Overview
This document provides information to validate the RBFS Consolidated BNG (C-BNG) implementation using the PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) network protocol. The guide contains information about general platform configuration, configuration of various access and routing protocols, subscriber management, Quality of Service (QoS) and troubleshooting. The document presents a single use case scenario and provides information specifically on how to validate this particular implementation and for more information on any specific application, refer to https://documents.rtbrick.com/.
This guide is not intended to be an exhaustive guide of all RBFS features and does not provide information on features such as Multicast, Lawful Intercept etc.
About the RBFS Consolidated BNG
C-BNG stands for Consolidated Broadband Network Gateway. A C-BNG is a BNG that contains all the BNG functionalities together in a single platform. Unlike the RBFS spine and leaf software images, where the functionalities are distributed to spine platforms and leaf platforms separately based on their roles, C-BNG platform contains all functionalities together in a single platform.
The RtBrick C-BNG is delivered as a Linux container that runs on platforms provided by the hardware ODM manufacturers. Platforms that support C-BNG include Edgecore AGR400, CSR320, and UfiSpace S9600. The RtBrick C-BNG software runs on powerful bare-metal switches as an open BNG.
The BNG is designed to dynamically deliver the following services:
-
Discovering and managing subscriber sessions for PPPoE subscribers
-
Providing authentication, authorization and accounting (AAA)
The basic C-BNG architecture for PPPoE subscribers is shown in Fig. 1.
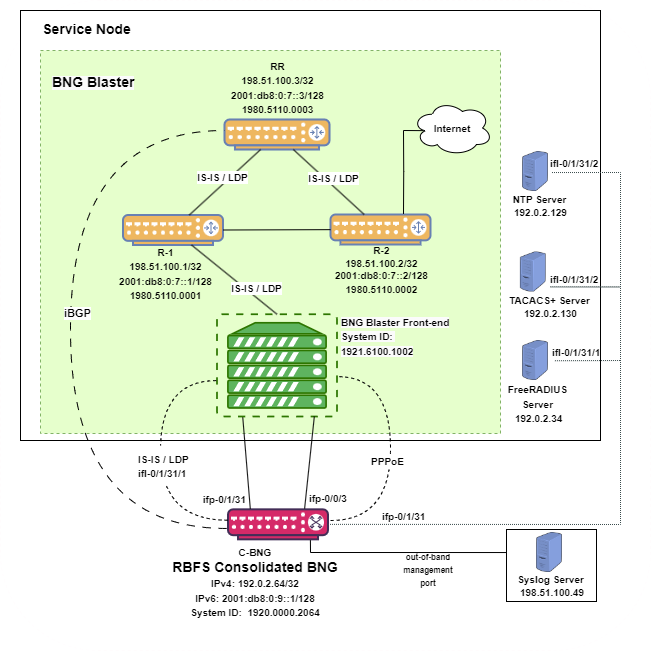
Fig. 1: Topology setup with C-BNG as a DUT (device under test) connected to BNG Blaster.
In this topology:
-
The Service Node is an Ubuntu server on which a new container is spawned with the associated interfaces for running BNG Blaster tests.
-
RtBrick’s homegrown BNG Blaster emulates both the routing and access functions and, in effect, tests the DUT.
-
The topology emulates PPPoE subscribers and traffic between RBFS switch and the core network.
-
The objective of this topology is to demonstrate complete PPPoE subscriber emulating and service along with routing to connect to the network uplink.
-
R-1, R-2 and RR are simulated using BNG Blaster. The
C-BNGforms an IS-IS L1 adjacency with the BNG blaster to discover R-1, R-2, and RR. The RR is the route reflector that replays a full internet feed of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, in total about 1.1 million prefixes. R-2 is the nexthop for all internet routes. -
Through DCHP, an IPv4 address needs to be assigned to the out-of-band management port.
Deployment
A C-BNG provides BNG functionality on a single bare-metal switch and eliminates the need to have a chassis-based system. It provides a low footprint and optimal power consumption based on BRCM chipsets, a compelling value proposition that has complete BNG and routing feature support.
C-BNG runs on small form-factor temperature-hardened hardware that allows deployments in street cabinets.
The rtbrick-toolkit is a meta package that can be used to install all the tools needed to work with RBFS images (container or ONL installer) and the RBFS APIs.
For more information, see RBFS and Tools Installation, and RBFS Licensing Guide.
Using the RBFS CLI
Connect to the C-BNG node.
$ ssh <C-BNG-management-ip> -l supervisor supervisor@<C-BNG-management-ip>'s password:
The password for C-BNG-management-ip should be entered here.
As a result, the CLI prompt appears like this:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net:~ $
Open the RBFS CLI.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net:~ $ cli
The CLI has three different modes:
-
operationmode is a read-only mode to inspect and analyze the system state -
configmode allows modifying the RBFS configuration -
debugmode provides advanced tools for troubleshooting
The switch-mode command allows switching between the different modes.
The show commands allow inspecting the system state.
The set and delete commands, which are only available in the configuration mode, allow modifying or deleting the current configuration. The commit command executes changes. RBFS provides a commit history that allows reviewing changes (show commit log) and restoring a previous configuration (rollback). There are also commands to ping destinations, capture network traffic, save the configuration to a file or load the configuration from a file.
The CLI supports abbreviating commands, provides suggestions by hitting the [tab] key and displays a context help by entering a ?.
For more information on how to use the RBFS CLI, see RBFS CLI User Guide.