Configuring IS-IS SR
Module Introduction
Before you start the hands-on part of this module, you should load the appropriate configuration and verify that the testbed is up and running by executing the corresponding robot file:
student@tour:~/trainings_resources/robot$ robot mpls_sr_isis/mpls_sr_isis_setup.robotIn order to get a better understanding, the lab setup is shown in the picture below.
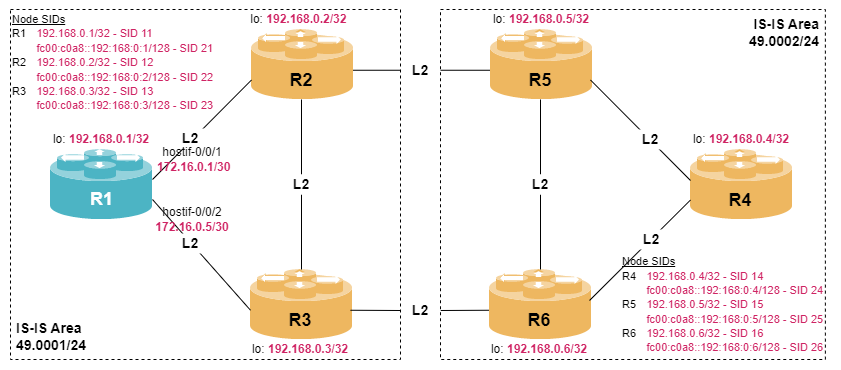
Configuring Prefix Segments
A prefix segment is a global IGP segment that is associated with an IGP prefix and represented by the Prefix-SID. The corresponding index can be set individually for IPv4 and IPv6 at the set instance <instance> protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing level.
| Prefix-SIDs must be unique in the SR domain. |
In addition, a segment routing global block (SRGB) must be defined. The SRGB consists of a base value and a range which defines how many prefix-SIDs the block contains. The SRGB is configured using the set instance <instance> protocol isis segment-routing srgb command hierarchy.
| For sake of simplicity and troubleshooting, it is strongly recommended to use identical SRGBs on all nodes within the SR domain. |
Configure IS-IS Segment Routing on router R1. The SRGB base should be 12000. The SID for the IPv4 loopback address is 11, and the SID for IPv6 loopback address is 21. Don’t forget to enable the appropriate address-families in instance default.
Click to reveal the answer
cfg> set instance default protocol isis segment-routing srgb base 12000
cfg> set instance default protocol isis segment-routing srgb range 100
cfg> set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv4 index 11
cfg> set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/0/0 segment-routing ipv6 index 21
cfg> set instance default address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast
cfg> set instance default address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast
cfg> set instance default address-family mpls unicast
cfg> commitNow that IS-IS Segment Routing is running, let’s have a look at the IS-IS database:
cfg> show isis database level-2 lsp id 1921.6800.0001.00-00
Instance: default, Level: 2
LSP ID: R1.00-00
Interface:
LSP Header:
Sequence: 0x5
Checksum: 0x7a12
Remaining lifetime: 65535 seconds
Flags: Attached: 0, Overload: 0
Packet:
Length: 213 bytes
Last received time: 2023-05-09T07:35:50.828477+0000
Expiry: expires in 18h 12m 12s 257739us
System ID: 1921.6800.0001
Dynamic Hostname TLV (137): R1
Protocols Supported TLVs (129):
Network layer protocol ID: IPv6
Network layer protocol ID: IPv4
Area Address TLVs (1):
Area address: 49.0001
Authentication TLV (10):
Type: md5
Value: f4686914a7943d7f6299e6c50c947710
IS Reachability TLVs (22):
IS neighbor: 1921.6800.0002.00
Adjacency SID:
none
IS neighbor: 1921.6800.0003.00
Adjacency SID:
none
IPv4 Reachability TLVs (135):
IPv4 prefix: 172.16.0.0/30 Metric: 100 Internal Up
IPv4 prefix: 172.16.0.4/30 Metric: 100 Internal Up
IPv4 prefix: 192.168.0.1/32 Metric: 0 Internal Up SID: 11 Flags: Node (2)
IPv6 Reachability TLVs (236):
IPv6 prefix: fc00:c0a8:0:1::/64 Metric: 100 Internal Up
IPv6 prefix: fc00:c0a8:0:3::/64 Metric: 100 Internal Up
IPv6 prefix: fc00:c0a8::192:168:0:1/128 Metric: 0 Internal Up SID: 21 Flags: Node (3)
Segment Routing TLVs (242/sub 2): (1)
SRGB: Base: 12000, Range: 100 (1)
IPv4 SID/Label Binding TLVs (149):
none
IPv6 SID/Label Binding TLVs (149):
none| 1 | There is a new IS-IS TLV that advertises the SRGB base and range, i.e., R1 has reserved labels 12000-12099 for segment routing. |
| 2 | For the IPv4 loopback prefix, a Prefix-SID of 11 has been added. |
| 3 | For the IPv6 loopback prefix, a Prefix-SID of 21 has been added. |
Consider R1 is an ingress LER. If we pick a prefix and inspect the routing table for ipv4 labeled-unicast, we can see that both next hops are using the same label, i.e., no matter which path is chosen, the same label is pushed to the packet. The reason is that the Prefix-SID is a global value (in this case of 14) and the label is calculated deterministically by adding the Prefix-SID to the SRGB base value:
cfg> show route ipv4 labeled-unicast prefix 192.168.0.4/32
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: labeled-unicast
Prefix/Label Source Pref Next Hop Interface Label
192.168.0.4/32 isis 18 172.16.0.2 hostif-0/0/1/0 16014
172.16.0.6 hostif-0/0/2/0 16014At the same time, R1 can be a transit LSR as well. What happens to incoming packets with label 16014?
cfg> show route mpls label 16014 detail
cfg>There is no entry for label 16014 in the routing table because R1 was configured with a SRGB base of 12000:
cfg> show isis segment-routing global-block
Instance: default, Level: 1
System SRGB Base SRGB Range
R1 12000 100
Instance: default, Level: 2
System SRGB Base SRGB Range
R1 12000 100
R2 16000 100
R3 16000 100
R4 16000 100
R5 16000 100
R6 16000 100| Also Prefix-SIDs are global segments, the fundamental concept of MPLS is that a router locally assigns labels. |
Keep in mind, that with segment routing, the incoming label is calculated from the local SRGB base and the Prefix-SID. In our case, packets must have label 12000+14=12014:
cfg> show route mpls label 12014 detail
Instance: default, AFI: mpls, SAFI: unicast
12014 (1)
Source: isis, Preference: 18
Next Hop: 172.16.0.6
Covering prefix: 172.16.0.6/32
Next Hop type: mpls transit, Next Hop action: None
Resolved in: default-ipv4-labeled-unicast
Egress interface: hostif-0/0/2/0, NextHop MAC: 7a:00:3f:c0:00:02
MPLS-Label: 16014 (2)
Next Hop: 172.16.0.2
Covering prefix: 172.16.0.2/32
Next Hop type: mpls transit, Next Hop action: None
Resolved in: default-ipv4-labeled-unicast
Egress interface: hostif-0/0/1/0, NextHop MAC: 7a:fc:da:c0:00:01
MPLS-Label: 16014 (2)| 1 | The incoming label is the local SRGB base value (12000) plus the corresponding Prefix-SID (14). |
| 2 | The outgoing label is the neighbors SRGB value (in both cases 16000) plus the corresponding Prefix-SID (14). |
| For ease of operation and troubleshooting, it is best practice to configure the same SRGB on all routers if possible. However, some implementations might not support specific ranges. |
By default, segment routing uses penultimate hop popping, i.e., the top-most label is removed on the next-to-last router. We can easily verify this behavior by inspecting the label associated with the Prefix-SID of the direct neighbor R2:
cfg> show route mpls label 12012 detail
Instance: default, AFI: mpls, SAFI: unicast
12012
Source: isis, Preference: 18
Next Hop: 172.16.0.2
Covering prefix: 172.16.0.2/32
Next Hop type: mpls php, Next Hop action: mpls label pop - next protocol ipv4
Resolved in: default-ipv4-labeled-unicast
Egress interface: hostif-0/0/1/0, NextHop MAC: 7a:fc:da:c0:00:01The output indicates that there is a next hop action of pop.
A complete list of Prefix-SIDs can be extracted by using the following command:
cfg> show isis segment-routing prefix-segment
Instance: default, Level: 1, No prefix-segment
Instance: default, Level: 2
System Prefix SID Flags
R1 192.168.0.1/32 11 Node
R1 fc00:c0a8::192:168:0:1/128 21 Node
R2 192.168.0.2/32 12 Node
R2 fc00:c0a8::192:168:0:2/128 22 Node
R3 192.168.0.3/32 13 Node
R3 fc00:c0a8::192:168:0:3/128 23 Node
R4 192.168.0.4/32 14 Node
R4 fc00:c0a8::192:168:0:4/128 24 Node
R5 192.168.0.5/32 15 Node
R5 fc00:c0a8::192:168:0:5/128 25 Node
R6 192.168.0.6/32 16 Node
R6 fc00:c0a8::192:168:0:6/128 26 NodeTo perform a data plane test, a traditional ping command that sends an ICMP echo message is insufficient. By default, RBFS does not use the labeled-unicast routing table to forward locally sourced packets; it only uses this table to resolve BGP nexthops. By adding the SAFI labeled-unicast option to the ping command, you can force the transmission of a labeled packet. However, since the remote end will reply with an unicast packet, this does not guarantee that the MPLS data path is functioning end-to-end.
RBFS supports MPLS LSP ping, as defined in RFC 8029, which allows administrators to verify an LSP. The concept is to send an MPLS echo request that is answered by an MPLS echo reply, rather than a typical UDP-based echo reply. The MPLS echo request contains specific information defined in RFC 8287 to verify the correct operation of the data plane. Let’s check the MPLS data plane using the mpls ping <fec>
command:
cfg> ping mpls 192.168.0.4/32 source-ip 192.168.0.1 count 3
Sending 3 MPLS echoes to isis FEC 192.168.0.4/32
Success: Response from 172.16.0.10: Egress for the FEC: seq = 1 rtt = 65.72 ms
Success: Response from 172.16.0.10: Egress for the FEC: seq = 2 rtt = 4.72 ms
Success: Response from 172.16.0.10: Egress for the FEC: seq = 3 rtt = 4.82 ms
--- 192.168.0.4/32 mpls ping statistics ---
3 sent, 3 received, 0 errors, 0% loss, time 3003.25 ms
rtt min/avg/max = 4.72/25.08/65.72 msConfiguring Adjacency Segments
An adjacency is a term for IS-IS neighborship between two routers over a link.
Configure Adjacency Segments on router R1. The SRLB base should be 8000 and the corresponding SIDs as follows:
| Interface | IPv4 Adj-SID | IPv4 Adj-SID |
|---|---|---|
hostif-0/0/1/0 |
412 |
612 |
hostif-0/0/2/0 |
413 |
613 |
Click to reveal the answer
cfg> set instance default protocol isis segment-routing srlb base 8000
cfg> set instance default protocol isis segment-routing srlb range 1000
cfg> set instance default protocol isis interface hostif-0/0/1/0 segment-routing point-to-point ipv4 adjacency-index 412
cfg> set instance default protocol isis interface hostif-0/0/1/0 segment-routing point-to-point ipv6 adjacency-index 612
cfg> set instance default protocol isis interface hostif-0/0/2/0 segment-routing point-to-point ipv4 adjacency-index 413
cfg> set instance default protocol isis interface hostif-0/0/2/0 segment-routing point-to-point ipv6 adjacency-index 613
cfg> commitThe IS-IS database reveals that Adjacency-SIDs have been associated with the neighbors:
cfg> show isis database level-2 lsp id 1921.6800.0001.00-00
Instance: default, Level: 2
LSP ID: R1.00-00
Interface:
LSP Header:
Sequence: 0x7
Checksum: 0xfc9
Remaining lifetime: 65535 seconds
Flags: Attached: 0, Overload: 0
Packet:
Length: 241 bytes
Last received time: 2023-05-09T08:34:21.661648+0000
Expiry: expires in 18h 11m 38s 822486us
System ID: 1921.6800.0001
Dynamic Hostname TLV (137): R1
Protocols Supported TLVs (129):
Network layer protocol ID: IPv6
Network layer protocol ID: IPv4
Area Address TLVs (1):
Area address: 49.0001
Authentication TLV (10):
Type: md5
Value: 399cf1c94ee9e4d0c72d82ffbac44b80
IS Reachability TLVs (22):
IS neighbor: 1921.6800.0002.00
Adjacency SID:
Value: 8412, Flags: Value, Local, Persistent (1)
Value: 8612, Flags: Ipv6 Encapsulation, Value, Local, Persistent (1)
IS neighbor: 1921.6800.0003.00
Adjacency SID:
Value: 8413, Flags: Value, Local, Persistent (2)
Value: 8613, Flags: Ipv6 Encapsulation, Value, Local, Persistent (2)
IPv4 Reachability TLVs (135):
IPv4 prefix: 172.16.0.0/30 Metric: 100 Internal Up
IPv4 prefix: 172.16.0.4/30 Metric: 100 Internal Up
IPv4 prefix: 192.168.0.1/32 Metric: 0 Internal Up SID: 11 Flags: Node
IPv6 Reachability TLVs (236):
IPv6 prefix: fc00:c0a8:0:1::/64 Metric: 100 Internal Up
IPv6 prefix: fc00:c0a8:0:3::/64 Metric: 100 Internal Up
IPv6 prefix: fc00:c0a8::192:168:0:1/128 Metric: 0 Internal Up SID: 21 Flags: Node
Segment Routing TLVs (242/sub 2):
SRGB: Base: 12000, Range: 100
IPv4 SID/Label Binding TLVs (149):
none
IPv6 SID/Label Binding TLVs (149):
none| 1 | Adjacency-SIDs for neighbor R2 for IPv4 and IPv6, respectively. |
| 2 | Adjacency-SIDs for neighbor R3. |
Remember, that the Adjaceny-SID value is a label, not an index. The Adjacency-SID is a local SID and has only a forwarding entry installed at the router where it is sourced:
cfg> show route mpls label 8612 detail
Instance: default, AFI: mpls, SAFI: unicast
8612
Source: isis, Preference: 18
Next Hop: fe80::78fc:daff:fec0:1
Covering prefix: fe80::78fc:daff:fec0:1/128
Next Hop type: mpls php, Next Hop action: mpls label pop - next protocol ipv6
Resolved in: default-ipv6-labeled-unicast
Egress interface: hostif-0/0/1/0, NextHop MAC: 7a:fc:da:c0:00:01Summary
This module outlined how to configure MPLS SR using Extensions of IS-IS. You should be familiar with the various types of segments and their operation.
If you have completed the exercise, you can check the results by executing
student@tour:~/trainings_resources/robot$ robot mpls_sr_isis/mpls_sr_isis_verify.robot