EVPN VPWS Configuration
Configuration Hierarchy
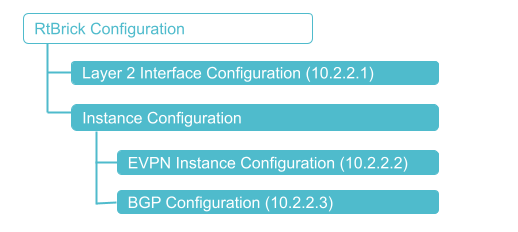
The diagram illustrates the EVPN-VPWS configuration hierarchy. All EVPN VPWS configurations are done within an instance, such as the default instance or an EVPN service instance.
Configuration Syntax and Commands
The following sections describe the EVPN-VPWS configuration syntax and commands.
Layer 2 Interface Configuration
EVPN-VPWS supports the configuration of Layer 2 logical interfaces.
Syntax:
set interface <name> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<name> |
Specify the name of the interface. Example: ifp-0/0/1. |
unit <unit-id> |
Create a logical interface (also referred to as a sub-interface) under the physical interface |
unit <unit-id> interface-type l2vpn-vpws |
Specify the type of the L2VPN interface. |
unit <unit-id> vlan <outer-vlan-id> |
Outer VLAN ID. |
unit <unit-id> instance <instance> |
Assign the logical interface to an instance. |
The following example shows an untagged interface configuration:
set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 0 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 0 interface-type l2vpn-vpws set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 0 instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 commit
The following example shows a single-tagged interface configuration:
set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 100 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 100 interface-type l2vpn-vpws set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 100 instance evpn-vpws-vrf2 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 100 vlan 100 commit
The following example shows a double-tagged interface configuration:
set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 200 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 200 interface-type l2vpn-vpws set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 200 instance evpn-vpws-vrf3 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 200 vlan 200 set interface ifp-0/0/17 unit 200 inner-vlan 201 commit
EVPN Instance Configuration
An EVPN Instance (EVI) is a routing and forwarding instance of EVPN that covers all the participating PE routers in a VPN. EVI is configured per customer on the PE routers. Each EVI has a unique route distinguisher and one or more route targets.
Syntax:
set instance <name> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
<name> |
A unique name for the EVPN routing instance. |
||
address-family <afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported value: l2vpn |
||
address-family <afi> <safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: evpn-vpws
|
||
protocol |
Specifies the routing protocol |
||
route-distinguisher <as-number | ipv4-address:id> |
The route distinguisher (RD) uniquely defines routes within an IPv4 network. PE routers use route distinguishers to identify which VPN a packet belongs to. Supported formats are <as-number:id> or <ipv4-address:id>. |
||
ipv4-router-id <ipv4-router-id> |
The router ID of the routing instance. |
||
route-target ( import | export ) <rt-value> |
Route targets (RT) are used to transfer routes between VPN instances. The RT identifies a subset of routes that should be imported to or exported from a particular VPN instance. You can configure an RT for importing or exporting routes or both. |
In the following configuration, VRF instance AFI has been set to AFI: l2vpn and SAFI: evpn-vpws.
set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 ipv4-router-id 192.1.6.3 set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 route-distinguisher 192.1.6.3:65006 set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 address-family l2vpn evpn-vpws set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 address-family l2vpn evpn-vpws route-target import target:192.1.6.0:65006 set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 address-family l2vpn evpn-vpws route-target export target:192.1.6.0:65006 commit
BGP Configuration
BGP L2VPN VFT (Virtual Forwarding Table) Configuration
Syntax:
set instance <name> protocol bgp <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
<name> |
Name of the routing instance |
||
address-family <afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported value: l2vpn |
||
address-family <afi> <safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported value: evpn-vpws
|
||
local-as <as-number> |
The AS number in four-byte format. The numbers allowed are from 1 to 4294967285. |
||
interface <name> |
Interface that is bound to L2VPN |
||
interface <name> local-service-id <local-service-id> |
Specify the local service ID that is used to establish an EVPN PW between two PEs |
||
interface <name> remote-service-id <remote-service-id> |
Specify the remote service ID that is used to establish an EVPN PW between two PEs |
The following example configures evpn-vpws-vrf1 instance for BGP L2VPN.
set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 protocol bgp local-as 65006 set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 protocol bgp address-family l2vpn evpn-vpws set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 protocol bgp address-family l2vpn evpn-vpws interface ifl-0/0/17/0 set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 protocol bgp address-family l2vpn evpn-vpws interface ifl-0/0/17/0 local-service-id 100 set instance evpn-vpws-vrf1 protocol bgp address-family l2vpn evpn-vpws interface ifl-0/0/17/0 remote-service-id 101 commit
BGP L2VPN EVPN Configuration
Configuring the BGP L2VPN EVPN Address Family
Syntax:
set instance <name> protocol bgp address-family l2vpn evpn
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<name> |
Name of the routing instance |
To configure BGP L2VPN EVPN on the default instance, enter the following command:
set instance default protocol bgp address-family l2vpn evpn commit
Configuring Address Families for Peer Groups
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol bgp peer-group <pg-name> address-family <afi> <safi> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported value: l2vpn. |
<safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported value: evpn |
extended-nexthop |
Enable extended-next-hop encoding for BGP peer groups to allow the transfer of IPv4 prefixes over an IPv6 connection. |
update-nexthop ( ipv4-address | ipv6-address ) <address> |
BGP nexthop address for routes advertised to this peer group |
To configure BGP L2VPN Peer Group on the default instance, enter the following command:
set instance default protocol bgp peer-group spine address-family l2vpn evpn commit