Subscriber Management Configuration Overview
RBFS Subscriber Management configuration involves setting up various profiles and parameters that control how subscribers interact with network services. This includes authentication, service access, protocol handling, and other functions organized under a structured configuration hierarchy. The profiles determine how subscribers authenticate, access network services, and use various protocols. The configuration starts with mandatory settings such as interface, access, and AAA profiles, followed by optional configurations for more features such as RADIUS, L2TP, and service profiles. Each profile plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient and secure subscriber management.
Configuration Hierarchy
The configuration of physical interfaces (IFP) and their associated VLANs is managed through a set of profiles that define parameters for various functions. These include authentication settings with AAA, service management for protocols such as IGMP and MLD, and access protocols such as PPPoE.
The following image illustrates how the subscriber management configuration and profile system are organized.
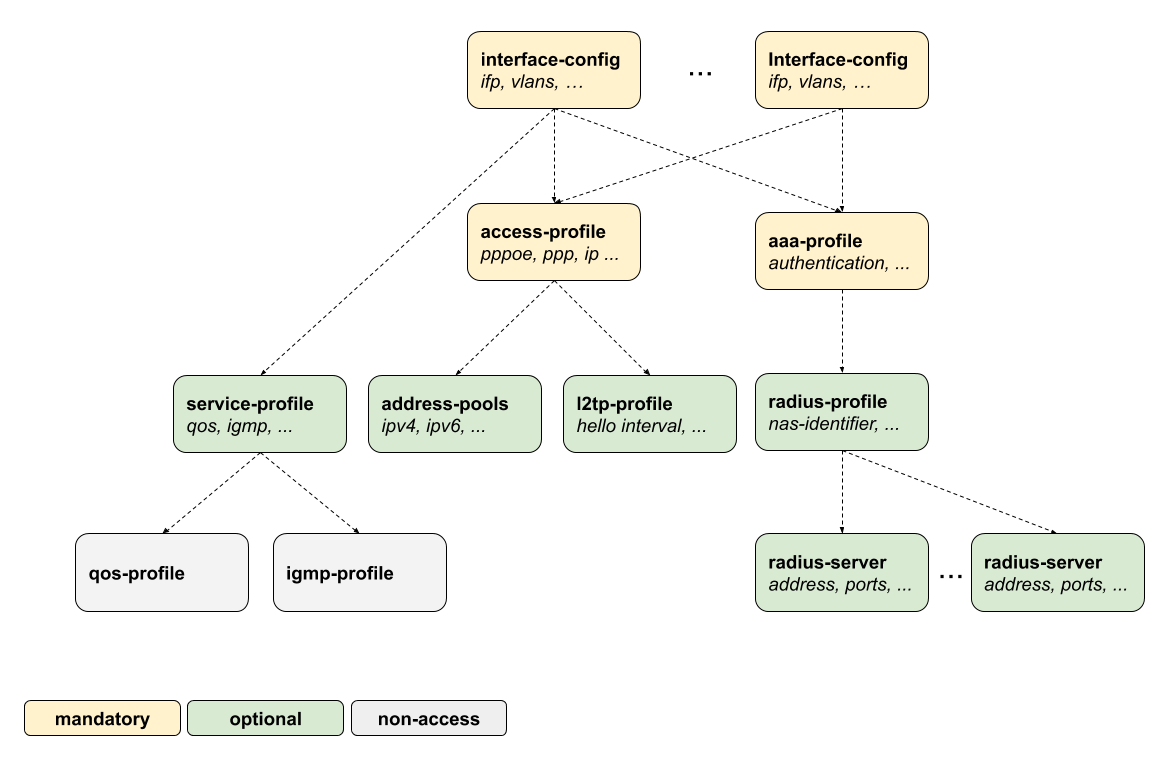
All subscriber management configurations and profiles are managed under the top-level hierarchy access. This hierarchy acts as the central point for defining and managing various access protocols, subscriber management profiles, and authentication settings that are crucial for network operations.
The following is the access command and all the high-level options available for Subscriber Management configurations.
supervisor@switch: cfg> set access <cr> aaa-profile Global AAA profile configuration access-profile Global access profile configuration chassis-id Chassis ID for this node [Range: <0-15>] dhcp-relay Global DHCP relay configuration dhcp-server Global DHCP server configuration dhcpv6-server Global DHCP server configuration interface Global interface profile configuration l2tp-pool Global L2TPv2 pool configuration l2tp-profile Global L2TPv2 profile configuration pool Global address pool configuration radius-profile Global AAA RADIUS profile configuration radius-server Global RADIUS server configuration service-profile Global service profile configuration terminate-history-timeout Terminate history timeout in hours [Range: <0-720>] user-profile Global user profile configuration
The following options can be configured directly at the global access level, rather than within subsections.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
This option must be set to a unique value for each redundancy cluster and is only needed for stateful redundancy. Default: 0 |
|
Change the retention period (in hours) for storing the termination history of subscribers after they have been disconnected. Default: 24 |
In the following sections, you will find comprehensive descriptions and steps for each configuration. The process begins with setting up the access interface configuration, which is the first step. This is then followed by other important access profile and AAA profile configurations, which are crucial for managing subscriber access.
-
interface-config Access Interface Configuration
-
access-profile Access Profile Configuration
-
aaa-profile AAA Profile Configuration
The second part covers the optional configurations:
-
radius-profile RADIUS Profile Configuration
-
radius-server RADIUS Server Configuration
-
service-profile Service Profile Configuration
-
l2tp-profile L2TP Profile Configuration
-
address-pools Address Pool Configuration
The user-profile and l2tp-pool are the only components not referenced by name. The key here is the user or pool name.
-
user-profile User Profile Configuration
-
l2tp-pool L2TP Tunnel Pool Configuration