RBFS Carrier-Grade Network Address Translation
Carrier-Grade NAT Overview
The rise of technologies and the rapid growth of mobile devices and cloud services worldwide resulted in the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses. Broadband service providers face a growing challenge as this 32-bit address is insufficient to meet the ever-growing demand and the cost of obtaining public IP addresses for every individual subscriber. Though the launch of IPv6 can address the IPv4 depletion problem, migrating to an IPv6 network becomes vastly complex and costly. IPv6 also does not provide backward compatibility with IPv4. Consequently, migrating to IPv6 is not an ideal solution for many broadband service providers.
RBFS Carrier Grade Network Address Translation (CG NAT) is a prominent technology solution that addresses the IPv4 exhaustion challenge of service providers. The solution helps to use private network addresses and to limit the use of publicly routable IPv4 addresses significantly.
Carrier-grade NAT allows service providers to provide triple-play services to a large number of their subscribers using a limited number of public IP addresses. It saves costs on public IPv4 addresses and conserves their IP pools.
The following diagram illustrates a high-level view of Carrier-Grade Network Address Translation.
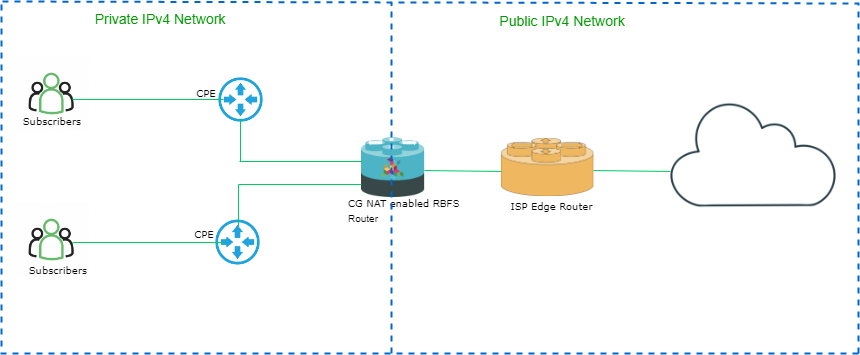
RBFS CG NAT Benefits
RBFS Carrier-grade NAT allows service providers to provide triple-play services to a large number of their subscribers using a limited number of public IP addresses.
Performance at Carrier-Grade
RBFS CG NAT is a solution that implements the functions of network address translation in the network of service providers. Service providers deploy NAT in a way that allows multiple subscribers to share a single global IP address and scale to several thousands of NAT translations, making it carrier-grade NAT. The solution offers carrier-grade scalability with fast translation rates and a large number of IP address and port translations.
Conserve Public IPv4 Addresses
RBFS CG NAT is a centralized address translation solution that can be deployed on the service provider network to stretch the limited pool of public IPv4 addresses even further. The solution helps service providers conserve expensive public IP addresses by enabling multiple customers to share a single public IP address. With NAT, one public IP address can manage hundreds of devices within the private network. It reduces the requirement of continually buying additional public IP addresses.
Enhance Security
In addition to stretching the limited pool of public IPv4 addresses even further, CG NAT also provides significant security benefits. It helps to enhance network security by keeping the internal addressing private from the external network. It makes it difficult for attackers to target specific devices on the network by preventing attacks that target specific IP addresses.
CG NAT also can improve security by providing a level of traffic filtering. The solution can block certain types of traffic from reaching internal devices by preventing all inbound traffic from a specific IP address or range of IP addresses that are associated with malicious activity.
Understanding RBFS CG NAT Implementation
RBFS supports Port Address Translation, also known as Network Address Port Translation (NAPT), which has the greatest potential to conserve IPv4 addresses for service providers. NAPT is known as a cost-effective method to allow multiple devices to connect to the Internet using a single Public IP address.
Network Address Port Translation
Network Address Port Translation (NPAT) is a kind of dynamic NAT in which port numbers are used to distinguish which traffic belongs to which IP address.
NAPT translates the source private IP address and port number to a public source address and port. Multiple source IP addresses can be translated to a single public IP address. PAT works with a single public IP address that is used for all private IP addresses, but a different port number is assigned to each private IP address.
When your device sends a request to the destination server, CG NAT assigns it a unique port number and translates the private IP address of the device into the public IP address. The destination server receives the request and responds to the port number mentioned in the IP header.
Port Block Allocation
Port block allocation (PBA) mode is an address translation option. This mode helps to reduce logging significantly by creating logs only during the allocation and release of each block of ports. The number of log entries is reduced because a log entry is created when the port block is assigned and not for each client connection.
Port block size determines the number of ports allocated in a port set. Port blocks have a fixed size that includes 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, and 2048.
The following table shows the port block size and available ports for a single public IP address in an IP pool for that block size.
Port Block Size |
Available Number Ports |
64 |
1008 |
128 |
504 |
256 |
252 |
512 |
126 |
1024 |
63 |
2048 |
31 |
Port block size allocation determines how many ports are allocated to a group of customers sharing a public IP address. Ports are dynamically assigned from the allocated block as needed. When a customer initiates an outbound connection, the device assigns an available port from the designated block for that customer.
The port block size allocated to each customer can be determined by factors such as the number of customers sharing a single public IP address and the expected volume of concurrent connections. Port block size allocation is customized based on individual customers' specific needs or service plans.
NAT Pool Chaining
A NAT pool contains a range of multiple public IP addresses. You can create multiple pools and associate them with a NAT service. Pool chaining is a method in which you can associate one pool with another. For a pool, you can define 'next pool name'; so that when the pool is exhausted with the IP addresses, the next pool that is defined will take over.
RBFS CG NAT Types
Static NAT
Static NAT associates one private IP address with one public IP address. This is a one-to-one mapping and you must manually define the mapping between a private and public address.
Dynamic NAT
In Dynamic NAT, internal private IP addresses are mapped with a public IP address and this mapping of a private IP address to a public IP address happens dynamically. The router dynamically picks an address from the address pool that is not currently assigned.
NAT44
The NAT44 functionality maps IPv4 subscriber private addresses to IPv4 public addresses. NAT44 is the NAT type that translates private IPv4 addresses into public IPv4 addresses from a specific pool of public IPv4 addresses.
Logging
RBFS CG NAT provides traffic monitoring capabilities to track and log network activities. The solution offers a flexible logging mechanism that can store information such as port numbers, time, destination, and address translation details.