Introduction to OSPF
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is an Interior Gateway Protocol that distributes routing information within a single Autonomous System (AS) in an IP network. OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that uses link-state information to form a routing table and exchange the routing information with the neighbors.
OSPF routers flood LSAs (link-state advertisements) to all other routers in an autonomous system. Routers generate routing tables using the information received from the LSAs and calculate the best path to other routers in the network. OSPF uses the Dijkstra (Shortest Path First) algorithm to calculate the best path.
LSAs contain local state information such as interfaces and the reachability of neighbors. Other routers, which receive this information as LSAs, build their LSDB (link-state database) using this information. In an OSPF network, all routers build and maintain information about the topology of that network.
Understanding OSPF Areas
OSPF allows for a logical partition of the autonomous system by dividing it into areas. This logical partitioning helps to limit the flooding of link-state updates within an area.
An OSPF Autonomous System can be maintained as a single-area network or can be divided as a multi-area network. In a single area AS, the topology provides link-state information of routers in the entire autonomous system.
While in a multi-area AS, the topology provides the link-state information of routers belonging to that particular area, not about routers in other areas in the autonomous system. Within an area, all OSPF routers maintain separate databases which are identical.
In a multi-area OSPF network, all areas are connected to the backbone area, known as Area 0.
Backbone Area
The backbone area, also known as Area 0, is connected to all other areas in an OSPF network. The backbone area, which acts as a central point of communication, receives LSAs from other areas and disseminates the same to other areas.
Area Border Router
Routers that connect one or more areas with the backbone area are called Area Border Router (ABR). One interface of the ABR is connected to the backbone, while other interfaces are connected to other areas. ABRs, which belong to multiple areas in an OSPF network, maintain separate LSDBs for each area that they are connected to.
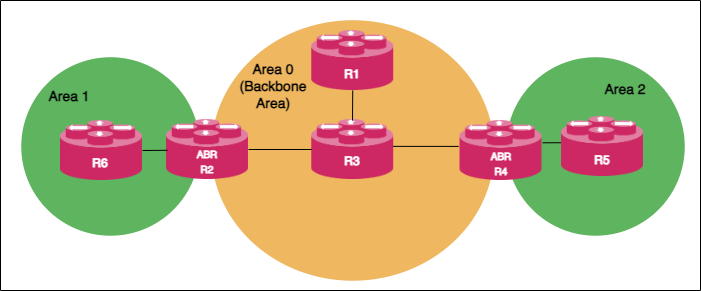
The following OSPF architectural diagram shows a simple OSPF network that is divided into areas. Area 1 and Area 2 are connected to the backbone area (Area 0) through the ABRs. Area 1 and Area 2 are not directly connected. They receive link state advertisements from each other from Area 0 which acts as the central point of communication for all other areas.
Autonomous System Boundary Router
ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router) serves as a gateway router to the OSPF autonomous system. ASBR can operate multiple protocols and work with other autonomous system routers which run other interior gateway protocols such as EIGRP, IS-IS, i-BGP, and so on. ASBR can import and translate different protocol routes into OSPF through the redistribution mechanism.
OSPF DR and BDR Election
An OSPF network chooses one router as a Designated Router (DR) and another as a Backup Designated Router (BDR) for a broadcast network.
DR acts as a central point of communication by receiving and distributing topology information. BDR takes over the role of DR if the DR fails. Routers in an OSPF network do not directly exchange routing information with each other. Instead, every router in the network updates routing information only with DR and BDR. DR, in turn, distributes the topology information with all other routers. This mechanism reduces network traffic significantly. OSPF chooses one router as DR and another router as BDR based on the following criteria:
-
The router with the highest priority value becomes the designated router and the router with the second highest priority value becomes the BDR. You can define the priority values for routers during the interface configuration.
-
If multiple routers have the same highest priority value, then the router with the highest router ID is elected as DR and the router with the second highest router ID value becomes the BDR.
You can choose a priority value from the range 0 - 255. Routers with the priority value '0' do not participate in the DR or BDR election.