Configuring OSPF SR
Module Introduction
Before you start the hands-on part of this module, you should load the appropriate configuration and verify that the testbed is up and running by executing the corresponding robot file:
student@tour:~/trainings_resources/robot$ robot mpls_sr_ospf/mpls_sr_ospf_setup.robotIn order to get a better understanding, the lab setup is shown in the picture below.
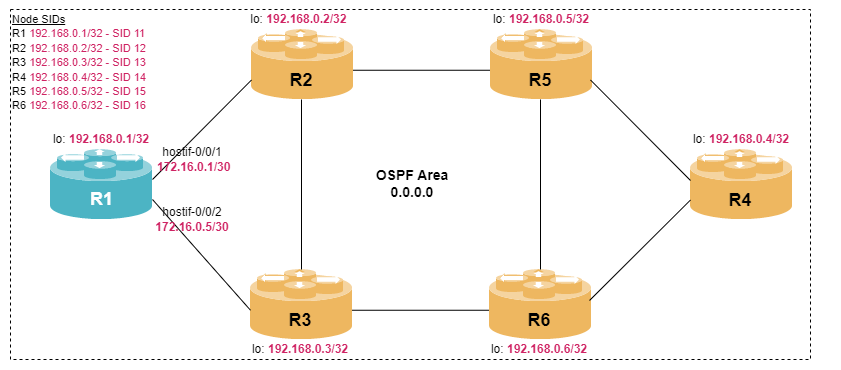
Configuring Prefix Segments
A prefix segment is a global IGP segment that is associated with an IGP prefix and represented by the Prefix-SID. The corresponding index can be set at the set instance <instance> protocol ospf address-family ipv4 area <area> interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing level.
| Prefix-SIDs must be unique in the SR domain. |
In addition, a segment routing global block (SRGB) must be defined. The SRGB consists of a base value and a range which defines how many prefix-SIDs the block contains. The SRGB i
s configured using the set instance <instance> protocol ospf address-family ipv4 segment-routing command hierarchy.
| For sake of simplicity and troubleshooting, it is strongly recommended to use identical SRGBs on all nodes within the SR domain. |
Configure OSPF Segment Routing on router R1. The SRGB base should be 12000. The SID for the IPv4 loopback address is 11. Note, that you need to enable the appropriate address-families in the default instance.
Click to reveal the answer
cfg> set instance default protocol ospf address-family ipv4 segment-routing status enable
cfg> set instance default protocol ospf address-family ipv4 segment-routing srgb base 12000
cfg> set instance default protocol ospf address-family ipv4 segment-routing srgb range 100
cfg> set instance default protocol ospf address-family ipv4 area 0.0.0.0 interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv4 index 11
cfg> set instance default address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast
cfg> set instance default address-family mpls unicast
cfg> commitAfter enabling OSPF-SR, we should be able to see IPv4 labeled-unicast routes in the routing table. Let’s check:
cfg> show route ipv4 labeled-unicast prefix 192.168.0.4/32
cfg>It seems, that no IPv4 labeled-unicast route was installed into the routing table. Let’s take a step back and examine the OSPF database:
cfg> show ospf database
Instance: default, Area: 0.0.0.0
Type Link State ID Advertising Router Age Sequence Checksum Cost Link Count
<...>
Opaque-Area 4.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 3600 0x80000004 0x81bf - -
Opaque-Area 4.0.0.0 192.168.0.2 529 0x80000003 0x95fb - -
Opaque-Area 4.0.0.0 192.168.0.3 530 0x80000003 0x8f01 - -
Opaque-Area 4.0.0.0 192.168.0.4 542 0x80000003 0x8906 - -
Opaque-Area 4.0.0.0 192.168.0.5 531 0x80000003 0x830b - -
Opaque-Area 4.0.0.0 192.168.0.6 530 0x80000003 0x7d10 - -
Opaque-Area 7.0.0.11 192.168.0.1 3600 0x80000004 0x7a58 - -
Opaque-Area 7.0.0.12 192.168.0.2 529 0x80000003 0x943b - -
Opaque-Area 7.0.0.13 192.168.0.3 530 0x80000003 0xac1f - -
Opaque-Area 7.0.0.14 192.168.0.4 537 0x80000003 0xc403 - -
Opaque-Area 7.0.0.15 192.168.0.5 531 0x80000003 0xdce6 - -
Opaque-Area 7.0.0.16 192.168.0.6 530 0x80000003 0xf4ca - -From the output above we can see that a number of new LSA messages of type opaque have been learned. Each router in the network advertises two opaque LSAs. Thus, new information has been learned and stored into the link-state database, but is not used. Let’s have a closer look at the router-LSAs once again:
cfg> show ospf database ls-id 192.168.0.1 detail
Instance: default, Area: 0.0.0.0 LSAs
LSA ID: 192.168.0.1
Advertising router: 192.168.0.1, LSA type: Router
Sequence number: 0x80000005, Checksum: 0x21cf, LSA age: 1094
Length: 84, Options: *|-|-|-|-|-|E|*, Flags: -|-|-|- (1)
<...>
cfg> show ospf database ls-id 192.168.0.4 detail
Instance: default, Area: 0.0.0.0 LSAs
LSA ID: 192.168.0.4
Advertising router: 192.168.0.4, LSA type: Router, Router ID: 192.168.0.3
Sequence number: 0x80000006, Checksum: 0x2650, LSA age: 1104
Interface: hostif-0/0/2/0, Neighbor address: 172.16.0.6
Length: 84, Options: *|O|-|-|-|-|E|*, Flags: -|-|-|- (2)
<...>| 1 | The O flag in the options field is not set. |
| 2 | The O flag in the options field is set. |
If you compare the router-LSA of router R1 and R2, you recognize that the O (opaque) field in the options field of your router is not set. Therefore, the opaque information is not used. In order to fix this, we need to enable
On R1, enable the opaque-capability in the OSPF configuration.
Click to reveal the answer
cfg> set instance default protocol ospf address-family ipv4 opaque-capability enable
cfg> commitNow that we have enabled the opaque capability, we should see IPv4 labeled-unicast routes:
cfg> show route ipv4 labeled-unicast prefix 192.168.0.4/32
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: labeled-unicast
Prefix/Label Source Pref Next Hop Interface Label
192.168.0.4/32 ospf 10 172.16.0.2 hostif-0/0/1/0 16014
172.16.0.6 hostif-0/0/2/0 16014