1. Overview
Label distribution protocol (LDP) is the most commonly used protocol in the MPLS network. It generates and distributes labels and thus helps in MPLS packet switching and forwarding. By using LDP, label-switching routers in an MPLS network can exchange label mapping information to create label-switched paths (LSPs) for switching data packets. RtBrick FullStack (RBFS) supports Dual-stack, which means LDP can exchange FEC-label bindings over either IPv4 or IPv6 networks.
1.1. Peer Discovery
LDP sends UDP multicast hello packets to discover its neighbors and establishes neighbor adjacency with other directly connected label switch routers (LSRs). The hello message is periodically sent on LDP-enabled interfaces.
1.2. Session Establishment
After peer discovery, “initialization messages” are sent to each other. In these messages, the session Parameters are sent to each other. The LDP sessions are maintained by periodic keep-alive message.
After the LDP neighbors are discovered, the TCP session is established and the LDP FSM is triggered, and LDP session becomes operational. LSRs start exchanging label mapping information with each other.
1.3. Dual-stack LDP
By default, RBFS is dual-stack capable, which means it can exchange IPv4/IPv6 FEC bindings over IPv4/IPv6 media (LDP over IPv4/IPv6).
To enable or disable a particular address family in RBFS, use "status <enable|disable>" CLI. For details, see LDP Address Family Configuration.
When LDP is enabled on an interface that supports both IPv4 and IPv6, LDP will start exchanging IPv4 hellos. To send an IPv6 hello, the source IPv6 address must be configured. For details about configuring the source address, see LDP Instance Configuration.
By default, both IPv4 and IPv6 hello will use the same transport preference as IPv6, but this can be changed by using the "connection-preference <ipv4|ipv6>" CLI. For details, see LDP Instance Configuration.
The following points should be noted regarding this functionality:
Source address:
-
Unless modified, IPv4 and IPv6 hellos will be sent with transport preference as IPv6 when the IPv6 source address is configured.
-
When the IPv6 source address is not configured, only IPv4 hello will be sent with transport-preference IPv4 and still act as a dual-stack router and exchange both IPv4 and IPv6 FEC bindings.
When IPv4 status is disabled:
-
Only IPv6 hello will be sent without Dual-stack TLV.
-
Only IPv6 FEC binding will be exchanged.
When IPv6 status is disabled:
-
Only IPv4 hello will be sent without Dual-stack TLV.
-
Only IPv4 FEC binding will be exchanged.
When both IPv4 and IPv6 statuses are enabled:
-
Both IPv4 and IPv6 hellos will be exchanged (IPv6 source address configuration is mandatory for sending IPv6 hello).
-
By default, the hello message uses IPv6 as the transport preference, unless otherwise specified.
-
Both IPv4 and IPv6 FEC bindings will be exchanged.
1.4. Label Generation
LDP generates label bindings for the IP addresses of the LDP-enabled loopback interfaces and then advertises them to all neighbors.
1.5. Label Management Modes
1.5.1. Label Advertisement Mode
LDP supports the Downstream Unsolicited feature in RBFS, where label bindings are advertised to all upstream neighbors. By default, label advertisement operates in the Downstream Unsolicited mode.
1.5.2. Label Distribution Control Mode
LDP supports the Ordered Label Distribution Control, where an LSR will initiate the transmission of the label mapping only for the prefix for which it has a label mapping from the next hop of the prefix or for which it is an egress.
1.5.3. Label Retention Mode
LDP supports the Liberal Label Retention Mode where all the label mapping advertisements for all routes received from all the LDP neighbors are retained.
1.6. Supported LDP Standards
| RFC Number | Description |
|---|---|
RFC 5036 |
LDP Specification The following modes are supported by RBFS for the features listed in RFC 5036:
|
RFC 5283 |
LDP Extension for Inter-Area Label Switched Paths (LSPs) |
RFC 5443 |
LDP IGP Synchronization |
RFC 7552 |
IPv6 Dual-Stack |
|
|
RFC and draft compliance are partial except as specified. |
1.7. Supported LDP Features
The following LDP features are supported in this release of RBFS:
-
Support for the following label management modes.
-
Downstream unsolicited mode in label advertisement
-
Ordered mode in the label distribution control
-
Liberal mode in label retention
-
-
Loop detection
-
Inter-area support
-
Tracking IGP metric
-
IGP LDP synchronization
-
LDP Dual-stack support
-
LDP TCP authentication
-
LDP redistribution
-
LDP policy configuration
1.8. Supported Platforms
Not all features are necessarily supported on each hardware platform. Refer to the Platform Guide for the features and the sub-features that are or are not supported by each platform.
2. Configuration Hierarchy
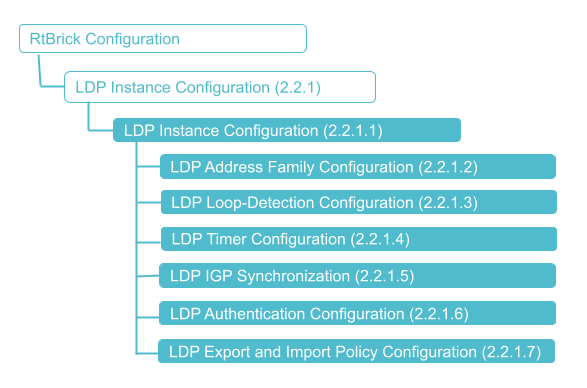
The diagram below illustrates the LDP configuration hierarchy.
2.1. Configuration Syntax and Commands
The following sections describe the LDP configuration syntax and commands.
2.1.1. LDP Instance Configuration
At this configuration hierarchy, you configure LDP protocol parameters which are generic to the LDP instance.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol ldp <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Name of the LDP instance. |
interface <name> |
Name of the logical interface. |
router-id <router-id> |
Router identifier in IPv4 format. |
address-family <afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, or ipv6. Refer to section 2.1.2, “LDP Address Family Configuration” for LDP address family configuration details. |
connection-preference <afi> |
Specifies the connection preference for the TCP session. Supported values: ipv4, or ipv6. By default, IPv6 is used as the preferred TCP connection if an IPv6 source address is configured. Refer to section 1.3, “Dual-stack LDP” for more information on the LDP Dual-stack behaviour. |
igp-synchronization <…> |
LDP IGP synchronization configuration. This option is supported only on interfaces running Intermediate System-to-System (IS-IS) or OSPFv2 processes. Refer to section 2.1.5, “LDP IGP Synchronization” for LDP-IGP synchronization configuration details. |
source-address <ipv4|ipv6> <source-address> |
Use the specified IP addresses (IPv4 or IPv6) as the transport address for the LDP session. For LDP over IPv6, the IPv6 source address is mandatory. Refer to section 1.3, “Dual-stack LDP” for more information on the LDP Dual-stack behavior. |
loop-detection <…> |
The LDP loop detection feature enables LDP to detect loops during an LSP establishment. Refer to section 2.1.3, “LDP Loop Detection Configuration” for the loop detection configuration details. |
timer <…> |
Specifies the Hello hold time, Hello interval, Keepalive hold time, and Keepalive interval. Refer to section 2.1.4, “LDP Timer Configuration” for the LDP timer configuration details. |
peer <ipv4|ipv6> <address> authentication-id <…> |
Specifies an IPv4 or IPv6 LDP peer attributes to apply TCP authentication. Refer to section 2.1.6, “LDP Authentication Configuration”. |
peer <ipv4|ipv6> <address> export-policy|import-policy <…> |
Specifies an IPv4 or IPv6 LDP peer attributes to apply import/export policy configurations. Refer to section 2.1.7, “LDP Import and Export Policy Configuration”. |
Example: LDP Instance Configuration
The following example shows some LDP instance configuration attributes. The further LDP configurations like timers and loop detection are shown in the examples in the subsequent sections.
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp
{
"rtbrick-config:ldp": {
"router-id": "198.51.100.1",
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/0/1"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/0/100"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/0/101"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1/102"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/2/1"
},
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/3/1"
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/0/1"
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/0/2"
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/0/3"
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/0/4"
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/0/5"
}
]
}
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
2.1.2. LDP Address Family Configuration
The address-family command allows you to enable the address families that LDP will route and configure settings that are specific to that address family.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol ldp address-family <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, ipv6 |
<afi> status <enable|disable> |
Enable or disable address family. By default, both IPv4 and IPv6 address families are enabled, as LDP supports dual stack. Refer to section 1.3, “Dual-stack LDP” for more information on the LDP Dual-stack behavior. |
<afi> redistribute <source> |
Specifies the source from which the routes are to be redistributed. The available options include |
<afi> redistribute <source> policy <policy> |
Specifies the name of the policy map. The redistribute attach point allows routes from other sources to be advertised by LDP. The policy can be applied only to the routes that are redistributed from other sources to LDP. |
Example 1: LDP Address Family Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp address-family
{
"rtbrick-config:address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv6",
"status": "disable"
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
Example 2: LDP Redistribution Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp address-family ipv4 redistribution direct
{
"rtbrick-config:redistribution": [
{
"source": "direct"
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
Example 3: LDP Policy Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp address-family ipv4 redistribution
{
"rtbrick-config:redistribution": [
{
"source": "direct",
"policy": "filter-link-addres"
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
2.1.3. LDP Loop Detection Configuration
The LDP loop detection feature enables LDP to detect loops during an LSP establishment.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol ldp loop-detection <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
hop-count <hop-count> |
Specifies the hop count limit for loop detection. Range: 0-255. Default: 32. |
status <enable|disable> |
Enables or disables loop detection. By default, this option is disabled. When this option is enabled, both hop count and path vector are enabled. |
vector-length <vector-length> |
Specifies the path vector length limit for loop detection. Range: 0-255. Default: 32. |
Example 1: LDP Loop Detection Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp loop-detection
{
"rtbrick-config:loop-detection": {
"enable": "true",
"hop-count": 64,
"vector-length": 64
}
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
2.1.4. LDP Timer Configuration
Specify the hello timer and hold-down timer for LDP adjacency. Similarly, specify the keepalive and keepalive timeout settings for the LDP session.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol ldp timer <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
hello hold-time <hold-time> |
Specifies the hello hold-time interval in seconds before declaring a neighbor to be down. Range: 0-65535. Default: 15. |
hello interval <interval> |
Specifies the hello messages interval in seconds. Range: 0-65535. Default: 5. |
session keepalive-interval <keepalive-interval> |
Specifies the session keepalive messages interval in seconds. Range: 1-65535. Default: 10. |
session keepalive-timeout <keepalive-timeout> |
Specifies the session keepalive timeout in seconds before declaring a session to be down. Range: 1-65535. Default: 30. |
Example 1: LDP Timer Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp timer
{
"rtbrick-config:timer": {
"hello": {
"interval": 10,
"hold-time": 20
},
"session": {
"keepalive-interval": 3000,
"keepalive-timeout": 5000
}
}
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
2.1.5. LDP IGP Synchronization
Synchronization between LDP and the underlying interior gateway protocol (IGP) ensures that the LDP path is fully established before the IGP path is used for forwarding traffic. LDP IGP synchronization is supported only on interfaces running Intermediate System-to-System (IS-IS) or OSPFv2 processes.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol ldp igp-synchronization <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
hold-timer <hold-timer> |
Specifies the hold-timer in seconds to limit how long the IGP session must wait before declaring the LDP synchronization. Range: 0-60. Default: 10. |
Example 1: LDP IGP Synchronization Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp igp-synchronization
{
"rtbrick-config:igp-synchronization": {
hold-timer": 60,
}
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
2.1.6. LDP Authentication Configuration
To meet the security requirements of LDP sessions, configure LDP authentication.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol ldp peer ipv4|ipv6 <address> authentication-id <authentication-id>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<address> |
Specifies the transport IP address of the peer. |
<authentication-id> |
Authentication Tuple Identifier |
Example 1: LDP Authentication Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp peer ipv4
{
"rtbrick-config:ipv4": [
{
"address": "192.168.1.2",
"authentication-id": "auth_id_1"
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
2.1.6.1. TCP Authentication Configuration
In the instance TCP authentication hierarchy, you can optionally enable MD5 or HMAC SHA authentication. Authentication is not configured for LDP directly, but for the TCP sessions used by LDP.
Syntax:
set instance <instance> tcp authentication <authentication-id> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<authentication-id> |
Authentication identifier |
type <type> |
Authentication identifier such as MD5 |
key1-id <key1-id> |
Key ID1 of the receiver |
key1-encrypted-text <key1-encrypted-text> |
Encrypted text of key1 |
key1-plain-text <key1-plain-text> |
Plain text of key1 |
key2-id <key2-id> |
Key ID2 of the receiver |
key2-encrypted-text <key2-encrypted-text> |
Encrypted text of key2 |
key2-plain-text <key2-plain-text> |
Plain text of key2 |
Example: LDP TCP Authentication Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default tcp authentication auth_id_1
{
"rtbrick-config:authentication": [
{
"authentication-id": "auth_id_1",
"type": "MD5",
"key1-id": 1,
"key1-encrypted-text": "$2a6fd7db50a18a9f1f16b5c5b4214fab0"
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
2.1.7. LDP Import and Export Policy Configuration
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol ldp peer ipv4|ipv6 <address> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<address> |
Specifies the IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
export-policy <export-policy> |
Export policy identifier |
import-policy <import-policy> |
Import policy identifier |
Example 1: LDP Export Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp peer ipv4
{
"rtbrick-config:ipv4": [
{
"address": "192.168.1.2",
"export-policy": "exp-policy1"
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
Example 3: LDP Import Configuration
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg> show config instance default protocol ldp peer ipv4
{
"rtbrick-config:ipv4": [
{
"address": "192.168.1.2",
"import-policy": "imp-policy1"
}
]
}
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: cfg>
3. LDP Operational Commands
3.1. LDP Show Commands
The LDP show commands provide detailed information about the LDP protocol operations.
3.1.1. LDP Summary
Syntax:
show ldp summary <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, the command displays the LDP summary information for all instances. |
instance <instance-name> |
Displays LDP summary information about the specified instance. |
Example: LDP summary for the default instance
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp summary
Instance: default
General information:
LDP identifier: 198.51.100.1:0, Version: 1
FEC resolution: Best match
Protocol preference: 9
LSR ID: 198.51.100.1
IPv4 Status: True
IPv6 Status: True
Modes:
Advertisement mode: Downstream Unsolicited
Advertisement control mode: Ordered
Label retention mode: Liberal
Capabilities:
IPv6 address family: - , Graceful restart: False
Loop detection: False
Hop count: -, Vector length: -
Timers:
Adjacency:
Hello: 5s, Holdtime: 15s
Targeted adjacency:
Hello: 15s, Holdtime: 45s
Session:
Keepalive: 10s, Holdtime: 30s
Statistics:
Adjacency:
Link adjacency: 5, Targeted adjacency: 0
Session:
Session in non-existent: 0, Session in initialized: 0
Session in opensent: 0, Session in openconfirm: 0
Session in operational: 2
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op>
3.1.2. LDP Neighbor
Syntax:
show ldp neighbor <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays information about LDP neighbors. |
detail |
Detailed information about the LDP neighbors. |
instance <instance-name> |
Displays LDP neighbor information about the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> detail |
Displays detailed LDP neighbor information about the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP neighbor information about the specified LDP identifier and instance. |
interface <name> |
Displays LDP neighbor information about the specified interface. |
interface <name> detail |
Displays detailed LDP neighbor information about the specified interface. |
ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP neighbor information about the specified LDP identifier. |
Example 1: Summary view of LDP Neighbor
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp neighbor Instance: default Interface LDP ID Transport IP Up Since Expires ifl-0/0/0/1 198.51.100.2:0 198.51.100.2 Thu Feb 09 12:17:15 in 11s ifl-0/0/2/1 198.51.100.3:0 198.51.100.3 Thu Feb 09 12:17:31 in 12s ifl-0/0/0/100 198.51.100.2:0 198.51.100.2 Thu Feb 09 12:17:15 in 11s ifl-0/0/0/101 198.51.100.2:0 198.51.100.2 Thu Feb 09 12:17:15 in 11s ifl-0/0/1/102 198.51.100.2:0 198.51.100.2 Thu Feb 09 12:17:15 in 11s supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op>
Example 2: Detailed View of LDP Neighbor
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp neighbor detail Instance: default LDP-Identifier: 198.51.100.2:0, Interface: ifl-0/0/0/1, Type: Link Negotiated holdtime: 15000, Expiry time: 13s 183407us Local link address: 192.0.2.1, Peer link address: 192.0.2.2 Local transport address: 198.51.100.1:0, Peer transport address: 198.51.100.2 Local holdtime: 15, Peer holdtime: 15, Up since: Tue May 02 13:28:17 Local transport preference : ipv4, Peer transport preference : ipv4 Last transition time: Tue May 02 13:38:52 GMT +0000 2023 <...>
3.1.3. LDP Session
Syntax:
show ldp session <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays a summary of LDP session information. |
detail |
Displays detailed information about the LDP sessions. |
instance <instance-name> |
Displays LDP session information about the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> detail |
Displays detailed LDP session information about the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP session information about the specified LDP identifier and instance. |
ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP session information about the specified LDP identifier. |
Example 1: Summary view of LDP Session
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp session Instance: default LDP ID Peer IP State Up/Down FECRcvd FECSent 198.51.100.2:0 198.51.100.2 Operational 0d:00h:29m:44s 15 15 198.51.100.3:0 198.51.100.3 Operational 0d:00h:29m:29s 15 15 supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op>
Example 2: Detailed View of LDP Session
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp session detail
Instance: default
LDP Identifier: 198.51.100.2:0, Peer IP: 198.51.100.2, Local IP: 198.51.100.1
Type: link, State: Operational, Uptime: 0d:00h:34m:35s
Reason:
Last transition: Thu Feb 09 12:17:28 GMT +0000 2023, Flap count: 0
Advertisement Mode:
Peer: Downstream unsolicited, Local: Downstream unsolicited
Negotiated: Downstream unsolicited
Timers:
Connect retry: 10s
Peer keepalive interval: 10s, Local keepalive interval: 10s
Peer keepalive timeout: 30s, Local keepalive timeout: 30s
Negotiated keepalive interval: 10s
Negotiated keepalive timeout: 30s
Received messages:
Initialization: 1, KeepAlive: 208, Notification: 0
Address: 1, Address Withdraw: 0, Label Mapping: 15
Label Withdraw: 0, Label Release: 0
Sent messages:
Initialization: 1, KeepAlive: 208, Notification: 0
Address: 1, Address Withdraw: 0, Label Mapping: 15
Label Withdraw: 0, Label Release: 0
Capability:
Typed WildCard FEC:
Local Support: True, Peer Support: True, Negotiated: True
Total received messages:
Initialization: 1, KeepAlive: 92, Notification: 0
Address: 2, Address Withdraw: 0, Label Mapping: 20
Total sent messages:
Initialization: 1, KeepAlive: 92, Notification: 0
Address: 2, Address Withdraw: 0, Label Mapping: 20
Label Withdraw: 0, Label Release: 0
<...>
3.1.4. LDP Address
Syntax:
show ldp address <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays a summary of all the interface addresses received from the LDP sessions. |
instance <instance-name> |
Displays LDP address information about the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> <afi> |
Displays LDP address of the specified address family (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, ipv6. |
instance <instance-name> ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP address information about the specified LDP identifier and instance. |
ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP address information about the specified LDP identifier. |
Example: Summary View of LDP Address
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp address Instance: default, LDP Identifier: 198.51.100.2:0, AFI: ipv4 198.51.100.61 198.51.100.102 198.51.100.63 198.51.100.94 198.51.100.2 198.51.100.65 198.51.100.222 198.51.100.21 198.51.100.2145 198.51.100.48 <...>
3.1.5. LDP Binding
Syntax:
show ldp binding <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays a summary of all the LDP label bindings. |
instance <instance-name> |
Displays LDP label binding information about the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> prefix <ip> |
Displays LDP label binding information about the specified prefix and instance. Supported prefix values: ipv4, ipv6. |
prefix <ip> |
Displays the LDP label binding information for the specified prefix. Supported prefix values: ipv4, ipv6. |
received |
Displays the LDP received label binding information of the LDP sessions. |
received instance <instance-name> |
Displays LDP received label binding information of the specified instance. |
received instance <instance-name> ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP received label binding information about the specified LDP identifier and instance. |
received ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP received label binding information of the specified LDP identifier. |
sent |
Displays the LDP sent label binding information of the LDP sessions. |
sent instance <instance-name> |
Displays LDP sent label binding information of the specified instance. |
sent instance <instance-name> ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP sent label binding information about the specified LDP identifier and instance. |
sent ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP sent label binding information of the specified LDP identifier. |
Example 1: Summary view of LDP Binding
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp binding
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4
Prefix In Label Out Label LDP ID Status
198.51.100.1/32 - label:3 - Best
label:20066 - 198.51.100.3:0 Non-best
label:20065 - 198.51.100.2:0 Non-best
198.51.100.11/32 - label:3 - Best
label:20066 - 198.51.100.3:0 Non-best
label:20065 - 198.51.100.2:0 Non-best
198.51.100.41/32 - label:3 - Best
label:20066 - 198.51.100.3:0 Non-best
label:20065 - 198.51.100.2:0 Non-best
198.51.100.44/32 - label:3 - Best
label:20066 - 198.51.100.3:0 Non-best
label:20065 - 198.51.100.2:0 Non-best
198.51.100.47/32 - label:3 - Best
label:20066 - 198.51.100.3:0 Non-best
label:20065 - 198.51.100.2:0 Non-best
198.51.100.2/32 label:3 label:20065 198.51.100.2:0 Best
label:20065 - 198.51.100.3:0 Non-best
198.51.100.21/32 label:3 label:20065 198.51.100.2:0 Best
label:20065 - 198.51.100.3:0 Non-best
198.51.100.42/32 label:3 label:20065 198.51.100.2:0 Best
label:20065 - 198.51.100.3:0 Non-best
<...>
Example 2: Summary view of LDP Binding for the specified prefix
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp binding prefix 198.51.100.2/32
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4
Prefix In Label Out Label LDP ID Status
198.51.100.2/32 label:3 label:20065 198.51.100.2:0 Best
label:20065 - 198.51.100.3:0 Non-best
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op>
3.1.6. LDP Route
Syntax:
show ldp route <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays a summary of LDP route information. |
instance <instance-name> |
Displays LDP route information for the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> <afi> |
Displays LDP route information for the specified address family and instance. Supported AFI values: ipv4, ipv6, and mpls. |
instance <instance-name> ipv4 prefix <ip> |
Displays LDP route information for the specified address family of IPv4 prefix and instance. |
instance <instance-name> ipv6 prefix <ip> |
Displays LDP route information for the specified address family of IPv6 prefix and instance. |
instance <instance-name> prefix <ip> |
Displays LDP route information for the specified prefix and instance. |
instance <instance-name> label <label> |
Displays LDP route information for the specified MPLS label and instance. |
instance <instance-name> mpls |
Displays LDP route information about MPLS labels. |
instance <instance-name> mpls label <label> |
Displays LDP route information for the specified MPLS label and instance. |
label <label> |
Displays LDP route information for the specified MPLS label. |
ipv4 |
Displays LDP route information about the IPv4 address family. |
ipv4 prefix <ip> |
Displays LDP route IPv4 address family information for the specified prefix. |
ipv6 |
Displays LDP route information about the IPv6 address family. |
ipv6 prefix <ip> |
Displays LDP route IPv6 address family information for the specified prefix. |
mpls |
Displays LDP route information about MPLS labels. |
mpls label <label> |
Displays LDP route information for the specified MPLS label. |
prefix <ip> |
Displays LDP route information for the specified prefix address. |
Example: Summary view of LDP Route
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp route Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: labeled-unicast Prefix/Label Advertised label Received label Next Hop Interface Metric 198.51.100.1/32 3 - - - - 198.51.100.2/32 20065 - 198.51.100.61 ifl-0/0/0/1 1000000 198.51.100.3/32 20067 20067 198.51.100.61 ifl-0/0/0/1 2000001 198.51.100.11/32 3 - - - - 198.51.100.21/32 20065 - 198.51.100.61 ifl-0/0/0/1 1000000 198.51.100.31/32 20067 20067 198.51.100.61 ifl-0/0/0/1 2000001 198.51.100.41/32 3 - - - - 198.51.100.42/32 20065 - 198.51.100.61 ifl-0/0/0/1 1000000 198.51.100.43/32 20067 20067 198.51.100.61 ifl-0/0/0/1 2000001 198.51.100.44/32 3 - - - - 198.51.100.45/32 20065 - 198.51.100.61 ifl-0/0/0/1 1000000 198.51.100.46/32 20067 20067 198.51.100.61 ifl-0/0/0/1 2000001 198.51.100.47/32 3 - - - - 198.51.100.48/32 20065 - 198.51.100.61 ifl-0/0/0/1 1000000 198.51.100.49/32 20067 20067 198.51.100.61 ifl-0/0/0/1 2000001 <...>
3.1.7. LDP Statistics
Syntax:
show ldp statistics <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, the command displays the LDP statistics for all instances. |
instance <instance-name> |
Displays LDP statistics information about the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Displays LDP statistics information about the specified LDP identifier and instance. |
Example: LDP statistics information
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp statistics
Instance: default, LDP ID: 198.51.100.2:0
Received messages:
Initialization: 1, KeepAlive: 558, Notification: 0
Address: 1, Address Withdraw: 0, Label Mapping: 15
Label Withdraw: 0, Label Release: 0
Sent messages:
Initialization: 1, KeepAlive: 558, Notification: 0
Address: 1, Address Withdraw: 0, Label Mapping: 15
Label Withdraw: 0, Label Release: 0
Instance: default, LDP ID: 198.51.100.3:0
Received messages:
Initialization: 1, KeepAlive: 557, Notification: 0
Address: 1, Address Withdraw: 0, Label Mapping: 15
Label Withdraw: 0, Label Release: 0
Sent messages:
Initialization: 1, KeepAlive: 557, Notification: 0
Address: 1, Address Withdraw: 0, Label Mapping: 15
Label Withdraw: 0, Label Release: 0
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op>
3.1.8. LDP TCP connection
Syntax:
show ldp tcp connection <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, the command displays the TCP connections used by LDP for all instances. |
detail |
Detailed list view of the TCP connections. |
detail instance <instance-name> |
Detailed list view of the TCP connections of the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> |
TCP connections summary of the specified instance. |
Example: Summary view of the LDP TCP connections
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> show ldp tcp connection Instance Local IP Remote IP Local port Remote port State default 198.51.100.1 198.51.100.2 646 64718 Established default 198.51.100.1 198.51.100.3 646 64718 Established supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op>
3.2. LDP Clear Commands
Clear commands allow resetting operational states.
3.2.1. Clear LDP Session
Syntax:
clear ldp session <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
all |
Clears all the LDP sessions. |
all soft-in |
Sends route refresh to all neighbors to receive FEC bindings. |
all soft-out |
Re-advertises all the routes previously sent to the peers. |
instance <instance-name> all |
Clears all the LDP sessions for the specified instance. |
instance <instance> all soft-in |
Sends route refresh to all neighbors to receive FEC bindings for the specified instance. |
instance <instance> all soft-out |
Re-advertises all the routes previously sent to the peers for the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> peer ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Clears the LDP session for the specified instance and peer LDP identifier. |
instance <instance> peer ldp-id <ldp-id> soft-in |
Sends route refresh to the specific peer to receive FEC bindings for the specified instance and peer ldp-id. |
instance <instance> peer ldp-id <ldp-id> soft-out |
Re-advertises all the routes previously sent to the specific peer for the specified instance and peer ldp-id. |
Example: The example below shows how to clear all the LDP sessions.
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> clear ldp session all LDP session cleared with instance default supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op>
3.2.2. Clear LDP Statistics
Syntax:
clear ldp statistics <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
all |
Clears all the LDP statistics. |
instance <instance-name> all |
Clears all the LDP statistics for the specified instance. |
instance <instance-name> peer ldp-id <ldp-id> |
Clears the LDP statistics for the specified instance and peer LDP identifier. |
Example: The example below shows how to clear all the LDP statistics.
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> clear ldp statistics all LDP statistics cleared for instance default supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op>
3.2.3. Clear LDP Neighbor
Syntax:
clear ldp neighbor <options>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
all |
Clears all the LDP neighbors. |
instance <instance-name> |
Clears the LDP neighbor for the specified instance. |
Example: The example below shows how to clear all the LDP neighbor.
supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op> clear ldp neighbor all LDP neighbor cleared with instance default supervisor@rtbrick>SPINE01: op>
©Copyright 2024 RtBrick, Inc. All rights reserved. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The trademarks, logos and service marks ("Marks") displayed in this documentation are the property of RtBrick in the United States and other countries. Use of the Marks are subject to RtBrick’s Term of Use Policy, available at https://www.rtbrick.com/privacy. Use of marks belonging to other parties is for informational purposes only.