorities to obtain communications network data for analysis or evidence. It is a method of intercepting certain data-streams of end-users in both directions, and tunnel the intercepted traffic to a Mediation Device (MD) with information about direction of capture and reference to the intercepted connection.
Leaf node is the Point of Interception (POI) and MD is the final Point of Collection (POC).
Supported Platforms
Not all features are necessarily supported on each hardware platform. Refer to the Platform Guide for the features and the sub-features that are or are not supported by each platform.
Components of Lawful Interception
The figure below shows the different components of the LI solution.
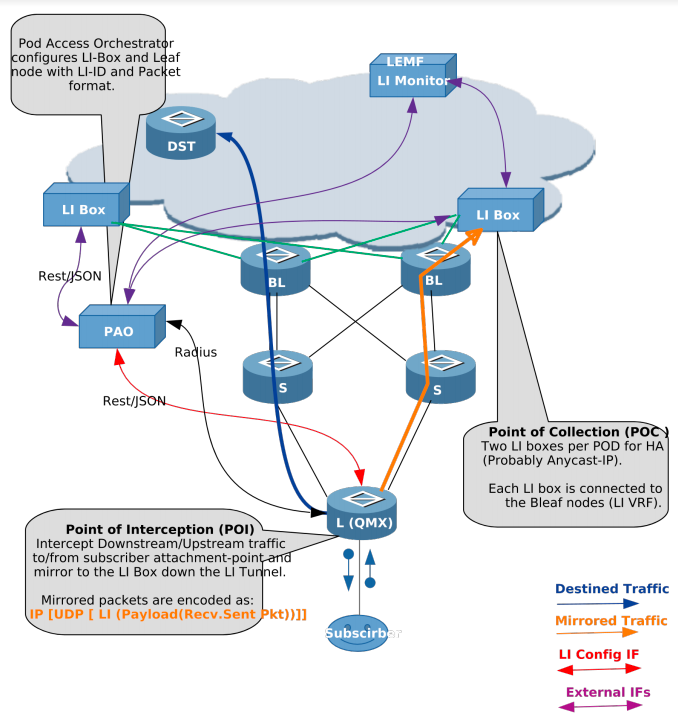
Definitions
- L(QMX)
-
Leaf node in the POD which is connected to subscribers.
- S/BL
-
Spine and Border Leaf in the POD, which can be replaced with just one node.
- LI Box
-
Lawful Intercept Box, which communicates to Law Enforcement Agency (LEMF) and relays mirrored traffic. Two LI boxes per POD are connected for redundancy.
- PAO
-
POD Access Orchestrator, which configures the LI Box and network nodes with LI configurations.
- DST
-
Destination node for traffic from subscribers.
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
|---|---|
LI |
Lawful Interception |
POI |
Point of Interception |
POC |
Point of Collection |
PAO |
Pod Access Orchestrator |
LIMS |
Lawful Interception Management System |
VRF |
Virtual Routing Instance |
LEMF |
Lawful Enforcement Monitoring Facility |
Leaf |
Access node |
PPPoE |
Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet |
L2TP |
Layer 2 Tunnelling Protocol |
MPLS |
Multi Protocol Label Switching |
Guidelines & Limitations
The unidentified LI traffic is subject to the following limitations when using more than seven UDP ports.
-
Currently, there is a restriction on UDP destination ports, which are limited to 7. The IP destination addresses (IP1 through IPn) can utilize any of the seven ports. The distribution of these seven ports is determined by the order in which requests are received, with priority given to those who arrive first.