1. Introduction
IS-IS, or Intermediate System to Intermediate System, is an open standard routing protocol. ISO published the standard as a way to route datagrams as part of their OSI stack. IETF later republished the standard, and added IP route support.
It is a link-state routing protocol, similar to OSPF. It forms neighbor adjacencies, has areas, exchanges link-state packets, builds a link-state database and runs the Dijkstra SPF algorithm to find the best path to each destination, which is installed in the routing table.
1.1. Segment Routing
IS-IS in RBFS supports segment routing based on RFC 8667. IS-IS segment routing extensions allow to advertise labels with prefixes.
|
|
RFC and draft compliance are partial except as specified. |
RBFS currently supports the following IS-IS segment routing features:
-
MPLS data plane
-
IPv4 prefixes (TLV 135) and IPv6 prefixes (TLV 236)
-
Prefix SID with node flag (Node SID) on loopback interface
-
Anycast SID
-
A single global SRGB block
-
Adjacency SIDs
1.2. IS-IS Flood Filter Configuration
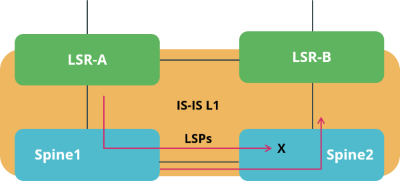
In IS-IS, by default all routers flood link-state packets, so that all routers will have a complete topology view. IS-IS flood filters allow to modify this behavior and limit the exchange of LSPs. For example, if two spine routers in a spine/leaf fabric are symmetrically connected to two upstream label-switch routers (LSR) like shown in the figure below, you can use a flood filter to not advertise LSPs learned from LSR A back to the LSR B via the second spine switch.
The flooding filter configuration is part of the global configuration hierarchy and therefore you can configure filtering globally, i.e. not per instance, so that the filter configurations can be reused across instances.
1.3. Supported Platforms
Not all features are necessarily supported on each hardware platform. Refer to the Platform Guide for the features and the sub-features that are or are not supported by each platform.
2. IS-IS Configuration
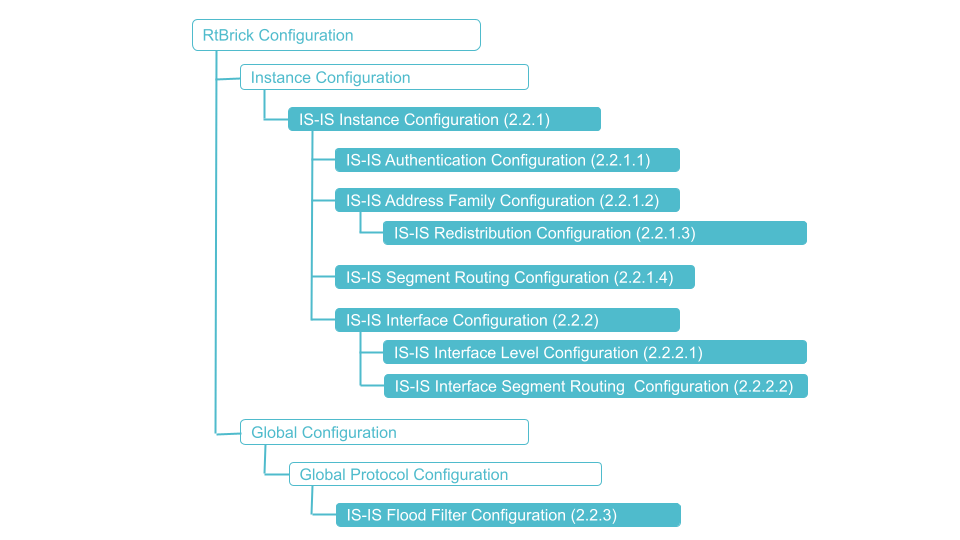
2.1. Configuration Hierarchy
The diagram below illustrates the IS-IS configuration hierarchy.
2.2. Configuration Syntax and Commands
The following sections describe the IS-IS configuration syntax and commands.
2.2.1. Instance Configuration
The instance configuration hierarchy includes parameters that are required for or used by IS-IS.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol isis <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<name> |
Name of the IS-IS instance |
area <area> |
IS-IS area-address. The area can be represented in 1, 3, 5, 13 bytes format. |
authentication <…> |
Specifies the authentication scheme for IS-IS. Refer to section 2.2.1.1 for the IS-IS authentication configuration details. |
holding-time <holding-time> |
Specifies how long a neighbor should consider this routing device to be operative without receiving another hello packet. Default value: 30 seconds Range: 1 through 3,180 seconds |
hostname <hostname> |
Specifies the hostname mapped to the system identifier. |
ignore-attached-bit [true/false] |
This configuration allows you to enable the routing device to ignore the attached bit on incoming Level 1 link-state PDUs. If the attached bit is ignored, no default route, which points to the routing device which has set the attached bit, is installed. |
interface <…> |
Name of the interface. Refer to section 2.2.2 for the interface configuration details. |
ipv6-disable [true/false] |
Specifies whether the ipv6-disable configuration is enabled or not. When you set this value to "true", it indicates that IPv6 configuration is disabled. |
[level-1/level-2] address-family <…> |
Protocol ISIS level-1/level-2 address-family configuration. Refer to section 2.2.1.2 for the address family configuration details. |
level1-to-level2 route-leak [enable/disable] |
Specifies whether the level1-to-level2 route-leak is enabled or not. When set to disable, IS-IS will not leak routing information from a Level 1 area to a Level 2 area. By default, this option is enabled. |
lsp-lifetime <lsp-lifetime> |
IS-IS link-state PDUs maximum lifetime, default 65535 seconds |
multipath <multipath> |
Load sharing among multiple ISIS paths, default 256 |
no-mpls-transit-path [true/false] |
When set to true, IS-IS will not install segment routing transit path, default false |
overload [true/false] |
When set to true, IS-IS overload bit is set, default false |
router-id <router-id> |
ISIS router identifier (ipv4 format: A.B.C.D) |
system-id <system-id> |
Specifies the system ID of the device. |
Example 1: IS-IS Instance Configuration
{
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"protocol": {
"isis": {
"system-id": "1000.9900.0001",
"overload": "false",
"holding-time": 100,
"area": "49.0001/24",
"hostname": "spine1",
"router-id": "198.51.100.199",
"authentication": {
"level-1": {
"check": "enable"
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
Example 2: Disabling IS-IS Route Leaking from a Level 1 Area to a Level 2 Area
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: cfg> show config instance default protocol isis level1-to-level2
{
"rtbrick-config:level1-to-level2": {
"route-leak": "disable"
}
}
2.2.1.1. IS-IS Authentication Configuration
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol isis authentication [level-1 | level-2] <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
check [disable / enable] |
Specifies an authentication check to reject PDUs that do not match the type or key requirements. You can enable or disable the authentication check. |
key-id1 <key-id1> / key-id2 <key-id2> |
The key ID allows you to specify the key identifiers for level-1/level-2 authentication. |
key1-encrypted-text <key1-encrypted-text> / key2-encrypted-text <key2-encrypted-text> |
Authentication key1 and key 2 encrypted text |
key1-plain-text <key1-plain-text> / key2-plain-text <key2-plain-text> |
The level-1/level-2 authentication keys specify the authentication keys (passwords) that are used by the neighboring routing devices to verify the authenticity of packets sent from this interface. For the key to work, you also must include the authentication-type statement. |
type |
Enables you to specify the authentication scheme for IS-IS. If you enable authentication, you must specify a password by including the authentication-key statement. The following authentication types are supported:
|
{
"ietf-restconf:data": {
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"protocol": {
"isis": {
<...>
"authentication": {
"level-1": {
"type": "md5",
"key1-encrypted-text": "$239928e897b1f0fb3a97ed426db21aba36ca48479744a7c71255ee2c4e747e859"
}
},
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1/0",
"type": "point-to-point",
"level-1": {
"snp-authentication": "enable",
"hello-authentication": "disable",
"metric": 10
},
"level-2": {
"snp-authentication": "enable",
"hello-authentication": "disable",
"metric": 10
}
},
<...>
2.2.1.2. IS-IS Address-Family Configuration
The address-family command allows you to enable the address families that IS-IS will route and configure settings that are specific to that address family.
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol isis [level-1 | level-2] address-family <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, ipv6 |
<safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast or labeled-unicast |
2.2.1.3. Configuring Route Redistribution
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol isis [level-1 | level-2] address-family <afi> <safi> redistribute <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<afi> |
Address family identifier (AFI). Supported values: ipv4, ipv6 |
<safi> |
Subsequent address family identifier (SAFI). Supported values: unicast or labeled-unicast |
redistribute <protocol> |
Specifies the source from which the routes are to be redistributed from. The available options include |
redistribute <protocol> <policy> |
Specifies the name of the policy map. The redistribute attach point allows routes from other sources to be advertised by IS-IS. Policy can be applied only to the routes that are redistributed from other sources to IS-IS. The support for inter-level leaking through policy is unavailable. |
Example: IS-IS address-family configuration
{
"rtbrick-config:isis": {
"system-id": "1000.9900.0001",
"area": "49.0001/24",
"hostname": "spine1",
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/2/0",
"type": "point-to-point",
"level-1": {
"metric": 1000
}
}
],
"level-1": {
"address-family": [
{
"afi": "ipv4",
"safi": "unicast",
"redistribute": [
{
"source": "bgp"
"policy": "filter-link-address"
}
]
}
]
}
}
2.2.1.4. Segment Routing Configuration
Syntax:
set instance <instance-name> protocol isis segment-routing <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
srgb base <srgb base> |
Specifies the segment routing global block (SRGB) in source packet routing. SRGB is used for prefix SIDs. |
srgb range <srgb range> |
IS-IS system range of labels from the base label. |
srlb base <srlb base> |
Specifies the segment routing local block (SRLB) in source packet routing. SRLB is used for adjacency SIDs. |
srlb range <srlb range> |
IS-IS system range of labels from the base label. |
Example: IS-IS Segment Routing Configuration
{
"rtbrick-config:isis": {
segment-routing: {
"srgb: {
"base": 5000,
"range": 1000
}
"srlb: {
"base": 5000,
"range": 1000,
}
2.2.2. Configuring IS-IS Interface
By default, there are no interfaces associated with IS-IS. You must configure at least one IS-IS interface for IS-IS adjacency formation.
Syntax:
set instance <instance> protocol isis interface <name> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<name> |
Specifies the name of the IS-IS interface. |
flood-filter <flood-filter> |
Specifies the IS-IS flood filter name |
level-1 / level-2 |
Specify IS-IS interface level configuration. Refer to section 2.2.2.1 for the IS-IS interface level configuration details. |
lsp-interval <lsp-interval> |
IS-IS system interface LSP interval, default 100 |
passive [true / false] |
Enable interface in passive mode, default false |
system-id <system-id> |
Interface level system id |
type [loopback / none / point-to-point] |
Specifies the type of the IS-IS system interface |
ldp-synchronization [enable / disable] |
Enable LDP IGP synchronization, default disable |
Example 1: IS-IS Interface Configuration
{
"rtbrick-config:isis": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1/0",
"lsp-interval": 200
}
]
}
}
Example 2: IS-IS Interface Level Flood Filter Configuration
{
"rtbrick-config:interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1/0",
"flood-filter": "spine1_lsr1_flood_filter"
}
]
}
Example 3: IS-IS Interface Configuration with enabled LDP synchronization
{
"rtbrick-config:isis": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1/0",
"lsp-interval": 200,
"ldp-synchronization": "enable"
}
]
}
}
2.2.2.1. IS-IS Interface Level Configuration
Syntax:
set instance <instance> protocol isis interface <name> [level-1 | level-2] <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
adjacency-disable [true/false] |
Specify the level-1/level-2 adjacency on an interface, default false |
hello-authentication [disable/enable] |
Authentication on hello packets |
metric <metric> |
Level-1/Level-2 metric on an interface, default 1000000 |
snp-authentication [enable/disable] |
Authentication on CSNP/PSNP packets |
Example: IS-IS Interface Level Configuration
{
"rtbrick-config:interface": [
{
"name": "ifl-0/0/1/0",
"lsp-interval": 200,
"level-1": {
"snp-authentication": "enable",
"hello-authentication": "enable",
"metric": 1000,
"adjacency-disable": "false"
}
}
]
}
2.2.2.2. Interface-level Segment Routing Configuration
Syntax:
set instance <instance> protocol isis interface <name> segment-routing <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
segment-routing [ipv4 / ipv6] anycast-index <anycast-index> |
Anycast index segment-ID. The prefix SIDs and anycast SIDs are applied on loopback interface only. |
segment-routing [ipv4 / ipv6] index <index> |
Prefix index segment ID. |
segment-routing point-to-point [ipv4 / ipv6] adjacency-index <adjacency-index> |
Adjacency index segment-ID. The adjacency SIDs are applied on active IS-IS interfaces on which adjacencies are established. |
Example 1: IS-IS Interface Level Segment Routing Configuration for Prefix and Anycast SID
"rtbrick-config:instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"protocol": {
"isis": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "lo-0/0/0",
"segment-routing": {
"ipv4": {
"index": 100
},
"ipv6": {
"index": 200
}
}
},
{
"name": "lo-0/0/1",
"segment-routing": {
"ipv4": {
"anycast-index": 110
},
"ipv6": {
"anycast-index": 210
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
Example 2: IS-IS Interface Level Segment Routing Configuration for Adjacency SID
{
"rtbrick-config:isis": {
"interface": [
{
"name": "ifp-0/0/1/0",
"type": "point-to-point",
"segment-routing": {
"point-to-point": {
"ipv4": {
"adjacency-index": 241
},
"ipv6": {
"adjacency-index": 261
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
2.2.3. IS-IS Global Configuration
2.2.3.1. IS-IS Flood Filter Configuration
Syntax:
set global protocol isis flood-filter <filter-name> <ordinal> <attribute> <value>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<filter-name> |
Filter-name which binds a flooding filter to an IS-IS interface |
<ordinal> |
Number to filter rule |
action [block/flood] |
Action required to flood or not |
ordinal-name <ordinal-name> |
Name for the filter rule |
system-id <system-id> |
IS-IS instance system-id |
system-id-mask <system-id-mask> |
System ID mask on which the filter should match |
Example: IS-IS Flood Filter Configuration
{
"rtbrick-config:flood-filter": [
{
"filter-name": "spine1_lsr1_flood_filter",
"ordinal": 1,
"ordinal-name": "spine1",
"system-id": "1920.0100.4001",
"action": "flood"
}
]
}
3. Operational Commands
3.1. IS-IS Show Commands
The IS-IS show commands provide detailed information about the IS-IS protocol operation and IS-IS routes.
3.1.1. IS-IS Overview
Syntax:
show isis overview
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays a summary of all the IS-IS instances |
Example: Summary view of all the IS-IS instances
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis overview Instance: default System ID: 1921.6800.1002 System hostname: No hostname configured Areas: 49.0001/24 Neighbor hold time: 30 sec LSP life time: 65535 se Overload bit set: False SRGB base: not defined SRGB range: not defined SRGB label values: not defined SRLB base: not defined SRLB range: not defined SRLB label values: not defined Authentication: Level 1: none, Level 2: none
3.1.2. IS-IS Interface
Syntax:
show isis interface <option>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays a summary of all the IS-IS interfaces |
instance |
Displays IS-IS interface information for an instance |
statistics |
Displays IS-IS interface statistics information |
detail |
Displays detailed output for all interfaces. |
Example 1: Summary view of the IS-IS interfaces
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis interface Instance: default Interface Level Adjacencies Metric Type Passive lo-0/0/4/1 1 0 1000000 loopback True ifl-0/1/2/12 1 0 1000000 point-to-point False ifl-0/1/6/16 1 0 1000000 point-to-point False
Example 2: Summary view of the IS-IS interfaces for a specific instance
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis interface instance default Instance: default Interface Level Adjacencies Metric Type Passive lo-0/0/4/1 1 0 1000000 loopback True ifl-0/1/2/12 1 0 1000000 point-to-point False ifl-0/1/6/16 1 0 1000000 point-to-point False
Example 3: Summary view of the IS-IS interfaces for a specific interface
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis interface ifl-0/1/6/16 Instance: default Interface: ifl-0/1/6/16, Level: 1 Type: point-to-point, Passive: False Metric: 1000000 Adjacencies: 1 CNSP: In: 24 Out: 34 Success: 24 Fail: 0 PSNP: In: 8 Out: 10 Success: 5 Fail: 1 LSP: In: 14 Out: 11 Success: 11 Fail: 2 In Purge: 0 In Auth Fail: 2 IIH: In: 121 Out: 163
Example 4: Summary view of the IS-IS interface statistics
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis interface statistics Instance: default Interface Level CSNP In CSNP Out CSNP Fail PSNP In PSNP Out PSNP Fail LSP In LSP Out LSP Fail IIH In IIH Out lo-0/0/4/1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ifl-0/1/2/12 1 32 32 0 9 6 1 9 10 0 117 138 ifl-0/1/6/16 1 22 32 0 6 6 1 9 8 0 115 138
Example 5: Detailed output of the IS-IS interface
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis interface detail
Instance: default
Interface: lo-0/0/0/0, Level: 1
Type: loopback, Passive: True
Metric: 1000000
Adjacencies: 0
CNSP: In: 0 Out: 0 Success: 0 Fail: 0
PSNP: In: 0 Out: 0 Success: 0 Fail: 0
LSP: In: 0 Out: 0 Success: 0 Fail: 0 In Purge: 0 In Auth Fail: 0
IIH: In: 0 Out: 0
Instance: default
Interface: ifl-0/0/0/0, Level: 1
Type: point-to-point, Passive: False
Metric: 1000000
Adjacencies: 1
CNSP: In: 3020 Out: 3020 Success: 3020 Fail: 0
PSNP: In: 2 Out: 2 Success: 2 Fail: 0
LSP: In: 2 Out: 2 Success: 2 Fail: 0 In Purge: 0 In Auth Fail: 0
IIH: In: 5589 Out: 5600
3.1.3. IS-IS Neighbor
Syntax:
show isis neighbor <option>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays a summary of all the IS-IS neighbors |
detail |
Displays detailed information for IS-IS neighbor |
instance |
Displays IS-IS neighbor information for an instance |
Example 1: Summary view of the IS-IS neighbor
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis neighbor Instance: default Interface System Level State Type Up since Expires ifl-0/1/2/12 1920.0100.4002.00 L1 Up P2P Mon Nov 02 06:18:36 in 28s 228094us ifl-0/1/6/16 1920.0000.0006.00 L1 Up P2P Mon Nov 02 06:18:30 in 24s 420225us
Example 2: Detailed view of the IS-IS neighbor
supervisor@S1-STD-17-1703: cfg> show isis neighbor detail
Instance: ip2vrf
System: isr6, Interface: ifl-0/0/2/0
State: Up, Level: L1, Adjacency type: P2P
Holding time: 30.0s, Expiry time: in 25s 332949us
Local IPv4 address: 198.51.100.27, Remote IPv4 address: 198.51.100.28
Local IPv6 address: 2001:db8:0:76::, Remote IPv6 address: 2001:db8:0:34::
IPv4 Adjacency SID: 11116, IPv6 Adjacency SID: 11117
Up since: Wed Feb 16 04:46:25 GMT +0000 2022, Last down reason: Admin reset
Last transition: 2022-02-16T04:46:25.300144+0000, Number of transitions: 14
Error counters:
Level mismatch: 0, Area mismatch: 0, System ID: 0, Subnet mismatch: 0
Hold timeout: 3, Neighbor down: 0, Interface down: 0, Admin reset: 1
Interface configuration: 0, Area configuration: 0, Other: 0
Example 3: Summary view of the IS-IS neighbor for the specified instance
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis neighbor instance default Instance: default Interface System Level State Type Up since Expires ifl-0/1/2/12 1920.0100.4002.00 L1 Up P2P Mon Nov 02 06:18:36 in 28s 678329us ifl-0/1/6/16 1920.0000.0006.00 L1 Up P2P Mon Nov 02 06:18:30 in 28s 88085us supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op>
Example 4: Detailed view of the IS-IS neighbor for the specified instance
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis neighbor instance default detail Instance: default System: 1920.0100.4002.00, Interface: ifl-0/1/2/12 State: Up, Level: L1, Adjacency type: P2P Holding time: 30.0s, Expiry time: in 21s 706586us Local IPv4 address: 198.51.100.22, Remote IPv4 address: 198.51.100.21 Local IPv6 address: 2001:db8:0:110::, Remote IPv6 address: 2001:db8:0:3433:: Up since: Mon Nov 02 06:18:36 GMT +0000 2020, Last down reason: NA Last transition: 2020-11-02T06:18:36.947601+0000, Number of transitions: 2 Error counters: Level mismatch: 0, Area mismatch: 0, System ID: 0, Subnet mismatch: 0 Hold timeout: 0, Neighbor down: 0, Interface down: 0, Admin reset: 0 Interface configuration: 0, Area configuration: 0, Other: 0 System: 1920.0000.0006.00, Interface: ifl-0/1/6/16 State: Up, Level: L1, Adjacency type: P2P Holding time: 30.0s, Expiry time: in 22s 832756us Local IPv4 address: 198.51.100.100, Remote IPv4 address: 198.51.100.101 Local IPv6 address: 2001:db8:0:10::, Remote IPv6 address: 2001:db8:0:6843:: Up since: Mon Nov 02 06:18:30 GMT +0000 2020, Last down reason: NA Last transition: 2020-11-02T06:18:30.356111+0000, Number of transitions: 2 Error counters: Level mismatch: 0, Area mismatch: 0, System ID: 0, Subnet mismatch: 0 Hold timeout: 0, Neighbor down: 0, Interface down: 0, Admin reset: 0 Interface configuration: 0, Area configuration: 0, Other: 0
3.1.4. IS-IS Hostname
Syntax:
show isis hostname
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays a summary of all the IS-IS dynamic hostnames |
Example: Summary view of IS-IS hostnames
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis hostname Instance System-ID Hostname default 1920.0100.4001 spine1 supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op>
3.1.5. IS-IS Database
Syntax:
show isis database <option>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays all the IS-IS databases |
detail |
Displays detailed information for IS-IS database |
instance |
Displays IS-IS database information for an instance |
lsp <lsp-id> |
Displays a summary of IS-IS database for the specified LSP ID. This command includes an option for entering the system ID part either by hostname or by ID. |
[level-1/level-2] lsp |
Displays a summary of IS-IS database LSP information for specified level |
system <system-id> |
Displays a summary of IS-IS database for all LSPs from a system |
[level-1/level-2] system |
Displays a summary of IS-IS database for all LSPs from a system on the specified level. |
[level-1/level-2] detail |
Displays detailed information for the specified level |
Example 1: Summary view of the IS-IS Database
supervisor@S1-STD-7-7001>bm01-tst.fsn.rtbrick.net: op> show isis database
Instance: default, Level: 1
LSP ID Sequence Checksum Lifetime Overload Attached
1921.6800.1002.00-00 0x3 0x9561 65535 0 0
1921.6800.1005.00-00 0x2 0x499b 65535 0 0
Instance: default, Level: 2
LSP ID Sequence Checksum Lifetime Overload Attached
1921.6800.1002.00-00 0x4 0x531a 65535 0 0Example 2: Summary view of the IS-IS database for the specified LSP
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis database lsp 1920.0100.4001.00-00 Instance: default, Level: 1 LSP ID: 1920.0100.4001.00-00 Interface: LSP Header: Sequence: 0xc Checksum: 0x9c74 Remaining lifetime: 65535 seconds Flags: Attached: 0, Overload: 0 Packet: Length: 168 bytes Last received time: 2020-11-02T06:46:46.473726+0000 Expiry: expires in 17h 52m 34s 950743us Dynamic Hostname TLV: spine1 Protocols Supported TLVs: Network layer protocol ID: IPv6 Network layer protocol ID: IPv4 Area Address TLVs: Area address: 49.0001 Authentication TLV: Value: 77b259cb36930819b0abb6120ceee2fd IS Reachability TLVs: IS neighbor: 1920.0000.0006.00 IS neighbor: 1920.0100.4002.00 IPv4 Reachability TLVs: IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.100/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.22/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.41/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up SID: 1 Flags: Node IPv6 Reachability TLVs: IPv6 prefix: 2001:db8:0:41::/32 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up Segment Routing TLVs: SRGB: Base: 10000, Range: 2000 Instance: default, Level: 2 LSP ID: 1920.0100.4001.00-00 Interface: LSP Header: Sequence: 0x12 Checksum: 0x6407 Remaining lifetime: 65535 seconds Flags: Attached: 0, Overload: 0 Packet: Length: 247 bytes Last received time: 2020-11-02T06:47:06.466723+0000 Expiry: expires in 17h 52m 54s 889789us Dynamic Hostname TLV: spine1 Protocols Supported TLVs: Network layer protocol ID: IPv6 Network layer protocol ID: IPv4 Area Address TLVs: Area address: 49.0001 Authentication TLV: none IS Reachability TLVs: IPv4 Reachability TLVs: IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.100/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.30/24 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.20/24 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.21/24 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.22/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.26/24 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up SID: 6 Flags: Re-advertisement, Node IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.41/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up SID: 1 Flags: Re-advertisement, Node IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.42/24 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up SID: 2 Flags: Re-advertisement, Node IPv6 Reachability TLVs: IPv6 prefix: 2001:db8:0:41::/32 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv6 prefix: 2001:db8:0:42::/32 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up Segment Routing TLVs: SRGB: Base: 10000, Range: 2000
Example 3: Detailed view of the IS-IS database for level-1
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis database level-1 detail Instance: default, Level: 1 LSP ID: 1920.0100.4001.00-00 Interface: LSP Header: Sequence: 0xc Checksum: 0x9c74 Remaining lifetime: 65535 seconds Flags: Attached: 0, Overload: 0 Packet: Length: 168 bytes Last received time: 2020-11-02T06:46:46.473726+0000 Expiry: expires in 17h 50m 31s 759013us Dynamic Hostname TLV: spine1 Protocols Supported TLVs: Network layer protocol ID: IPv6 Network layer protocol ID: IPv4 Area Address TLVs: Area address: 49.0001 Authentication TLV: Value: 77b259cb36930819b0abb6120ceee2fd IS Reachability TLVs: IS neighbor: 1920.0000.0006.00 IS neighbor: 1920.0100.4002.00 IPv4 Reachability TLVs: IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.100/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.22/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.41/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up SID: 1 Flags: Node IPv6 Reachability TLVs: IPv6 prefix: 2001:db8:0:41::/32 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up Segment Routing TLVs: SRGB: Base: 10000, Range: 2000 LSP ID: 1920.0100.4002.00-00 Interface: ifl-0/1/2/12 LSP Header: Sequence: 0x9 Checksum: 0x89a6 Remaining lifetime: 65534 seconds Flags: Attached: 0, Overload: 0 Packet: Length: 149 bytes Last received time: 2020-11-02T06:45:59.814186+0000 Expiry: expires in 17h 49m 44s 99010us Dynamic Hostname TLV: none Protocols Supported TLVs: Network layer protocol ID: IPv6 Network layer protocol ID: IPv4 Area Address TLVs: Area address: 49.0001 Authentication TLV: Value: 5892f2d37d7f23abcfcb48466276659c IS Reachability TLVs: IS neighbor: 1920.0100.4001.00 IPv4 Reachability TLVs: IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.30/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.22/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.42/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up SID: 2 Flags: Node IPv6 Reachability TLVs: IPv6 prefix: 2001:db8:0:42::/32 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up Segment Routing TLVs: SRGB: Base: 70000, Range: 2000
Example 4: Summary view of the IS-IS database for the specified instance
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis database instance default
Instance: default, Level: 1
LSP ID Sequence Checksum Lifetime Expiry Overload Attached
1920.0000.0006.00-00 0xa 0x8beb 65534 in 17h 44m 13s 390502us 0 0
1920.0000.0007.00-00 0x5 0xdfbb 65533 in 17h 15m 49s 869683us 0 0
1920.0000.0008.00-00 0x6 0x76f3 65533 in 17h 15m 51s 959359us 0 0
1920.0000.0009.00-00 0x6 0x5b18 65533 in 17h 15m 51s 667570us 0 0
spine1.00-00 0xc 0x9c74 65535 in 17h 43m 55s 63659us 0 0
1920.0100.4002.00-00 0x9 0x89a6 65534 in 17h 43m 7s 403686us 0 0
Instance: default, Level: 2
LSP ID Sequence Checksum Lifetime Expiry Overload Attached
spine1.00-00 0x12 0x6407 65535 in 17h 44m 15s 21189us 0 0Example 5: Summary view of the IS-IS database for the specified instance and LSP
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis database instance default lsp 1920.0100.4001.00-00 Instance: default, Level: 1 LSP ID: 1920.0100.4001.00-00 Interface: LSP Header: Sequence: 0xc Checksum: 0x9c74 Remaining lifetime: 65535 seconds Flags: Attached: 0, Overload: 0 Packet: Length: 168 bytes Last received time: 2020-11-02T06:46:46.473726+0000 Expiry: expires in 17h 52m 34s 950743us Dynamic Hostname TLV: spine1 Protocols Supported TLVs: Network layer protocol ID: IPv6 Network layer protocol ID: IPv4 Area Address TLVs: Area address: 49.0001 Authentication TLV: Value: 77b259cb36930819b0abb6120ceee2fd IS Reachability TLVs: IS neighbor: 1920.0000.0006.00 IS neighbor: 1920.0100.4002.00 IPv4 Reachability TLVs: IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.100/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.22/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.41/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up SID: 1 Flags: Node IPv6 Reachability TLVs: IPv6 prefix: 2001:db8:0:41::/32 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up Segment Routing TLVs: SRGB: Base: 10000, Range: 2000 Instance: default, Level: 2 LSP ID: 1920.0100.4001.00-00 Interface: LSP Header: Sequence: 0x12 Checksum: 0x6407 Remaining lifetime: 65535 seconds Flags: Attached: 0, Overload: 0 Packet: Length: 247 bytes Last received time: 2020-11-02T06:47:06.466723+0000 Expiry: expires in 17h 52m 54s 889789us Dynamic Hostname TLV: spine1 Protocols Supported TLVs: Network layer protocol ID: IPv6 Network layer protocol ID: IPv4 Area Address TLVs: Area address: 49.0001 Authentication TLV: none IS Reachability TLVs: IPv4 Reachability TLVs: IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.100/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.30/24 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.20/24 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.21/24 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.22/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.26/24 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up SID: 6 Flags: Re-advertisement, Node IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.41/24 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up SID: 1 Flags: Re-advertisement, Node IPv4 prefix: 198.51.100.42/24 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up SID: 2 Flags: Re-advertisement, Node IPv6 Reachability TLVs: IPv6 prefix: 2001:db8:0:41::/32 Metric: 1000000 Internal Up IPv6 prefix: 2001:db8:0:42::/32 Metric: 2000000 Internal Up Segment Routing TLVs: SRGB: Base: 10000, Range: 2000
3.1.6. IS-IS Route
Syntax:
show isis route <option>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Without any option, this command displays a summary of the IS-IS route information |
instance |
Displays IS-IS route information for an instance |
<afi> <safi> |
Routing information for the specified AFI/SAFI. Supported SAFI values are 'unicast' and 'labeled-unicast'. |
Example 1: Summary view of the IS-IS routes
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis route
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: unicast
Prefix Level Metric Type Next Hop Interface
198.51.100.100/24 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
198.51.100.30/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.21 ifl-0/1/2/12
198.51.100.20/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16
198.51.100.21/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16
198.51.100.22/24 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
198.51.100.26/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16
198.51.100.41/24 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
198.51.100.42/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.21 ifl-0/1/2/12
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: labeled-unicast
Prefix Level Metric SID Index Next Hop Interface Label
198.51.100.26/24 1 2000000 6 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16 10006
198.51.100.42/24 1 2000000 2 198.51.100.21 ifl-0/1/2/12 10002
Instance: default, AFI: ipv6, SAFI: unicast
Prefix Level Metric Type Next Hop Interface
2001:db8:0:41::/32 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
2001:db8:0:42::/32 1 2000000 Internal 2001:db8:0:3433:: ifl-0/1/2/12Example 2: Summary view of the IS-IS routes for the specified instance
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis route instance default
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: unicast
Prefix Level Metric Type Next Hop Interface
198.51.100.100/24 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
198.51.100.30/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.21 ifl-0/1/2/12
198.51.100.20/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16
198.51.100.21/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16
198.51.100.22/24 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
198.51.100.26/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16
198.51.100.41/24 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
198.51.100.42/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.21 ifl-0/1/2/12
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: labeled-unicast
Prefix Level Metric SID Index Next Hop Interface Label
198.51.100.26/24 1 2000000 6 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16 10006
198.51.100.42/24 1 2000000 2 198.51.100.21 ifl-0/1/2/12 10002
Instance: default, AFI: ipv6, SAFI: unicast
Prefix Level Metric Type Next Hop Interface
2001:db8:0:41::/32 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
2001:db8:0:42::/32 1 2000000 Internal 2001:db8:0:3433:: ifl-0/1/2/12Example 3: Summary view of the IS-IS routes for the specified instance and address family (IPv4 unicast).
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis route instance default ipv4 unicast
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: unicast
Prefix Level Metric Type Next Hop Interface
198.51.100.100/24 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
198.51.100.30/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.21 ifl-0/1/2/12
198.51.100.20/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16
198.51.100.21/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16
198.51.100.22/24 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
198.51.100.26/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16
198.51.100.41/24 1 1000000 Internal n/a local
198.51.100.42/24 1 2000000 Internal 198.51.100.21 ifl-0/1/2/12Example 4: Summary view of the IS-IS routes for the specified instance and address family (IPv4 labeled-unicast).
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis route instance default ipv4 labeled-unicast
Instance: default, AFI: ipv4, SAFI: labeled-unicast
Prefix Level Metric SID Index Next Hop Interface Label
198.51.100.26/24 1 2000000 6 198.51.100.101 ifl-0/1/6/16 10006
198.51.100.42/24 1 2000000 2 198.51.100.21 ifl-0/1/2/12 10002Example 5: Summary view of the IS-IS routes for the specified instance and address family (IPv6 unicast).
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis route instance default ipv6 unicast Instance: default, AFI: ipv6, SAFI: unicast Prefix Level Metric Type Next Hop Interface 2001:db8:0:41::/32 1 1000000 Internal n/a local 2001:db8:0:42::/32 1 2000000 Internal 2001:db8:0:3433:: ifl-0/1/2/12
3.1.7. IS-IS Segment Routing
Syntax:
show isis segment-routing <option>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
global-block |
Displays Segment routing global block (SRGB) information |
global-block instance <instance> |
Displays Segment routing global block (SRGB) information for the specified instance |
label-binding |
Displays the IS-IS segment routing label bindings information |
label-binding instance <instance> |
Displays the IS-IS segment routing label bindings for the specified instance |
prefix-segment |
Displays the IS-IS prefix segments information |
prefix-segment <instance> |
Displays the IS-IS prefix segments for the specified instance |
adjacency-segment |
Displays the IS-IS segment routing adjacency SIDs |
Example 1: Summary view of the IS-IS segment routing global block
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis segment-routing global-block Instance: default, Level: 1 System SRGB Base SRGB Range isr1 1000 1000 isr2 2000 1000 isr5 5000 1000 isr6 6000 1000 Instance: default, Level: 2 System SRGB Base SRGB Range isr2 2000 1000 isr3 3000 1000 isr4 4000 1000 isr5 5000 1000
Example 2: Summary view of the IS-IS segment routing label binding
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis segment-routing label-binding Instance: default, Level: 1 System Prefix Range SID Flags isr1 198.51.100.81/24 3 10 None isr2 198.51.100.71/24 3 20 None Instance: default, Level: 2 System Prefix Range SID Flags isr2 198.51.100.81/24 3 10 Re-advertisement isr5 198.51.100.81/24 3 10 Re-advertisement isr5 198.51.100.71/24 3 20 Re-advertisement
Example 3: Summary view of the IS-IS segment routing prefix segment
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis segment-routing prefix-segment Instance: default, Level: 1 System Prefix SID Flags isr1 198.51.100.90/24 100 Node isr1 2001:db8:0:10::/32 102 Node isr2 198.51.100.91/24 200 Node isr2 2001:db8:0:11::/32 202 Node Instance: default, Level: 2 System Prefix SID Flags isr2 198.51.100.90/24 100 Re-advertisement, Node isr2 198.51.100.91/24 200 Node isr2 198.51.100.92/24 500 Re-advertisement, Node isr2 198.51.100.93/24 600 Re-advertisement, Node isr2 2001:db8:0:10::/32 102 Re-advertisement, Node
Example 4: Summary view of the IS-IS segment routing adjacency-segment
supervisor@S1-STD-17-1703: cfg> show isis segment-routing adjacency-segment Instance: ip2vrf, Level: 1 System Label Flags isr1 11116 Value, Local, Persistent isr1 11117 Ipv6 Encapsulation, Value, Local, Persistent isr2 11112 Value, Local, Persistent Instance: ip2vrf, Level: 2 System Label Flags
3.1.8. IS-IS SPF
Syntax:
show isis spf <option>
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
result |
Displays a summary of the IS-IS SPF results |
result <instance> |
Displays a summary of the IS-IS SPF results for the specified instance |
result [level-1/level2] |
Displays a summary of the IS-IS SPF results for the specified level. |
Example 1: Summary view of the IS-IS SPF result
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis spf result
Instance: default, Level: 1
Destination Node Metric Neighbor Node Interface Nexthop Address
1920.0000.0006.00 1000000 1920.0000.0006.00 ifl-0/1/6/16 IPv4 198.51.100.101
1920.0000.0006.00 ifl-0/1/6/16 IPv6 2001:db8:0:6843::
1920.0100.4001.00 0 local
1920.0100.4002.00 1000000 1920.0100.4002.00 ifl-0/1/2/12 IPv6 2001:db8:0:3433::
1920.0100.4002.00 ifl-0/1/2/12 IPv4 198.51.100.21
Instance: default, Level: 2
Destination Node Metric Neighbor Node Interface Nexthop Address
1920.0100.4001.00 0 localExample 2: Summary view of the IS-IS SPF result for level-1
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis spf result level-1
Instance: default, Level: 1
Destination Node Metric Neighbor Node Interface Nexthop Address
1920.0000.0006.00 1000000 1920.0000.0006.00 ifl-0/1/6/16 IPv4 198.51.100.101
1920.0000.0006.00 ifl-0/1/6/16 IPv6 2001:db8:0:6843::
1920.0100.4001.00 0 local
1920.0100.4002.00 1000000 1920.0100.4002.00 ifl-0/1/2/12 IPv6 2001:db8:0:3433::
1920.0100.4002.00 ifl-0/1/2/12 IPv4 198.51.100.21Example 3: Summary view of the IS-IS SPF result for level-2
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis spf result level-2
Instance: default, Level: 2
Destination Node Metric Neighbor Node Interface Nexthop Address
1920.0100.4001.00 0 localExample 4: Summary view of the IS-IS SPF result of a specific instance for level-1
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis spf result instance default level-1
Instance: default, Level: 1
Destination Node Metric Neighbor Node Interface Nexthop Address
1920.0000.0006.00 1000000 1920.0000.0006.00 ifl-0/1/6/16 IPv4 198.51.100.101
1920.0000.0006.00 ifl-0/1/6/16 IPv6 2001:db8:0:6843::
1920.0100.4001.00 0 local
1920.0100.4002.00 1000000 1920.0100.4002.00 ifl-0/1/2/12 IPv6 2001:db8:0:3433::
1920.0100.4002.00 ifl-0/1/2/12 IPv4 198.51.100.21Example 5: Summary view of the IS-IS SPF result of a specific instance for level-2
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> show isis spf result instance default level-2
Instance: default, Level: 2
Destination Node Metric Neighbor Node Interface Nexthop Address
1920.0100.4001.00 0 local3.2. IS-IS Clear Commands
Clear commands allow to reset operational states.
3.2.1. IS-IS Interface
Syntax:
clear isis interface <option> …
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
statistics |
Clears the statistics of all IS-IS interfaces. |
Example: The example below shows how to clear IS-IS interface statistics.
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> clear isis interface statistics
3.2.2. IS-IS Neighbor
Syntax:
clear isis neighbor <option> …
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
neighbor |
Clears neighbors of the default instance |
neighbor instance <instance_name> |
Clears neighbors of the specified instance |
neighbor instance <instance_name> interface <interface-name> |
Clears the specified interface of a specified neighbor instance |
Example: The example below shows how to clear neighbors of the specified instance
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> clear isis neighbor instance default
3.2.3. IS-IS Database
Syntax:
clear isis database <option> …
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
Instance |
Clears neighbors of the default instance |
level-1 |
Clears area level-1 |
level-2 |
Clears area level-2 |
lsp |
Clears IS-IS database for the specific LSP ID |
System |
Clears the LSDB system ID |
Example: The example below shows how to clear the database instance
supervisor@rtbrick>spine1: op> clear isis database instance default
The LSDB data is cleared for instance default
©Copyright 2024 RtBrick, Inc. All rights reserved. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The trademarks, logos and service marks ("Marks") displayed in this documentation are the property of RtBrick in the United States and other countries. Use of the Marks are subject to RtBrick’s Term of Use Policy, available at https://www.rtbrick.com/privacy. Use of marks belonging to other parties is for informational purposes only.