Protocol Configurations
This validated solution design topology uses IS-IS as the interior gateway protocol to distribute IP routing information among the routers in an Autonomous System (AS). The Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) is used to exchange label mapping information for MPLS traffic. And, iBGP is used for exchanging routing and reachability information within ASs.
One thus needs to configure the following protocols:
-
IS-IS: To ensure IP connectivity on the core network.
-
LDP: To establish MPLS LSP tunnels for MPLS data transmission on the network.
-
iBGP: To exchange routing information within an AS.
Configure IS-IS
The following steps provide the commands to execute various IS-IS protocol functionalities. For more detailed information about IS-IS configuration, see the IS-IS User Guide.
-
Configure IS-IS system-id, area, hostname and interfaces.
set instance default protocol isis system-id 1920.0000.2064 set instance default protocol isis area 49.0001/24 set instance default protocol isis hostname C-BNG set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/1/31/10 set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/1/31/10 type point-to-point set instance default protocol isis interface ifl-0/1/31/10 level-2 adjacency-disable true set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/1/0 set instance default protocol isis interface lo-0/0/1/0 passive true commit
IS-IS instance configuration on interface is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show config instance default protocol isis
{
"rtbrick-config:isis": {
"system-id": "1920.0000.2064",
"area": [
"49.0001/24"
],
"hostname": "C-BNG",
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/1/31/10",
"type": "point-to-point",
"level-2": {
"adjacency-disable": "true"
}
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/1/0",
"passive": "true"
}
]
}
}
Configure LDP on the Interfaces
The following steps provide the commands to execute various LDP functionalities. For more detailed information about LDP configuration, see LDP User Guide.
-
Configure LDP on the router interface.
set instance default protocol ldp router-id 192.0.2.64 set instance default protocol ldp interface ifl-0/1/31/10 set instance default protocol ldp interface lo-0/0/1/0 commit
Configuration for LDP on the interface is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp
{
"rtbrick-config:ldp": {
"router-id": "192.0.2.64",
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/1/31/10"
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/1/0"
}
]
}
}
Configure BGP
The following steps provide the commands to execute the various BGP functionalities quickly. For more detailed information about BGP configuration, see the BGP User Guide.
-
Configure BGP local AS, router-id, and hostname
set instance default protocol bgp local-as 4200000001 set instance default protocol bgp router-id 192.0.2.64 set instance default protocol bgp hostname C-BNG commit
BGP local AS, router-id, and hostname configurations are shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp
{
"rtbrick-config:bgp": {
"local-as": 4200000001,
"hostname": "C-BNG",
"router-id": "192.0.2.64",
<....>
-
Enable the IPv4 and IPv6 address families which are to be supported on the specific BGP instance.
set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast resolve-nexthop safi labeled-unicast set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv6 unicast resolve-nexthop safi labeled-unicast commit
BGP address family configuration is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp address-family
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"resolve-nexthop": {
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
}
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"resolve-nexthop": {
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
}
}
]
}
-
Create the peer group with the specific remote AS configurations and the address family that is to be negotiated with the peer which will be attached to the peer group later.
set instance default protocol bgp peer-group RR set instance default protocol bgp peer-group RR remote-as 4200000001 set instance default protocol bgp peer-group RR address-family ipv4 unicast set instance default protocol bgp peer-group RR address-family ipv6 labeled-unicast set instance default protocol bgp peer-group RR address-family ipv6 unicast commit
BGP peer-group configuration is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer-group
{
"rtbrick-config:peer-group": [
{
"pg-name": "RR",
"remote-as": 4200000001,
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
},
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast" }
]
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
-
Add a BGP peer and associate it with the specific peer group.
set instance default protocol bgp peer set instance default protocol bgp peer ipv4 198.51.100.3 192.0.2.64 set instance default protocol bgp peer ipv4 198.51.100.3 192.0.2.64 peer-group RR commit
Configuration for adding a BGP peer and associating it with a peer group is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer
{
"rtbrick-config:peer": {
"ipv4": [
{
"peer-address": "198.51.100.3",
"update-source": "192.0.2.64",
"peer-group": "RR"
}
]
}
}
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
-
Configure the IPv6 unicast address family with
send-labelas true, then address-family IPv6 labeled-unicast gets negotiated with the peer.
set instance default protocol bgp peer-group RR address-family ipv6 unicast send-label true commit
The following configuration shows the BGP IPv6 unicast address family with send-label as true.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp peer-group RR address-family ipv6 unicast
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"safi": "unicast",
"send-label": "true"
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
-
Set the resolve-nexthop, if the BGP nexthop attribute of the BGP routes needs to be resolved under ipv4/ipv6 labeled-unicast routing table. It configures only resolve-nexthop safi. Based on the nexthop-type (ipv4 or ipv6), it gets looked up into either IPv4 labeled-unicast or IPv6 labeled-unicast.
set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast resolve-nexthop safi labeled-unicast commit
Resolve nexthop configuration is shown below:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast resolve-nexthop
{
"rtbrick-config:resolve-nexthop": {
"safi": "labeled-unicast"
}
}
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
-
To redistribute the routes (belonging to a specific source) into BGP, execute the following command. The following command redistributes
directroutes into BGP.
set instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute direct commit
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg> show config instance default protocol bgp address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute
{
"rtbrick-config:redistribute": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: cfg>
Configuring the Service Node
Configuring Interfaces on the Service Node for RADIUS Connectivity from C-BNG
To configure interfaces on the Service Node for RADIUS connectivity from C-BNG, enter the following commands:
sudo ip link add link SN1-3-C1 name SN1-3-C1.100 type vlan id 100 sudo ifconfig SN1-3-C1.100 192.0.2.34/27
SN1-3-C1 is the internal nomenclature that denotes the interface name on Service Node that connects to the C-BNG.
|
Configuring Interfaces on the Service Node for NTP and TACACS Connectivity from C-BNG
To configure interfaces on the Service Node for NTP and TACACS connectivity from C-BNG, enter the following commands:
sudo ip link add link SN1-3-C1 name SN1-3-C1.200 type vlan id 200 sudo ifconfig SN1-3-C1.200 192.0.2.98/27 sudo ifconfig lo:1 192.0.2.129 netmask 255.255.255.255 up sudo ifconfig lo:2 192.0.2.130 netmask 255.255.255.255 up
Configuring Routes on the Service Node
To configure routes on the Service Node that provides reachability to the RADIUS, TACACS and NTP servers, enter the following commands:
sudo ip route add 192.0.2.74/32 via 192.0.2.33 sudo ip route add 192.0.2.131/32 via 192.0.2.97 sudo ip route add 192.0.2.128/32 via 192.0.2.97
BNG Blaster Configuration for Protocols
BNG Blaster is an open-source network testing platform for access and routing protocols. It can emulate massive PPPoE and IPoE (DHCP) subscribers including IPTV, and L2TP (LNS). There are various routing protocols supported such as IS-IS and BGP. So, one can use this platform for end-to-end BNG and non-BNG router testing.
For more information about BNG Blaster, see https://github.com/rtbrick/bngblaster
For information about installing BNG Blaster, see https://rtbrick.github.io/bngblaster/install.html
Downloading the Blaster Configuration File
The following is the configuration file that is used in BNG Blaster for validating PPPoE, BGP, IS-IS, and LDP.
Click here to download the BNG Blaster configuration file (blaster.json).
Generating Supporting Files for Protocols
-
Generating BGP Internet Prefixes
Enter the following commands to generate BGP internet prefixes.
bgpupdate -f internet.bgp -a 4200000001 -n 198.51.100.2 -N 1 -p 172.16.0.0/24 -P 1000000 bgpupdate -f internet.bgp -a 4200000001 -n 198.51.100.2 -N 1 -p 2004::/48 -m 10000 -M 5 -P 150000 --append
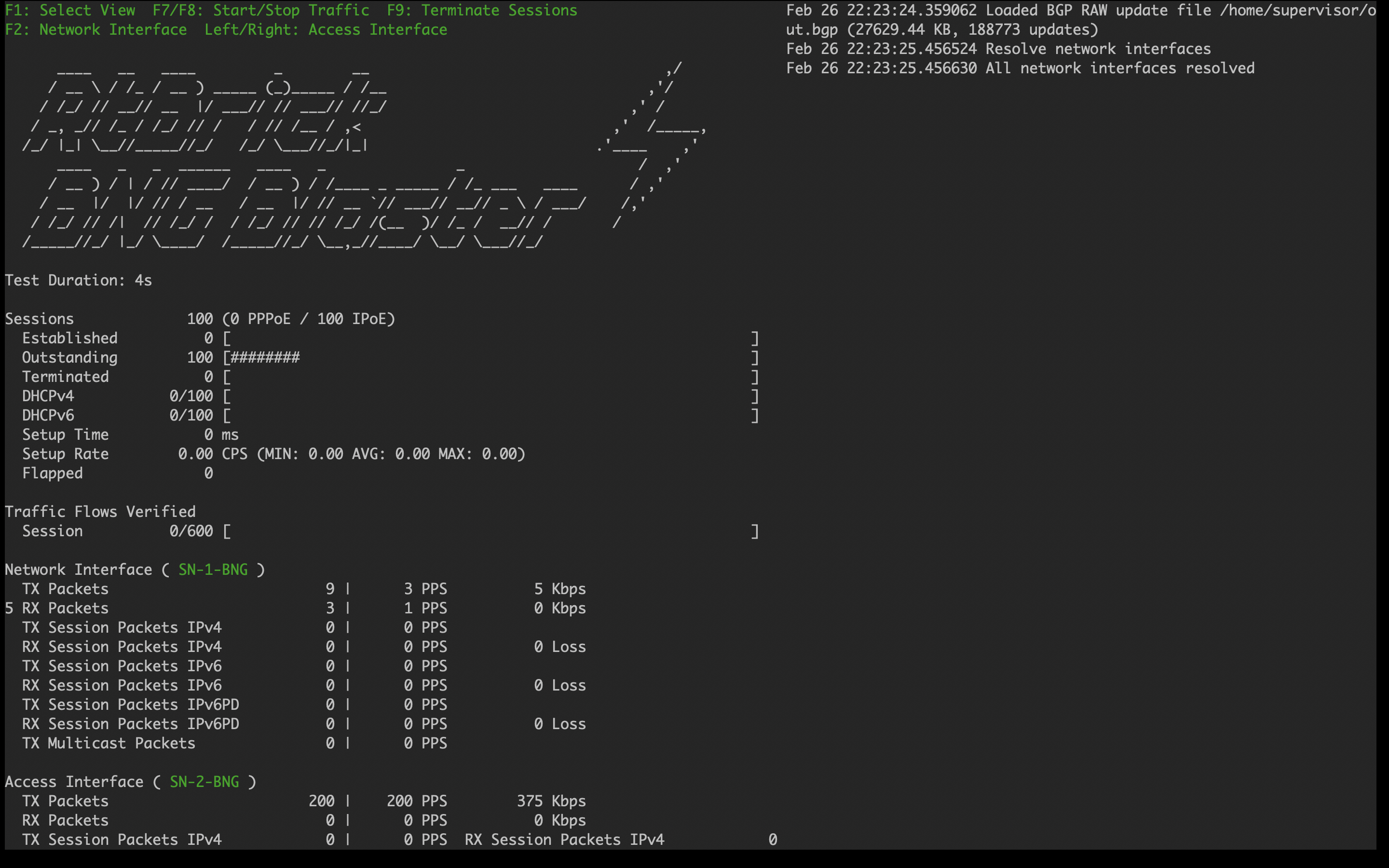
Ensure that the command execution has finished (as shown below) before continuing.
[2023-04-05 10:19:32][INFO ] init 1000000 IPv4 prefixes [2023-04-05 10:19:56][INFO ] open file internet.bgp (replace) [2023-04-05 10:25:31][INFO ] finished
After the generation of the internet.bgp file, the "raw-update-file" attribute of the blaster.json file needs to be updated as follows:
"raw-update-file": "/home/supervisor/internet.bgp"
| For more information about downloading the blaster.json file, see section Downloading the Blaster Configuration File. |
-
Generating MRT FIle for IS-IS
Below is the JSON file (isis_3node.json) which is used to simulate R-1, R-2, and RR on BNG Blaster.
Click here to download the` isis_3node.json` file.
This JSON file needs to be converted to MRT format using the following command:
lspgen -r isis_3node.json -m isis.mrt
After converting the file to isis.mrt, it needs to be updated in the IS-IS section in the blaster.json file as shown below.
"mrt-file": "/home/supervisor/isis.mrt"
-
Generate labels for the IS-IS prefixes using "ldpupdate" command as shown below:
ldpupdate -l 192.0.2.65 -p 198.51.100.1/32 -P 3 -M 3 -f out.ldp
The detail of the generated file needs to be added to the LDP section in the blaster.json file as shown below:
"raw-update-file": "/home/supervisor/out.ldp"
Validating Protocols on RBFS Consolidated BNG
Validating IS-IS Adjacency, Routes and Reachability
Run the following command to show IS-IS adjacency.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show isis neighbor
Instance: default
Interface System Level State Type Up since Expires
ifl-0/1/31/10 BNG-Blaster L1 Up P2P Wed Mar 29 05:23:24 in 22s 242106usAfter configuring IS-IS protocol, check the IPv4 unicast routes, populated by IS-IS using the following command:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show route ipv4 unicast source isis instance default
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: unicast
Prefix/Label Source Pref Next Hop Interface
192.0.2.2/27 isis 15 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
192.0.2.65/32 isis 15 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
198.51.100.1/32 isis 15 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
198.51.100.2/32 isis 15 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
198.51.100.3/32 isis 15 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
198.51.100.101/31 isis 15 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
198.51.100.103/31 isis 15 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
198.51.100.105/31 isis 15 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10Ping the address 192.0.2.65 as follows:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> ping 192.0.2.65 68 bytes from 192.0.2.65: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=9.0436 ms 68 bytes from 192.0.2.65: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=2.0959 ms 68 bytes from 192.0.2.65: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=4.7229 ms 68 bytes from 192.0.2.65: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=9.2496 ms 68 bytes from 192.0.2.65: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=2.6149 ms Statistics: 5 sent, 5 received, 0% packet loss
Validating LDP Adjacency, Routes and Reachability
Run the following commands to show LDP neighbor and LDP session.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show ldp neighbor
Instance: default
Interface LDP ID Transport IP Up Since Expires
ifl-0/1/31/10 192.0.2.65:0 192.0.2.65 Wed Mar 29 05:21:11 in 11ssupervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show ldp session
Instance: default
LDP ID Peer IP State Up/Down FECRcvd FECSent
192.0.2.65:0 192.0.2.65 Operational 0d:03h:55m:49s 5 5After configuring the LDP protocol, check the IPv4 labeled unicast routes, populated by LDP using the following command:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show route ipv4 labeled-unicast source ldp
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: labeled-unicast
Prefix/Label Source Pref Next Hop Interface Label
192.0.2.2/27 ldp 9 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10 -
192.0.2.65/32 ldp 9 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10 -
198.51.100.1/32 ldp 9 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10 10000
198.51.100.2/32 ldp 9 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10 10001
198.51.100.3/32 ldp 9 192.0.2.2 ifl-0/1/31/10 10002Ping the labeled unicast address 198.51.100.1 as follows:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> ping 198.51.100.1 instance default afi ipv4 safi labeled-unicast 68 bytes from 198.51.100.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=6.3289 ms 68 bytes from 198.51.100.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=2.8249 ms 68 bytes from 198.51.100.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.8587 ms 68 bytes from 198.51.100.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=5.9599 ms 68 bytes from 198.51.100.1: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=4.3811 ms Statistics: 5 sent, 5 received, 0% packet loss
The command argument labeled-unicast takes the ICMP requests through a labeled path while validating IP connectivity and hence, it prepends an MPLS label.
|
Validating BGP Adjacency, Routes and Reachability
Run the following commands to show BGP session and state.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show bgp peer
Instance: default
Peer Remote AS State Up/Down Time PfxRcvd PfxSent
198.51.100.3 4200000001 Established 0d:00h:01m:24s 1150000 5After configuring BGP, check the IPv4 unicast routes, populated by BGP using the following command:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show route ipv4 unicast source bgp instance default
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: unicast
Prefix/Label Source Pref Next Hop Interface
172.16.0.0/24 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
172.16.1.0/24 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
172.16.2.0/24 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
172.16.3.0/24 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
172.16.4.0/24 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
172.16.5.0/24 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
172.16.6.0/24 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
172.16.7.0/24 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
172.16.8.0/24 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
172.16.9.0/24 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
<...>This command will list all the 1 million IPv4 BGP internet prefixes.
Pinging an IPv4 route (source: bgp) from the C-BNG.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> ping 172.16.1.0 68 bytes from 172.16.1.0: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=6.0527 ms 68 bytes from 172.16.1.0: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=6.2893 ms 68 bytes from 172.16.1.0: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=2.5573 ms 68 bytes from 172.16.1.0: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=4.6964 ms 68 bytes from 172.16.1.0: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=5.6455 ms Statistics: 5 sent, 5 received, 0% packet loss
Check the IPv6 unicast routes, populated by BGP using the following command:
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> show route ipv6 unicast source bgp instance default
Instance: default, AFI: ipv6, SAFI: unicast
Prefix/Label Source Pref Next Hop Interface
2004::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:1::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:2::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:3::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:4::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:5::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:6::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:7::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:8::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:9::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:a::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:b::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:c::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:d::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:e::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
2004:0:f::/48 bgp 200 198.51.100.2 ifl-0/1/31/10
<...>Pinging an IPv6 route (source: bgp) from the C-BNG.
supervisor@rtbrick>C-BNG.rtbrick.net: op> ping 2004:0:1:: 68 bytes from 2004:0:1::: icmp_seq=1 ttl=253 time=10.0398 ms 68 bytes from 2004:0:1::: icmp_seq=2 ttl=253 time=2.9673 ms 68 bytes from 2004:0:1::: icmp_seq=3 ttl=253 time=6.2365 ms 68 bytes from 2004:0:1::: icmp_seq=4 ttl=253 time=7.9022 ms 68 bytes from 2004:0:1::: icmp_seq=5 ttl=253 time=1.5511 ms Statistics: 5 sent, 5 received, 0% packet loss