1. Overview of RBFS In-band Management
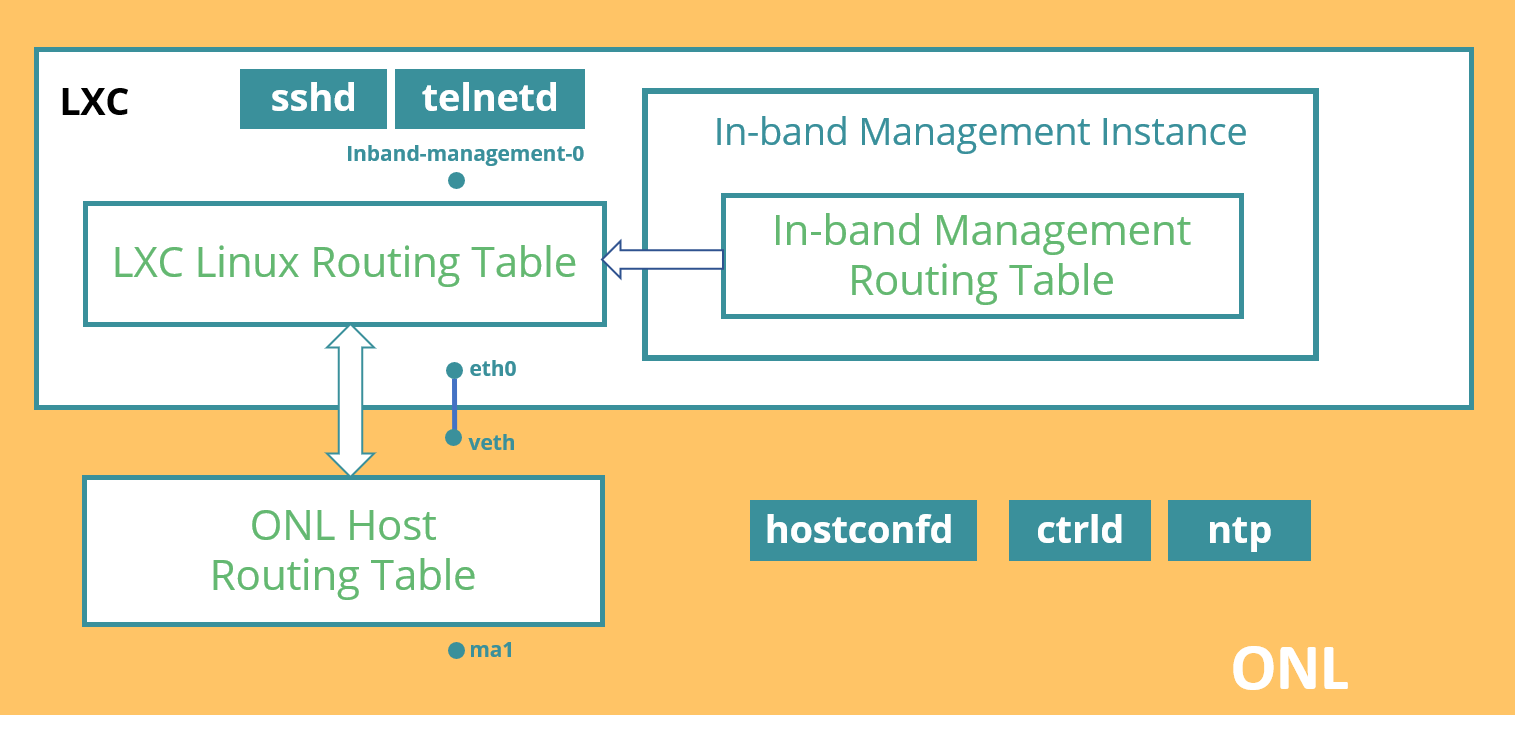
RBFS is mostly deployed on an ONL host as a Linux container. The ONL host is only reachable through the out-of-band management interface. In order to use services like NTP, and TACACS, which are run on ONL, or to use services like ssh, snmpd running in LXC container, one must use an out-of-band management connection. In-band management provides a way to access these services which are running in ONL and LXC containers via physical traffic ports.
The RBFS creates a Linux kernel interface named inband-mgmt-0 when in-band management is enabled on an instance. The loopback IPs of the in-band instance are then assigned to this Linux interface, and the routes of this instance are downloaded to the LXC container, then to ONL. Trap rules are installed in the hardware depending on the in-band service enabled.
1.1. Supported Platforms
Not all features are necessarily supported on each hardware platform. Refer to the Platform Guide for the features and the sub-features that are or are not supported by each platform.
2. Configuring In-band Management
2.1. Enabling In-band Management in an Instance
Use the following CLI syntax to enable in-band management in an instance:
set inband management instance <instance-name>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. All the IFLs in this instance will be enabled with in-band management service after executing this command |
The following example configures the management instance in which in-band management will be enabled:
set inband management instance managementThe following example shows in-band management in an instance:
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
}
]
}2.2. Enabling In-band Management Services
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> <service> <true/false>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. All the IFLs in this instance will be enabled with in-band management service after executing this command |
<service> |
Specifies the supported services to enable: apigw, ctrld, ntp, snmp, ssh, tacacs, telnet. By enabling any of these services, hosts reachable via the physical interface in the inband instance can access the services. |
<true | false> |
A |
Example: Enabling In-band Management Services
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
"ssh": "true",
"ctrld": "true"
}
]
}
2.2.1. Enabling API Gateway (APIGW) Service
To access the APIGW service running in the ONL, this service has to be enabled in in-band management.
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> apigw <true/false>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. |
<true | false> |
A |
Example: Enabling APIGW In-band Management Services
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
"apigw": "true",
}
]
}
2.2.2. Enabling CTRLD Service
To access the CTRLD service running in the ONL, the CTRLD service has to be enabled in in-band management.
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> ctrld <true/false>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. |
<true | false> |
A |
Example: Enabling CTRLD In-band Management Services
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
"ctrld": "true",
}
]
}
2.2.3. Enabling NTP service
To access the NTP service running in the ONL, this service has to be enabled in in-band management.
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> ntp <true/false>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. |
<true | false> |
A |
Example: Enabling NTP In-band Management Services
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
"ntp": "true",
}
]
}
2.2.4. Enabling SNMP service
To access the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) service running in the ONL, this service has to be enabled in in-band management.
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> snmp <true/false>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. |
<true | false> |
A |
Example: Enabling SNMP In-band Management Services
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
"snmp": "true",
}
]
}
2.2.5. Enabling SSH service
To access the ssh service running in the LXC container hosting RBFS, ssh service has to be enabled.
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> ssh <true/false>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. |
<true | false> |
A |
Example: Enabling SSH In-band Management Services
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
"ssh": "true",
}
]
}
2.2.6. Enabling TACACS Service
To access the TACACS service running in the ONL, this service has to be enabled in in-band management.
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> tacacs <true/false>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. |
<true | false> |
A |
Example: Enabling TACACS In-band Management Services
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
"tacacs": "true",
}
]
}
2.2.7. Enabling Telnet Service
To access the telnet service running in the LXC container hosting RBFS, telnet service has to be enabled.
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> telnet <true/false>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. |
<true | false> |
A |
Example: Enabling Telnet In-band Management Services
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
"telnet": "true",
}
]
}
2.3. Enabling Connection Tracking
Enabling connection tracking in inband installs dynamic ACLs for all the connection/packet initiated by the device so that the response packets are not dropped at the hardware.
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> connection-tracking true
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. |
true |
Enables all in-band management services. |
Example: Enabling Connection Tracking in In-band Management
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "default",
"connection-tracking": "true"
}
]
}
2.4. Enabling All Services in In-band Management
Enabling this service will allow access to all services running in LXC/ONL. Once this service is enabled, packets that don’t hit any of the other acls/services in RBFS are redirected to LXC/ONL.
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> all true
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. |
true |
Enables all in-band management services. |
Example: Enabling all In-band Management Services
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
"all": "true",
}
]
}
2.5. Enabling In-band Management for a Specific Source
Enabling any of the in-band services as mentioned in the previous section will expose this service to all the sources which are reachable via in-band service.
To restrict this to specific source prefixes, source-prefix-list has to be enabled using the following command.
By configuring this, the hosts having IPs in the mentioned source prefix list only can access this service.
Syntax:
set inband management instance <instance-name> source-prefix-list <source-prefix-list-name>
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
<instance-name> |
Routing instance name in which in-band management has to be enabled. |
<source-prefix-list-name> |
Specifies the name of the source prefix-list which is configured in 'set forwarding-options prefix-list' command. |
Example: Enabling source prefix list in In-band Management Services
"rtbrick-config:inband-management": {
"instance": [
{
"name": "management",
"source-prefix-list": "source-prefix1"
}
]
}
3. In-Band Management Operational Commands
The In-band Management show commands provide detailed information about the In-band Management operations.
3.1. Verifying In-band Management on LXC Container
In the LXC container, there will be a new interface named inband-mgmt-0 on enabling in-band management. All the loopback address as well as route in in-band instance should be assigned to this interface.
The example below shows how to verify if inband-mgmt-0 interface is created and if the routing for management traffic is pointing to it.
supervisor@rtbrick:~$ ip link show
<...>
5: inband-mgmt-0: <POINTOPOINT,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1492 qdisc pfifo_fast state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 500
link/none
supervisor@rtbrick:~$ ip route show
198.51.100.1/24 dev inband-mgmt-0 proto rtb_fibd scope link
<...>
3.2. Verifying In-band Management on ONL
The example below shows how to verify Linux routing tables on ONL host and LXC container.
root@bl2-pod1:~# ip route show default via 198.51.100.202 dev ma1 proto rtb_routesync metric 4294966272 default via 198.51.100.10 dev lxcbr0 proto rtb_routesync scope rtb_umc metric 128 198.51.100.81/24 via 198.51.100.10 dev lxcbr0 proto rtb_routesync scope rtb_umc metric 128 198.51.100.30/24 dev lxcbr0 proto kernel scope link src 198.51.100.31 198.51.100.55 via 198.51.100.10 dev lxcbr0 proto rtb_routesync scope rtb_umc metric 128 198.51.100.119/23 dev ma1 proto kernel scope link src 198.51.100.112 supervisor@rtbrick:~$ ip route show default via 198.51.100.31 dev eth0 proto rtb_routesync scope rtb_umc metric 4294966400 default dev inband-mgmt-0 proto rtb_fibd scope link 198.51.100.81/24 dev inband-mgmt-0 proto rtb_fibd scope link 198.51.100.30/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 198.51.100.10 198.51.100.55 dev inband-mgmt-0 proto rtb_fibd scope link 198.51.100.119/23 via 198.51.100.31 dev eth0 proto rtb_routesync scope rtb_umc metric 128 198.51.100.112 via 198.51.100.31 dev eth0 proto rtb_routesync scope rtb_umc metric 128
©Copyright 2024 RtBrick, Inc. All rights reserved. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The trademarks, logos and service marks ("Marks") displayed in this documentation are the property of RtBrick in the United States and other countries. Use of the Marks are subject to RtBrick’s Term of Use Policy, available at https://www.rtbrick.com/privacy. Use of marks belonging to other parties is for informational purposes only.