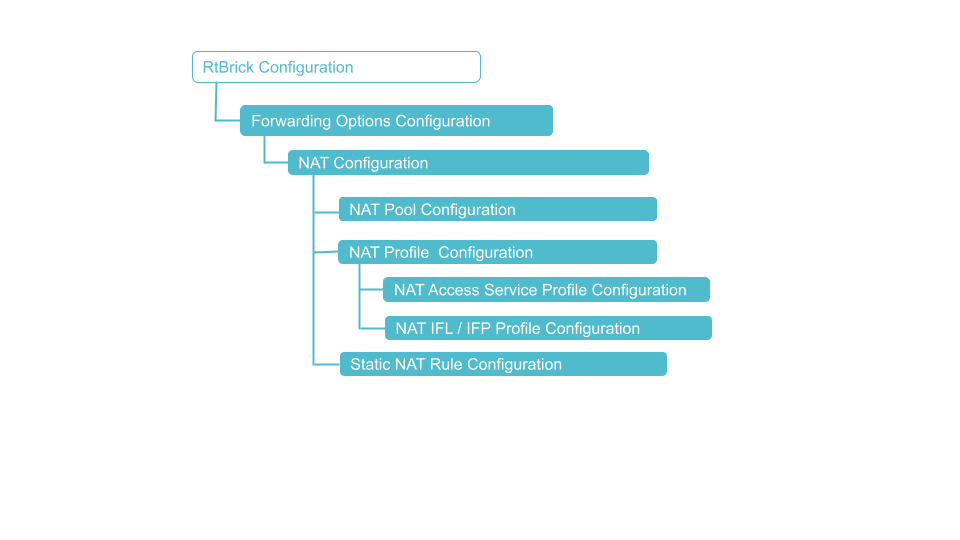
Carrier Grade NAT Configuration
CG NAT Configuration
You must perform the following tasks to configure CG NAT.
-
Configure NAT Service Profile
-
Configure NAT Profile
-
Configure NAT Pool
-
Configure NAT Port Block Size
-
Configure NAT Rule
Configuration Syntax and Commands
The following sections describe the CG NAT configuration syntax and commands.
Configuring NAT Service
Syntax:
set access service-profile <profile-name> <option>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
profile-name |
Name of the NAT service profile. |
acl |
Subscriber ACL related attributes |
address-translation |
Configure NAT for subscriber |
http-redirect |
HTTP redirect related attributes |
igmp |
IGMP related attributes |
qos |
QoS related attributes |
Configuring NAT Profile
A NAT profile defines how the NAT device has to perform the IP address translation. NAT profile allows you to define an instance, IP address pools, maximum number of translations, port block size and mapping a particular internal IP address with a particular external IP address for a deterministic address translation.
You can create NAT profile for an RBFS instance using the 'instance' option. Also, you can define the TCP or UDP traffic type for the profile.
arge groups of translation addresses using large-scale NAT (LSN) pools and grouping of address-translation-related options
Syntax:
set forwarding-options address-translation profile <profile-name> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
profile-name |
Specify the NAT profile name. |
instance |
Specify the instance. |
ip-protocol |
Specify the protocol: TCP or UDP. |
max-rules |
Specify the maximum number of translations for an interface. Supported port block sizes include 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, and 2048. |
pool |
Specify the name of the public IP address pool. |
The following commands configure the NAT profile named nat_profile1. The nat profile nat_profile1 is configured on the instanced vrf1 with a pool attached nataddr_pool1.
set forwarding-options address-translation profile nat_profile1 set forwarding-options address-translation profile nat_profile1 instance vrf1 set forwarding-options address-translation profile nat_profile1 pool nataddr_pool1 set forwarding-options address-translation profile nat_profile1 max-rules 100 set forwarding-options address-translation profile nat_profile1 ip-protocol TCP ageing-timeout 600 set forwarding-options address-translation profile nat_profile1 ip-protocol UDP ageing-timeout 300 set forwarding-options address-translation profile nat_profile1 ip-protocol ALL ageing-timeout 300
Example Configuration:
supervisor@rtbrick>cbng1.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options address-translation profile
{
"rtbrick-config:profile": [
{
"profile": "nat_profile1",
"instance": "vrf1",
"pool": "nataddr_pool1",
"max-rules": "100",
"ip-protocol": {
"TCP": {
"ageing-timeout": 600
},
"UDP": {
"ageing-timeout": 300
},
"ALL": {
"ageing-timeout": 300
}
}
}
]
}
NAT Pool Configuration
IP address pools include a set of IP addresses used for Network Address Translation. You can create public IPv4 address pools. These pools allocate IP addresses to the subscribers when the address translation occurs. One pool includes a group of public IPv4 addresses. While configuring a pool, you can define the group of public IPs belonging to that pool by specifying the lowest and highest IP addresses.
The system allows you to create multiple pools and define the association among them. You can define the next pool that takes over when the current pool gets exhausted with the IP addresses. When one pool gets exhausted, the next pool takes over and starts serving the IP addresses to subscribers when the address translation occurs.
In addition, you can define the port block allocation by specifying the port block size for that pool. So, each public IP in the pool can be allocated a certain number of ports based on the port block size defined.
Syntax:
set forwarding-options address-translation pool <pool-name> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<pool-name> |
Name of the address pool |
ipv4-address |
Configure IPv4 address pool. |
high |
Specify the highest IPv4 address in the address pool. You must specify the highest IP address in the range of IP addresses. |
low |
Specify the lowest IPv4 address in the address pool. You must specify the lowest IP address in the range of IP addresses. |
next-pool-name |
Specify the name of the next address pool that is to be used if this address pool is allocated completely. |
port-block-size |
The number of ports allocated in a block. The default value is 256. For information, about port block allocation, see … |
Example Configuration:
The following commands configure nataddr_pool1, the next pool nataddr_pool2, and port block size as 1024. The lowest IP address is 100.100.100.1 and the highest is 100.100.100.5.
set forwarding-options address-translation pool nataddr_pool1 set forwarding-options address-translation pool nataddr_pool1 next-pool-name nataddr_pool2 set forwarding-options address-translation pool nataddr_pool1 port-block-size 1024 set forwarding-options address-translation pool nataddr_pool1 ipv4-address low 100.100.100.1 set forwarding-options address-translation pool nataddr_pool1 ipv4-address high 100.100.100.5
Example Configuration:
supervisor@rtbrick: cfg> show config forwarding-options address-translation pool
{
"rtbrick-config:pool": [
{
"pool-name": "nataddr_pool1",
"next-pool-name": "nataddr_pool2",
"port-block-size": "1024",
"ipv4-address": {
"low": "100.100.100.1",
"high": "100.100.100.5"
}
]
}
NAT Rule Configuration
A NAT rule defines a match condition and a corresponding action. After you specify NAT rules, each packet is matched with each NAT rule. If a packet matches the condition specified in a rule, then the action corresponding to that match occurs. Match rules govern how the translation of private IP addresses to public IP addresses is performed.
With NAT rules, you can define how address translation is applied to traffic, and how to handle various protocols and data traffic, such as TCP and UDP, to ensure proper address translation and the mappings of internal addresses to external addresses.
Rules also define how inbound and outbound traffic is handled, how different protocols are handled, and how to handle various protocols, and data traffic such as TCP, UDP to ensure the proper address translation of traffic.
Syntax:
set forwarding-options address-translation rule <rule-name> ordinal <ordinal-value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<rule-name> |
Specify the name of the rule. |
<ordinal-value> |
Specify the ordinal value. An ordinal value is a numerical representation that indicates its relative position or order. |
instance |
Configure NAT for an instance. |
ip-protocol |
Specify UDP or TCP. |
local |
Specify the private IPv4 address that needs to be translated. |
public |
Specify the public IPv4 address. This public IP will be mapped with the private IP in the translation table. |
Port Block Size Configuration
You can configure port block size for an IP address pool. Based on the block size set, the number of ports is allocated.
Syntax:
set forwarding-options address-translation pool <pool-name> port-block-size <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<pool-name> |
Specify the name of the pool. |
port-block-size |
Specify the value. Supported values include 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, and 2048. |
The following commands configure the public IP pool nataddr_pool10 and port-block-size as 2048. The IP pool includes includes public IP that begins with 100.100.102.51 and 100.100.102.100.
set forwarding-options address-translation pool nataddr_pool10 set forwarding-options address-translation pool nataddr_pool10 port-block-size 2048 set forwarding-options address-translation pool nataddr_pool10 ipv4-address low 100.100.102.51 set forwarding-options address-translation pool nataddr_pool10 ipv4-address high 100.100.102.100
supervisor@rtbrick>ec24.q2c.u9.r2.nbg.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config forwarding-options address-translation pool nataddr_pool10
{
"rtbrick-config:pool": [
{
"pool-name": "nataddr_pool10",
"port-block-size": "2048",
"ipv4-address": {
"low": "100.100.102.51",
"high": "100.100.102.100"
}
}
]
}
NAT Access Service Profile Configuration
Syntax:
set access interface [double-tagged | single-tagged | untagged] <interface-name> <outer-vlan-min> <outer-vlan-max> <inner-vlan-min> <inner-vlan-max> service-profile-name nat_service
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
service-profile |
Configure global service profile. |
<outer-vlan-min> |
Specify the value for the outer VLAN minimum. Range: 1 - 4094. |
<outer-vlan-max> |
Specify the value for the outer VLAN maximum. Range 1 - 4094. |
<inner-vlan-min> |
Specify the value for the inner VLAN minimum. Range: 1 - 4094. |
<inner-vlan-max> |
Specify the value for the inner VLAN maximum. Range 1 - 4094. |
service-profile-name |
Specify the name of the service profile. |
nat_service |
Service profile name. |
The following commands configure interface as double-tagged ifp-0/0/17 and outer VLAN minimum value is 1000, maximum value as 1007, inner VLAN minimum value as 84 and maximum value as 4084.
set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/17 1000 1007 84 4084 set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/17 1000 1007 84 4084 access-type IPoE set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/17 1000 1007 84 4084 access-profile-name ipoe set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/17 1000 1007 84 4084 service-profile-name nat_service set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/17 1000 1007 84 4084 aaa-profile-name ipoe-aaa set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/17 1000 1007 84 4084 gateway-ifl lo-0/0/0/100 set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/16 1000 1007 84 4084 set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/16 1000 1007 84 4084 access-type PPPoE set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/16 1000 1007 84 4084 access-profile-name pppoe set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/16 1000 1007 84 4084 service-profile-name nat_service set access interface double-tagged ifp-0/0/16 1000 1007 84 4084 aaa-profile-name ipoe-aaa
{
"rtbrick-config:interface": {
"double-tagged": [
{
"interface-name": "ifp-0/0/16",
"outer-vlan-min": 1000,
"outer-vlan-max": 1007,
"inner-vlan-min": 84,
"inner-vlan-max": 4084,
"access-type": "PPPoE",
"access-profile-name": "pppoe",
"service-profile-name": "nat_service",
"aaa-profile-name": "ipoe-aaa"
},
{
"interface-name": "ifp-0/0/17",
"outer-vlan-min": 1000,
"outer-vlan-max": 1007,
"inner-vlan-min": 84,
"inner-vlan-max": 4084,
"access-type": "IPoE",
"access-profile-name": "ipoe",
"service-profile-name": "nat_service",
"aaa-profile-name": "ipoe-aaa",
"gateway-ifl": "lo-0/0/0/100"
}
]
}
}