LDP-signaled L2VPN Overview
The LDP-signaled L2VPN uses Targeted Label Distribution Protocol (T-LDP) for signaling to establish Pseudowire over the MPLS backbone network. The Pseudowire is a point-to-point (P2P) service that connects two locations using the MPLS core network and uses T-LDP for signaling. The Pseudowire uses MPLS tunnels to traverse the backbone network. It offers a Layer 2 packet forwarding mode that connects attachment circuits (ACs). The RBFS implementation of LDP-signaled L2VPN is in accordance with RFC 4447 which supports L2VPN using LDP for signaling.
Supported Standards
| RFC Number | Description |
|---|---|
4447 |
Pseudowire Setup and Maintenance Using the Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) |
| RFC and draft compliance are partial except as specified. |
LDP-signaled L2VPN Network Model
As shown in the figure below, a LDP-signaled L2VPN network contains the following building blocks:
-
Customer edge (CE)—Customer device directly connected to the service provider network.
-
Provider edge (PE)—Service provider device connected to CEs. PEs provide access to the Pseudowire network and forward traffic between customer network sites by using public tunnels.
-
Attachment circuit (AC)—A physical or virtual link between a CE and a PE.
-
Pseudowire (PW)—A virtual bidirectional connection between two PEs. A PW comprises a pair of virtual links in opposite directions.
-
MPLS transport tunnel—A connection that carries one or more PWs across the MPLS core or IP backbone, such as an MPLS tunnel.
-
Cross-connect—A connection formed by two physical or virtual circuits, such as ACs and PWs, that switches packets between them.
The figure below shows the protocol packet exchange process in the LDP-signaled L2VPN.
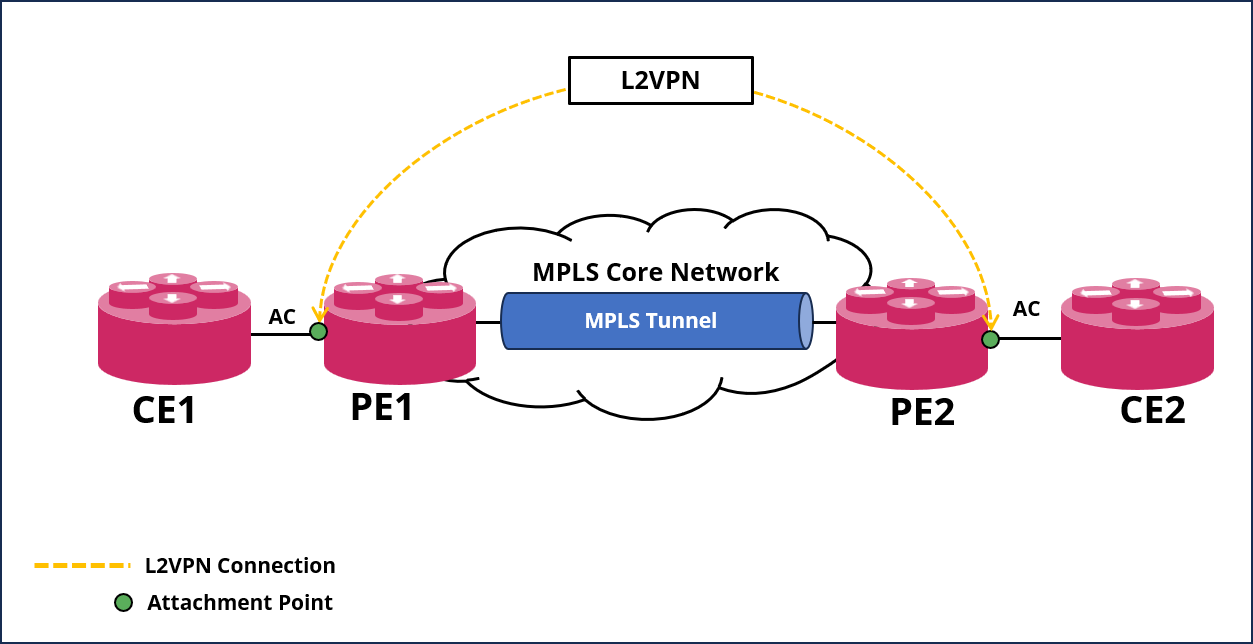
PE1 and PE2 are each configured with a LDP L2VPN instance with T-LDP neighbors to carry the Pseudowire (PW) tunnel information. After the PE receives packets from the AC, it adds the PW label and sends them to the peer PE through the MPLS transport tunnel. After the other PE receives the packet via the MPLS transport path, it removes the PW label of the packets and forwards the packets to the AC bound to the PW.
Pseudowire Redundancy
Pseudowire redundancy is supported only for the Provider Edge (PE) routers.
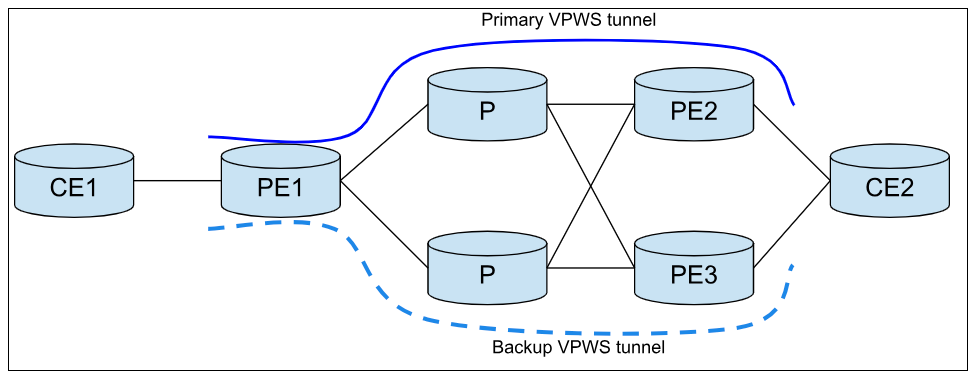
As shown in the figure above, PE1 has two VPWS tunnels. The tunnel from PE1 to PE2 is the primary tunnel, while the tunnel from PE1 to PE3 serves as the backup tunnel. Switching back to the primary pseudowire is not performed even if it recovers.
In the scenario with PE1 and PE2, where P3 acts as redundancy as shown in the diagram above, switching switching is exclusively executed by PE1 when certain conditions are met:
-
The LDP session with the primary remote PE is down.
-
A label withdrawal occurs from PE2.
-
The MPLS tunnel to PE2 is down.
-
The "request switch-over ldp l2vpn" operational command can be entered to switch to the backup PE. For details, see the request switch-over section.
Guidelines and Limitations
-
The
control-wordflag is disabled by default, which can be enabled if required. For more details, see the Configuring LDP-signaled L2VPN section.